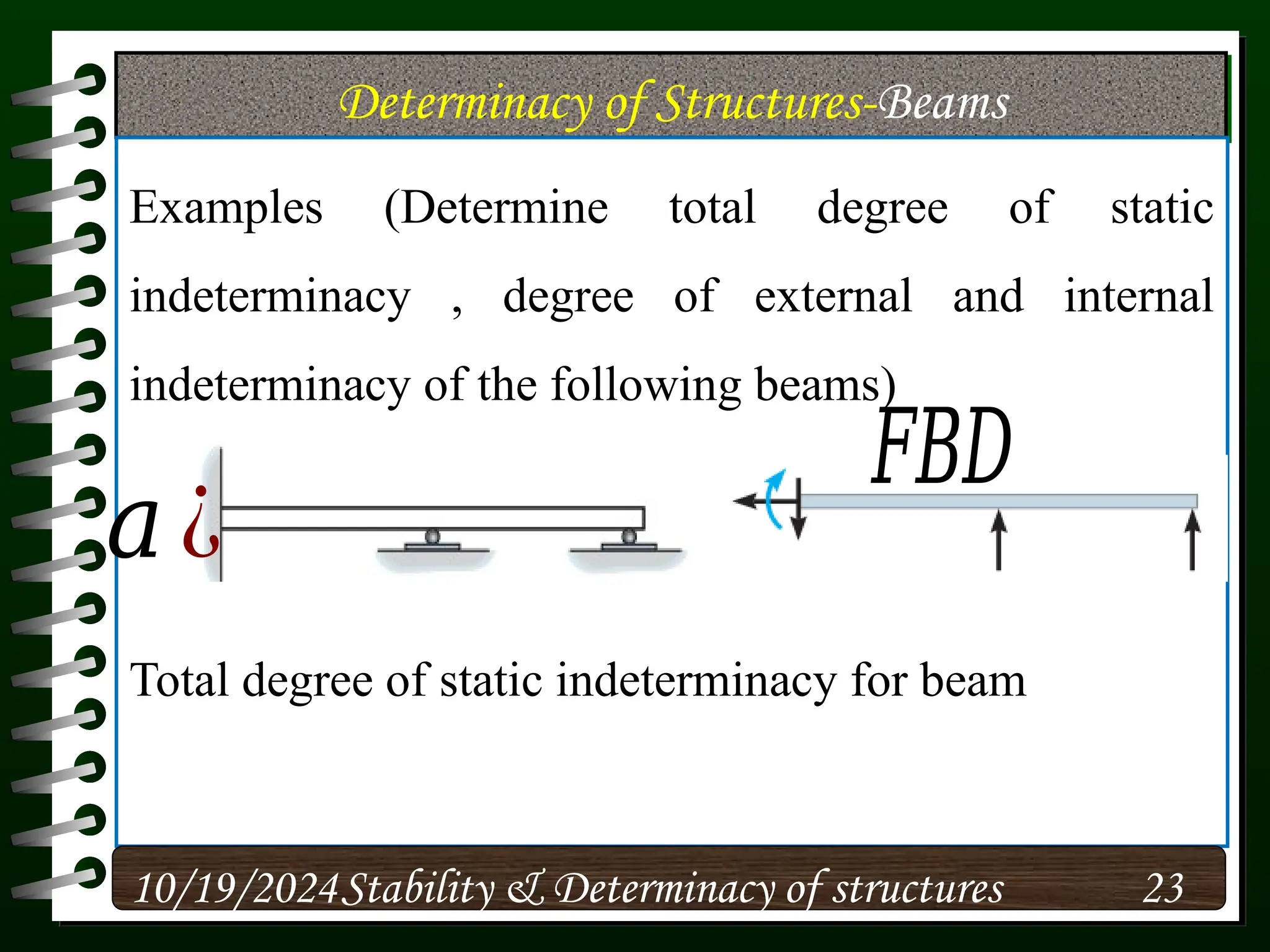
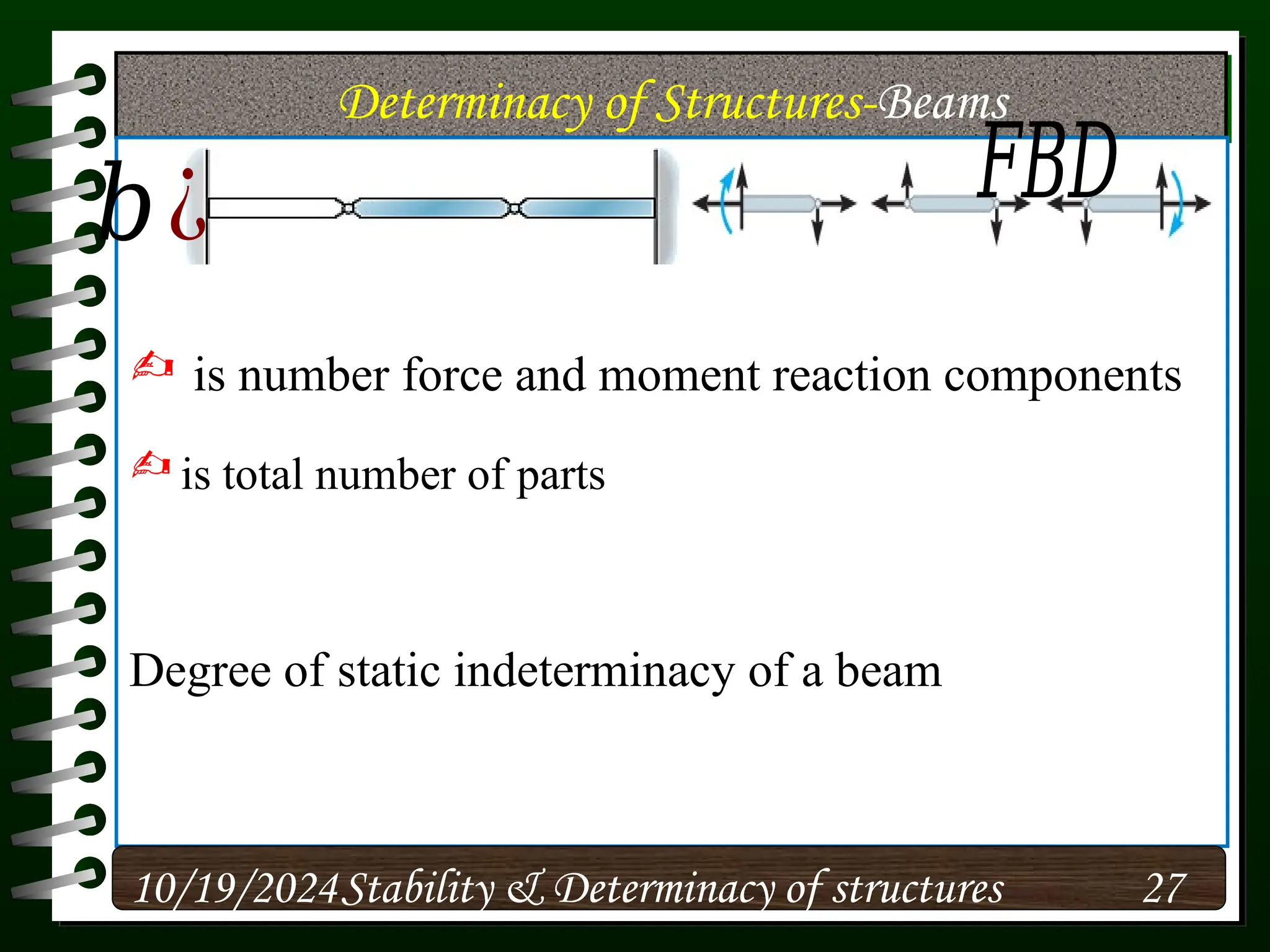
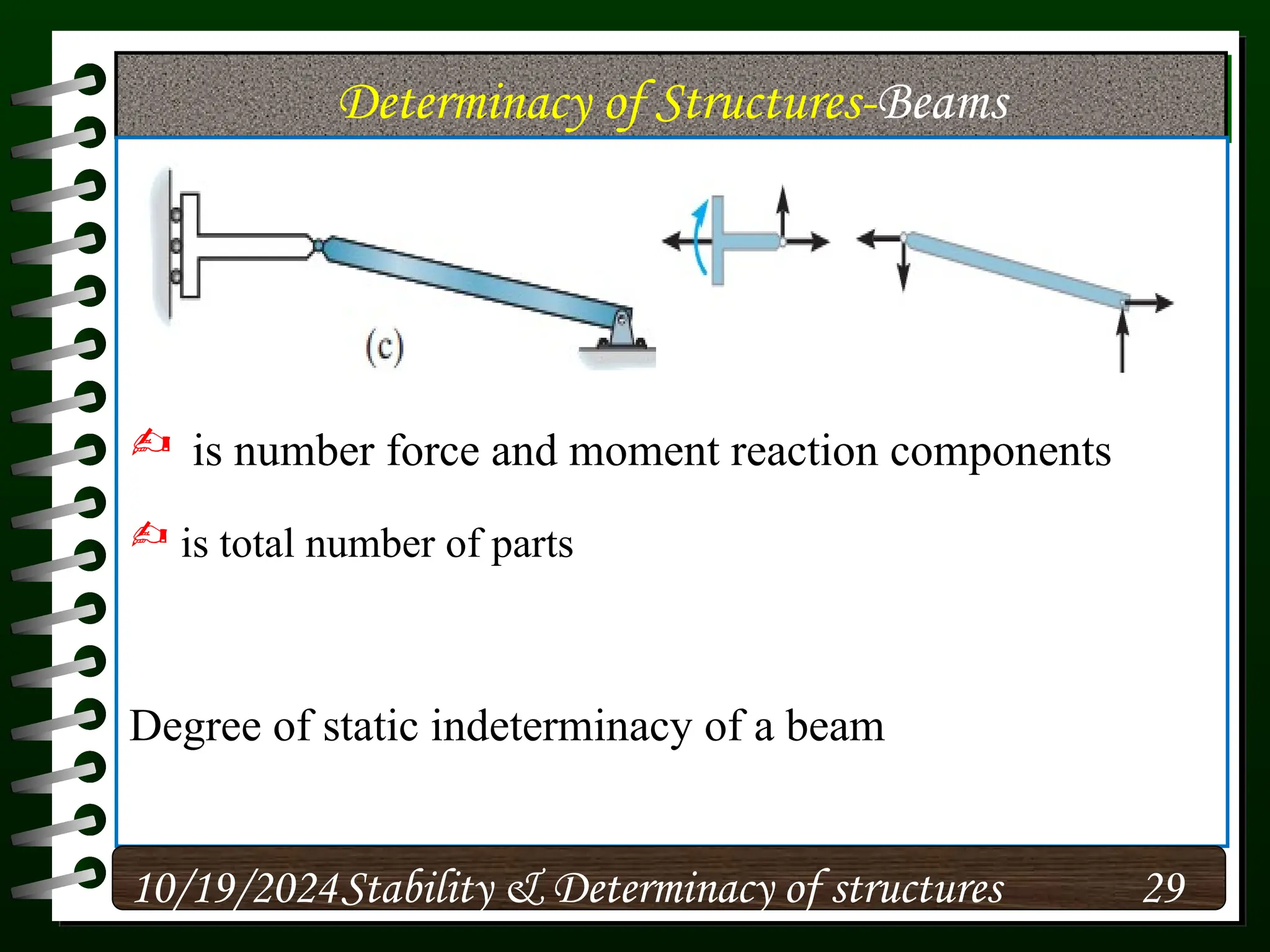
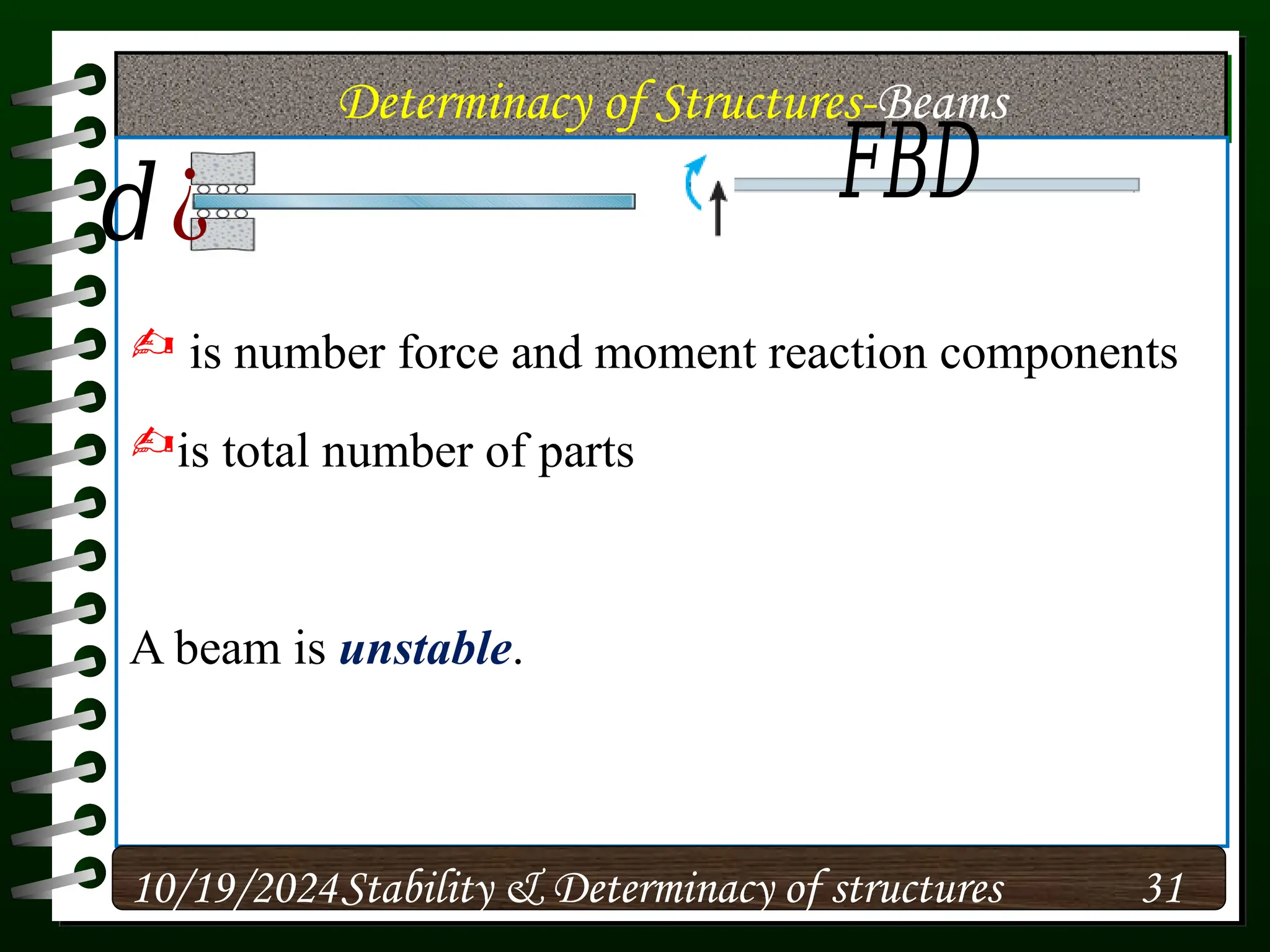
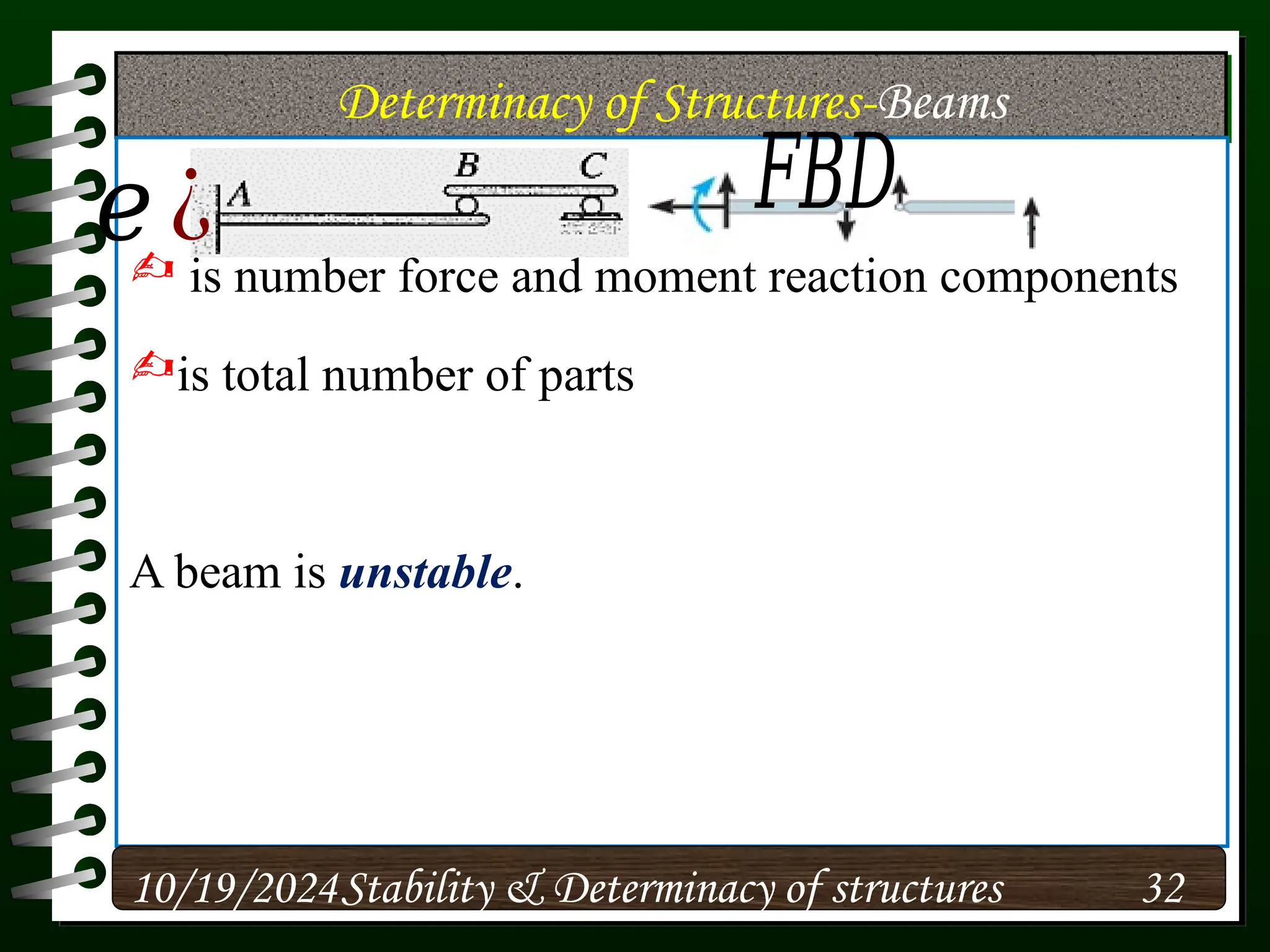
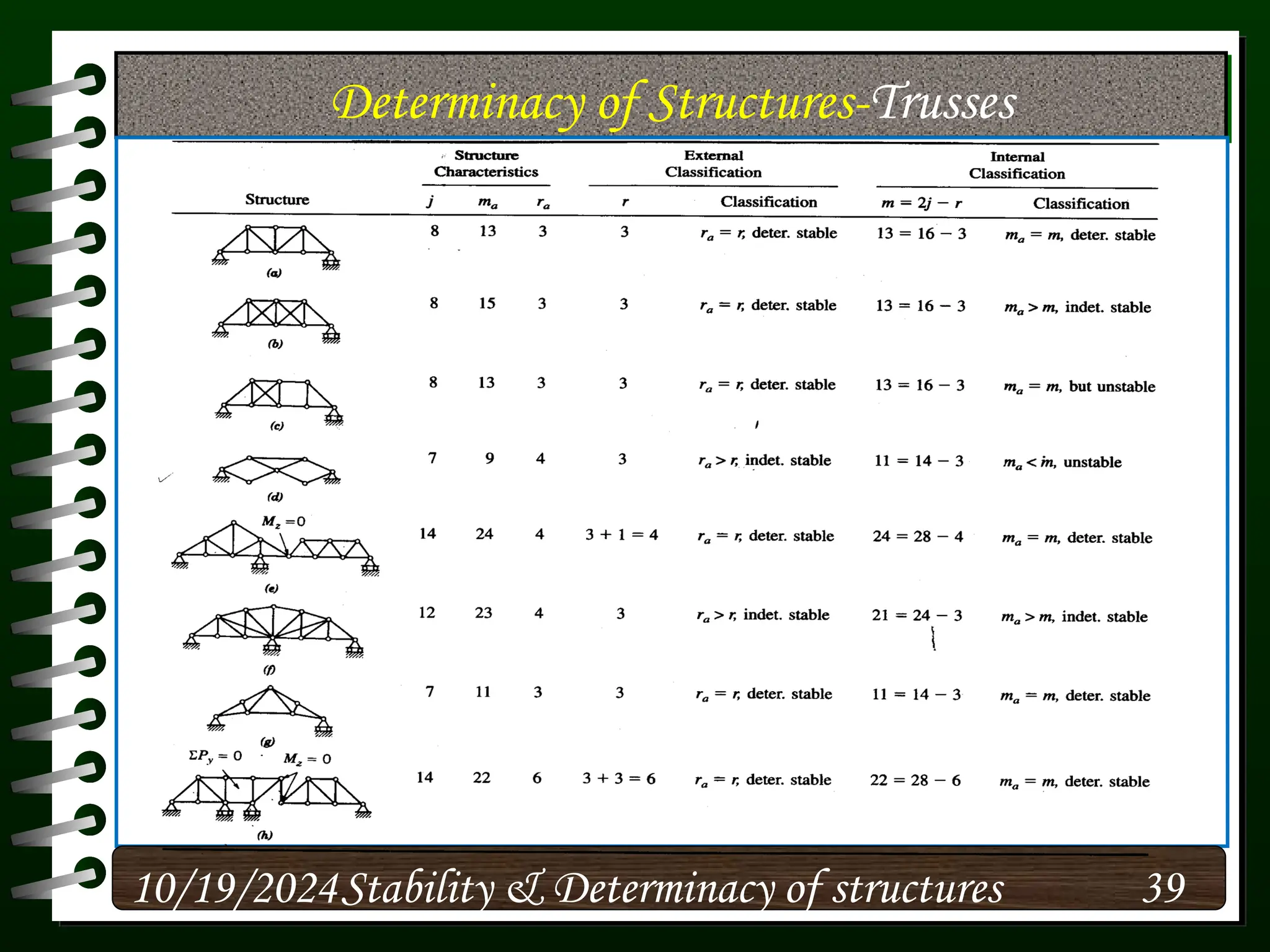
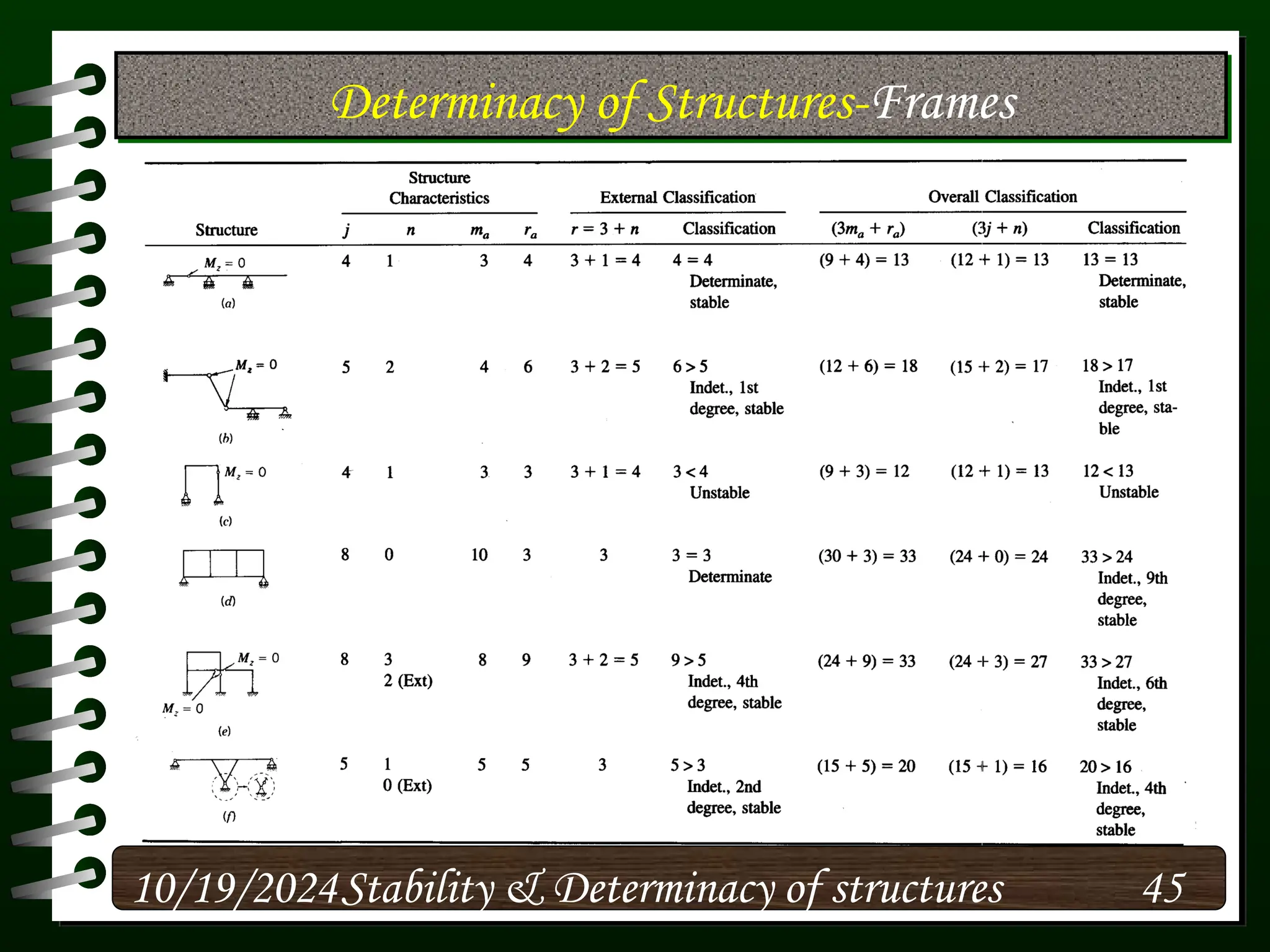
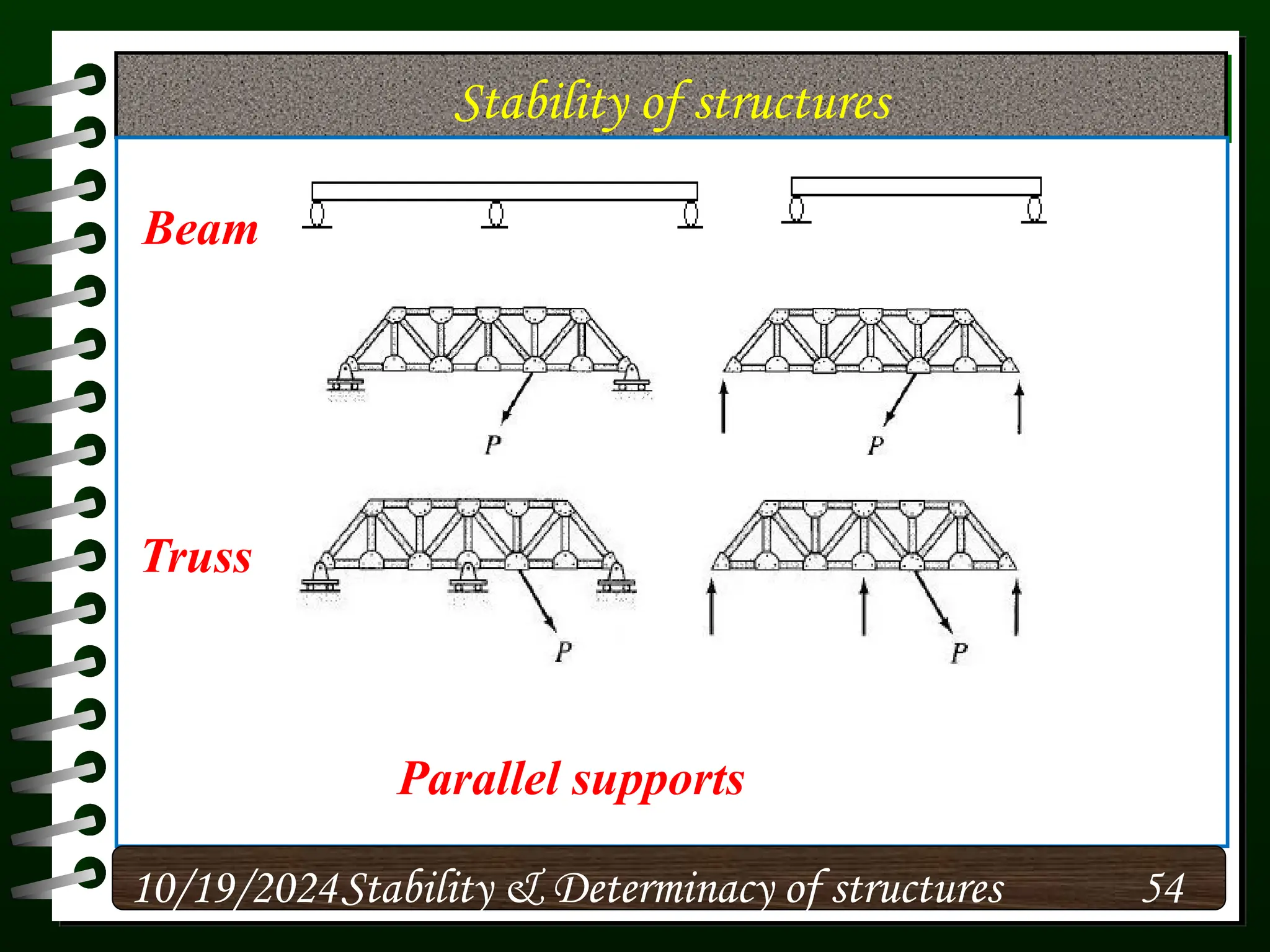
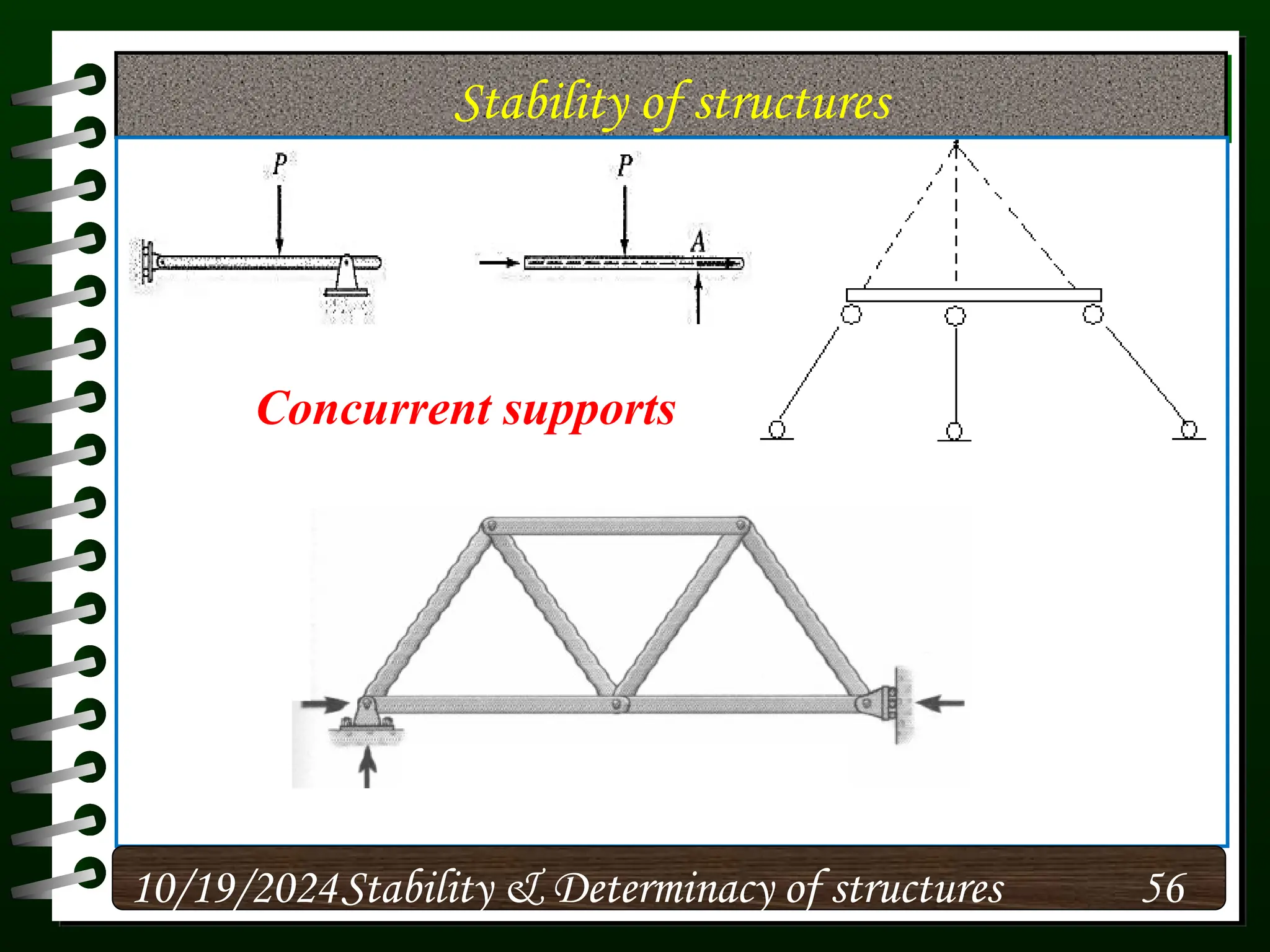
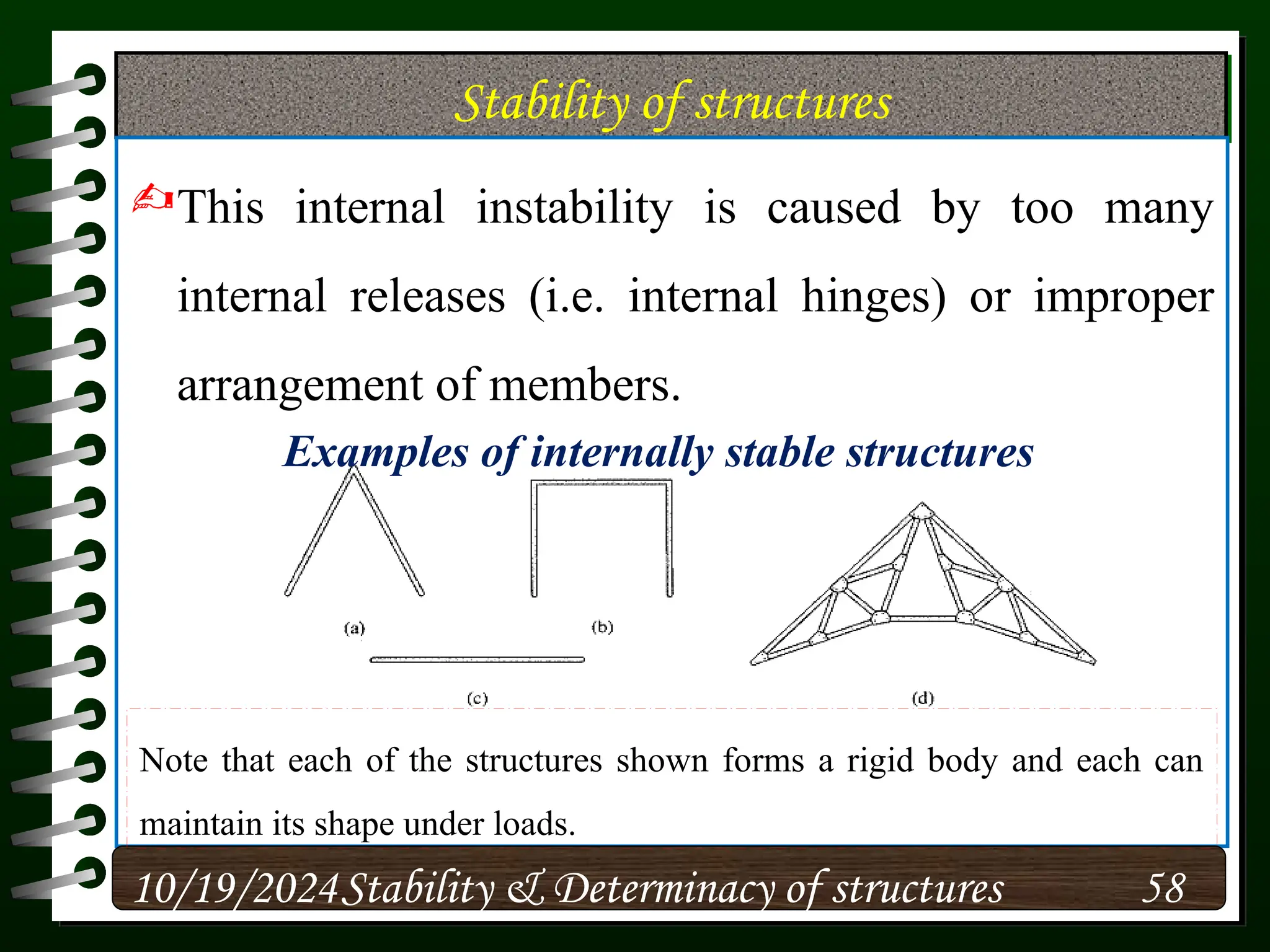
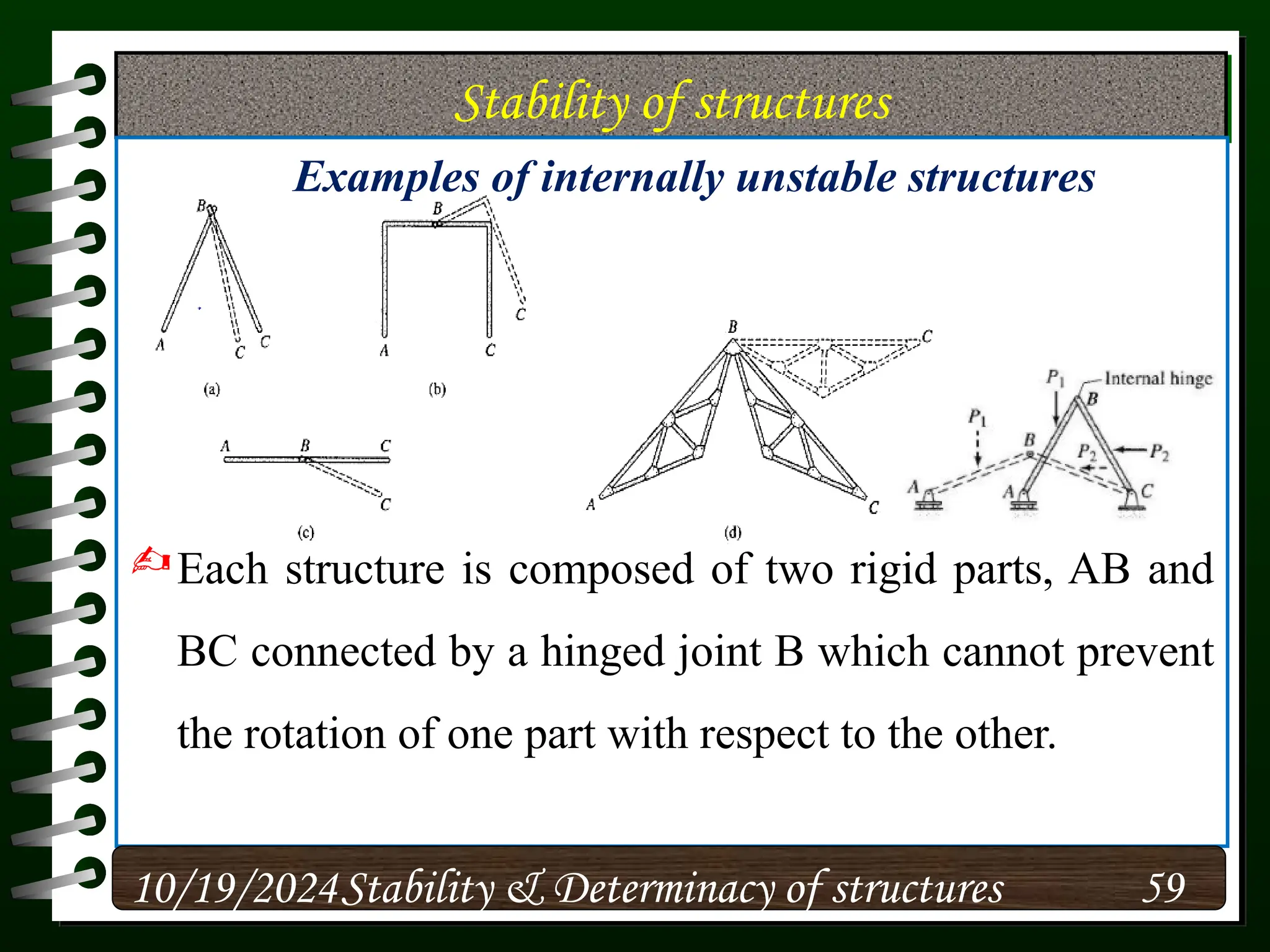
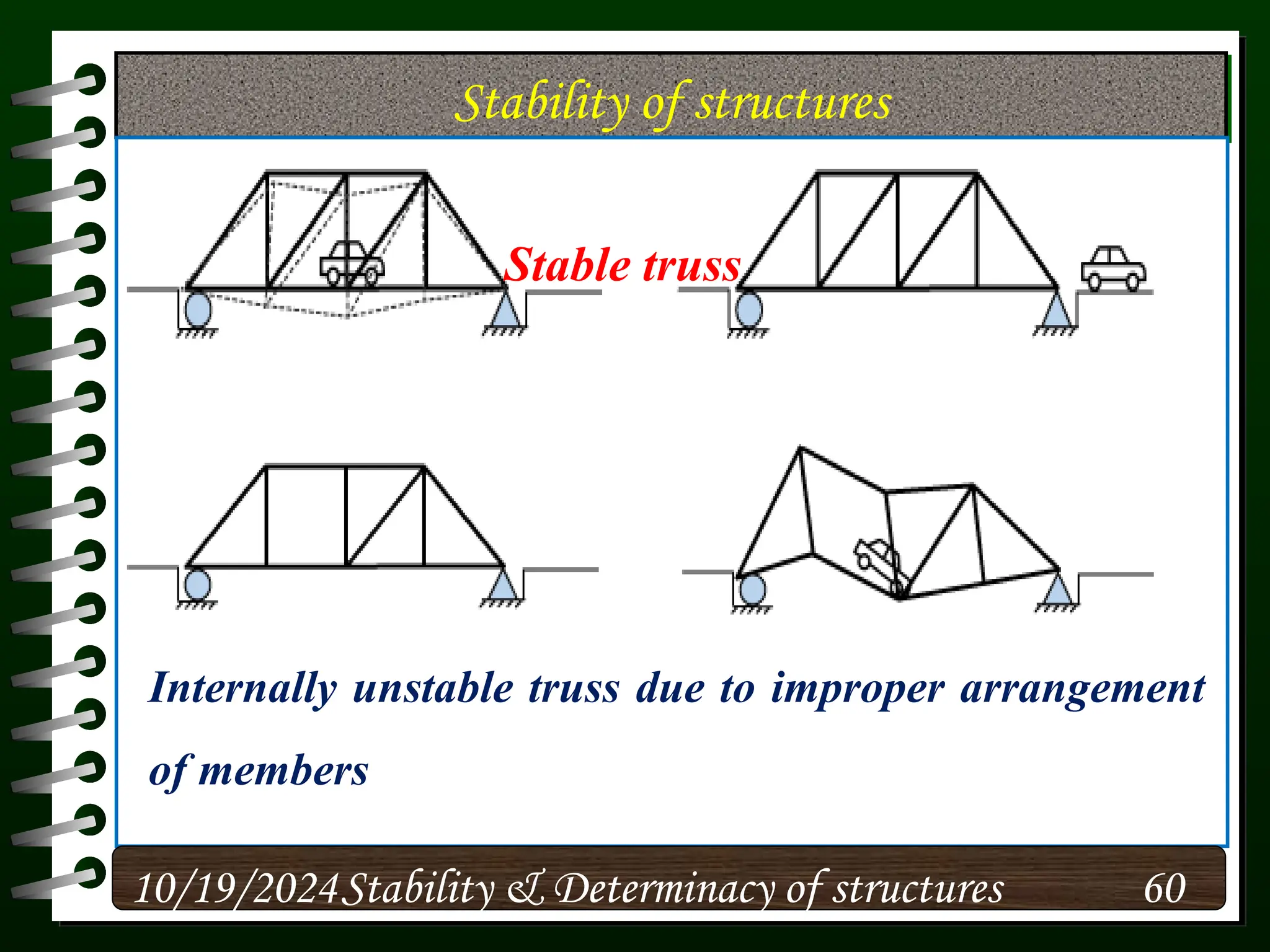
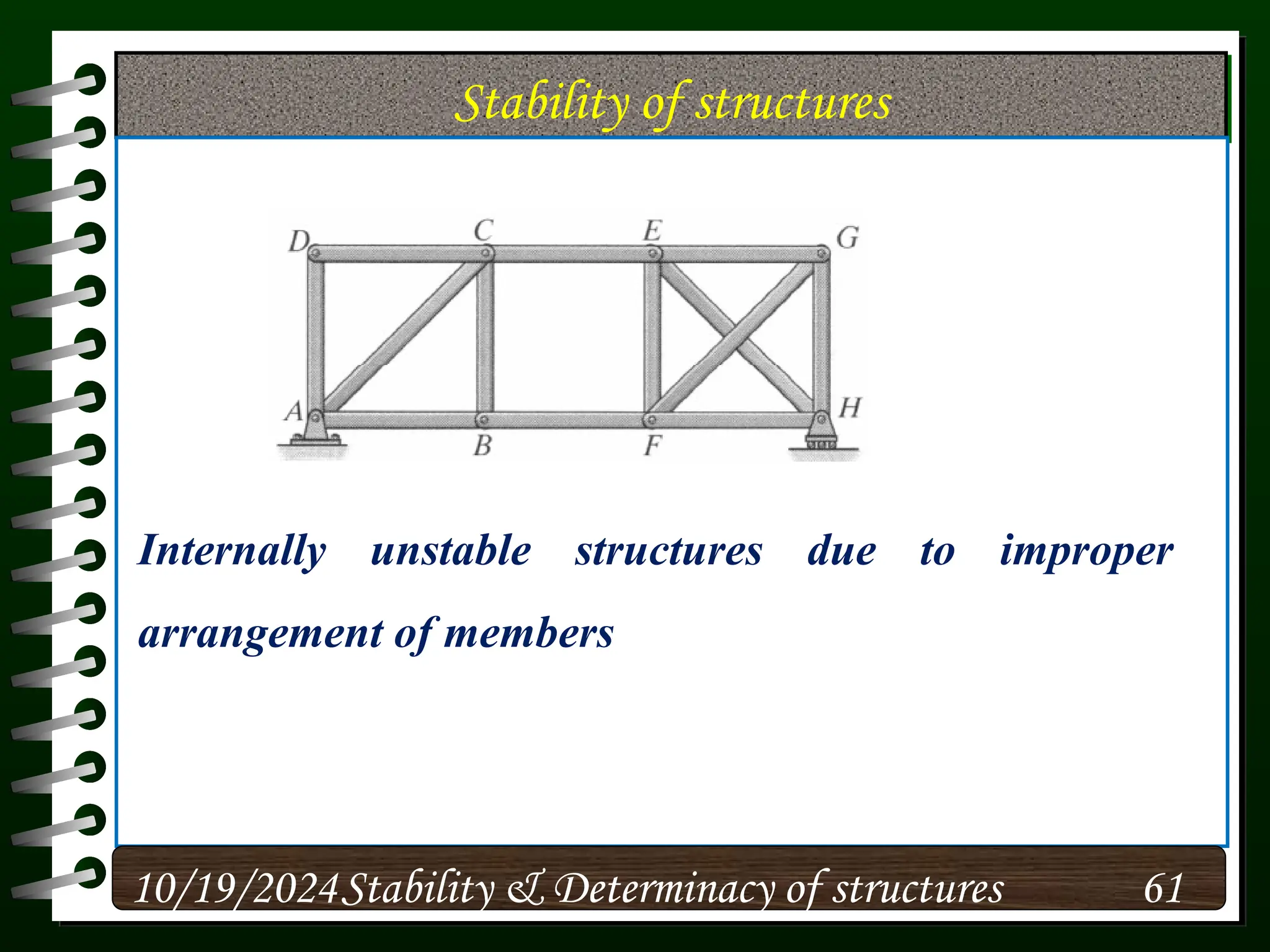
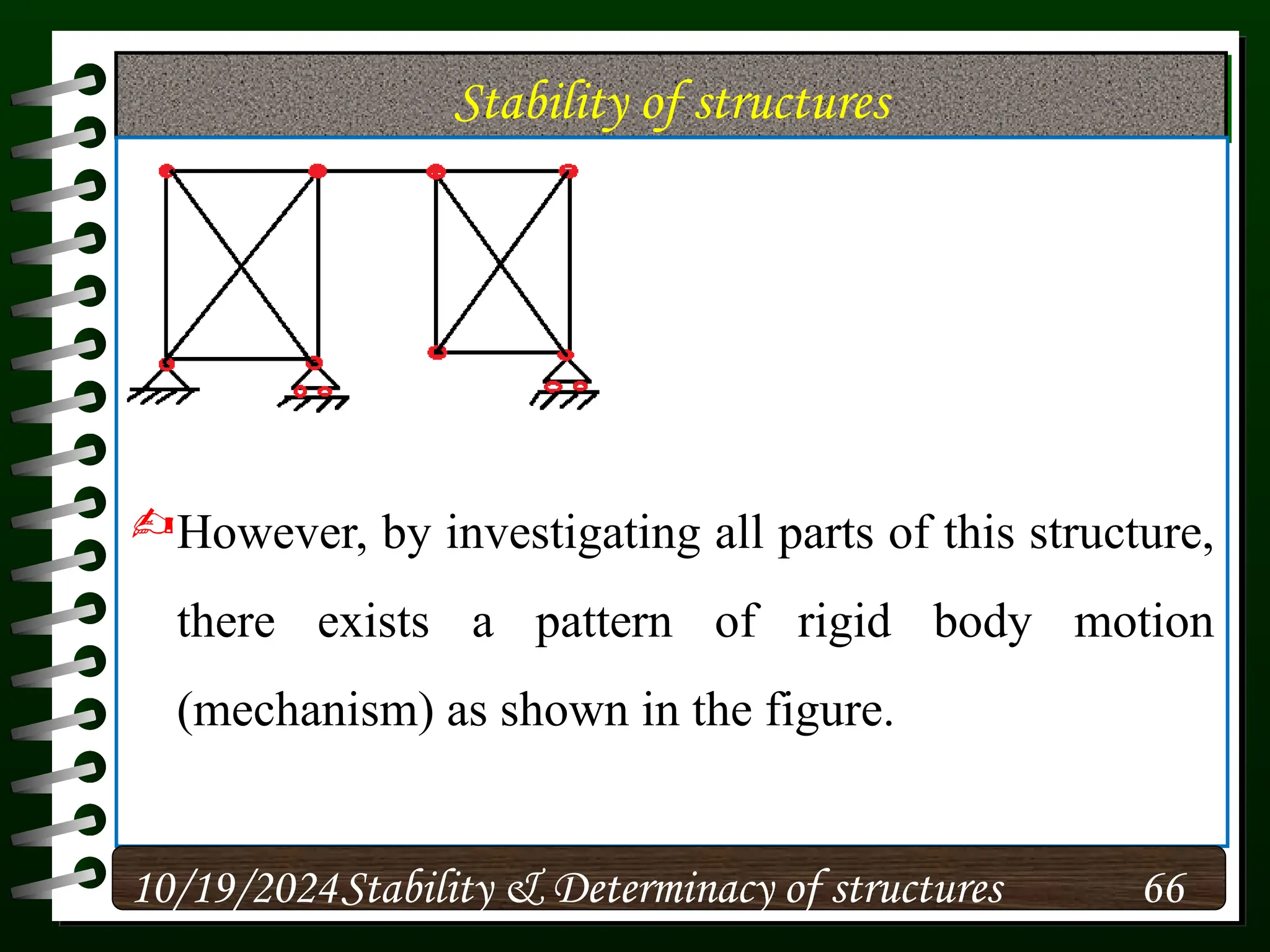
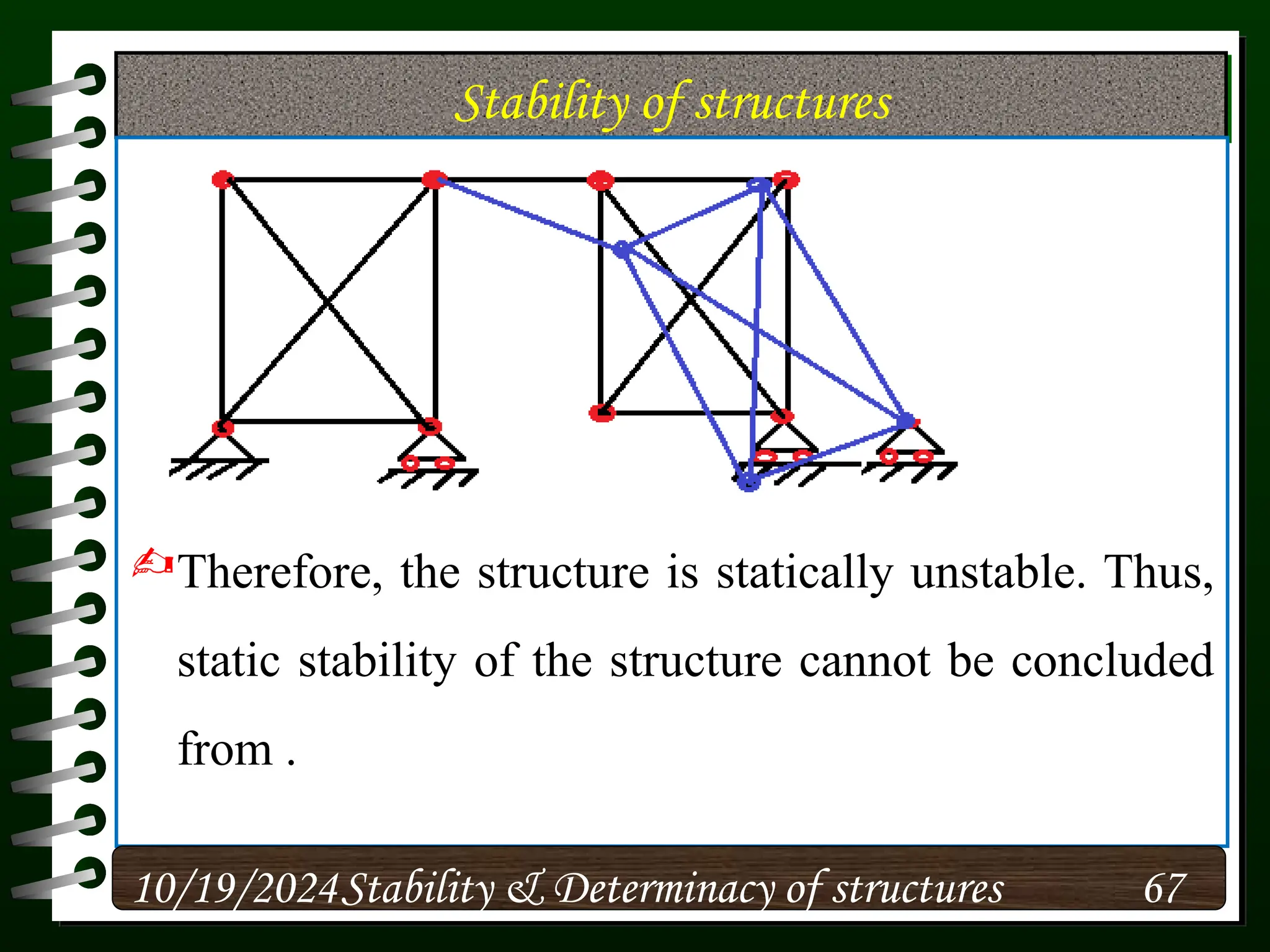
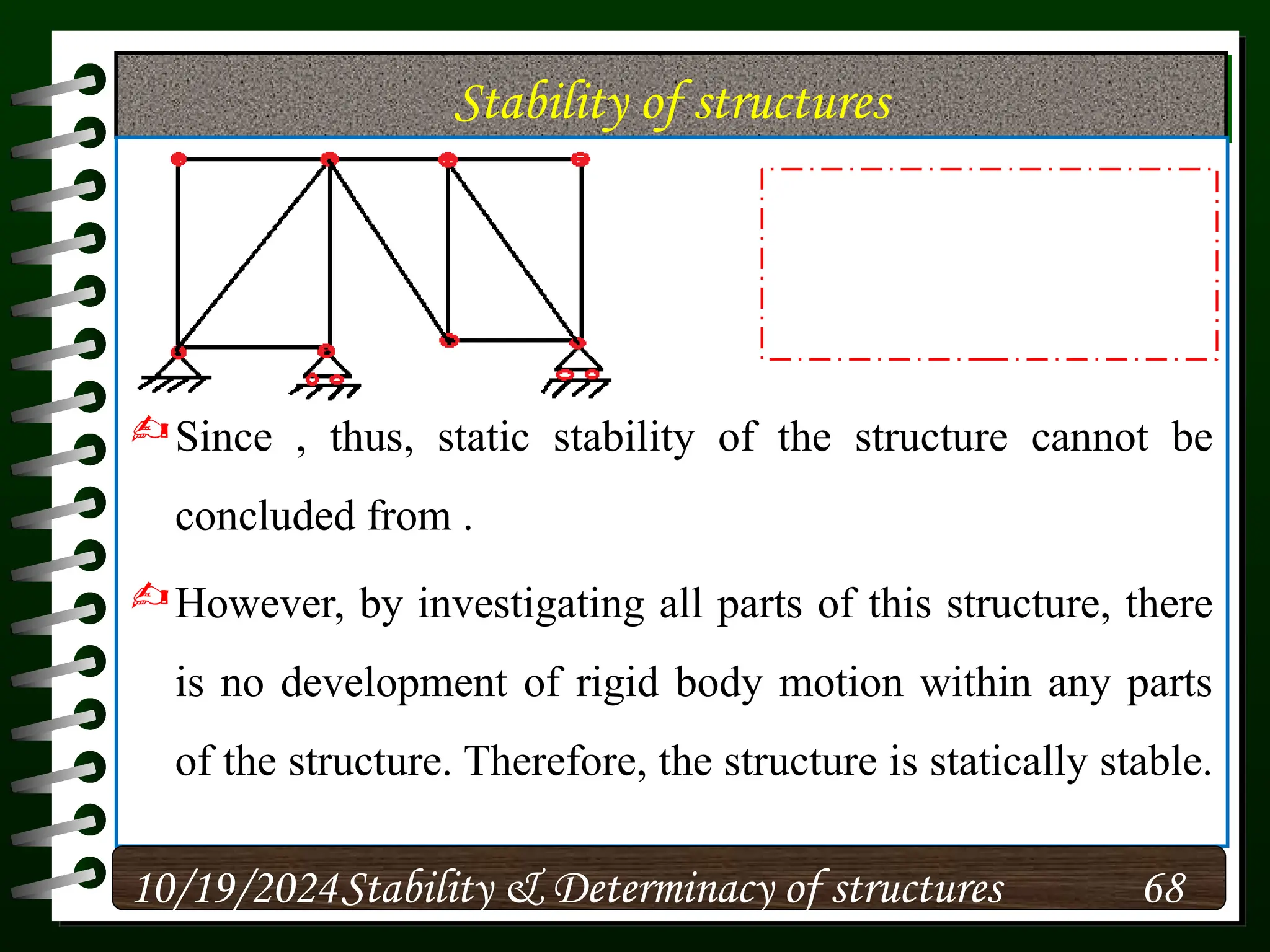
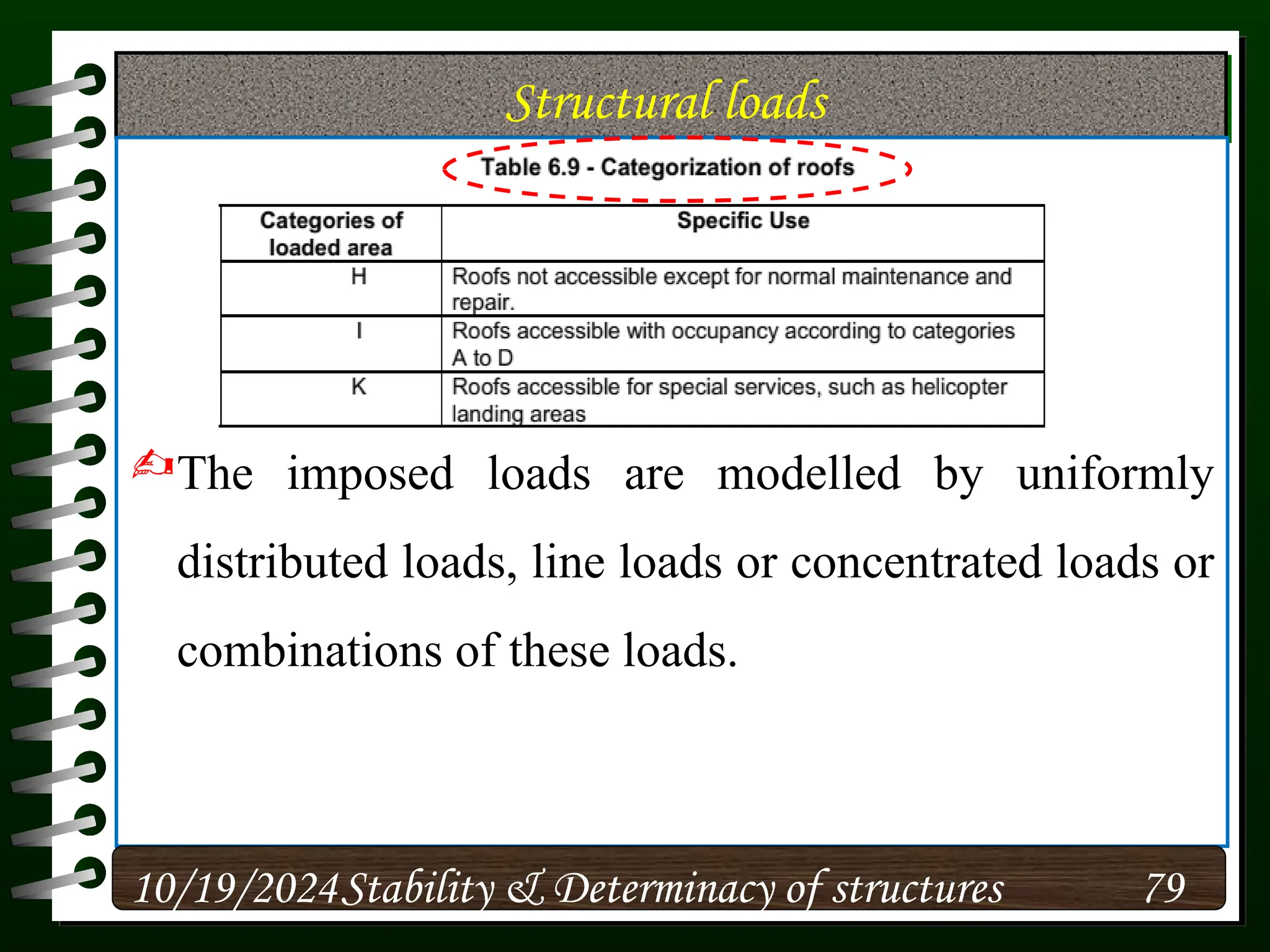
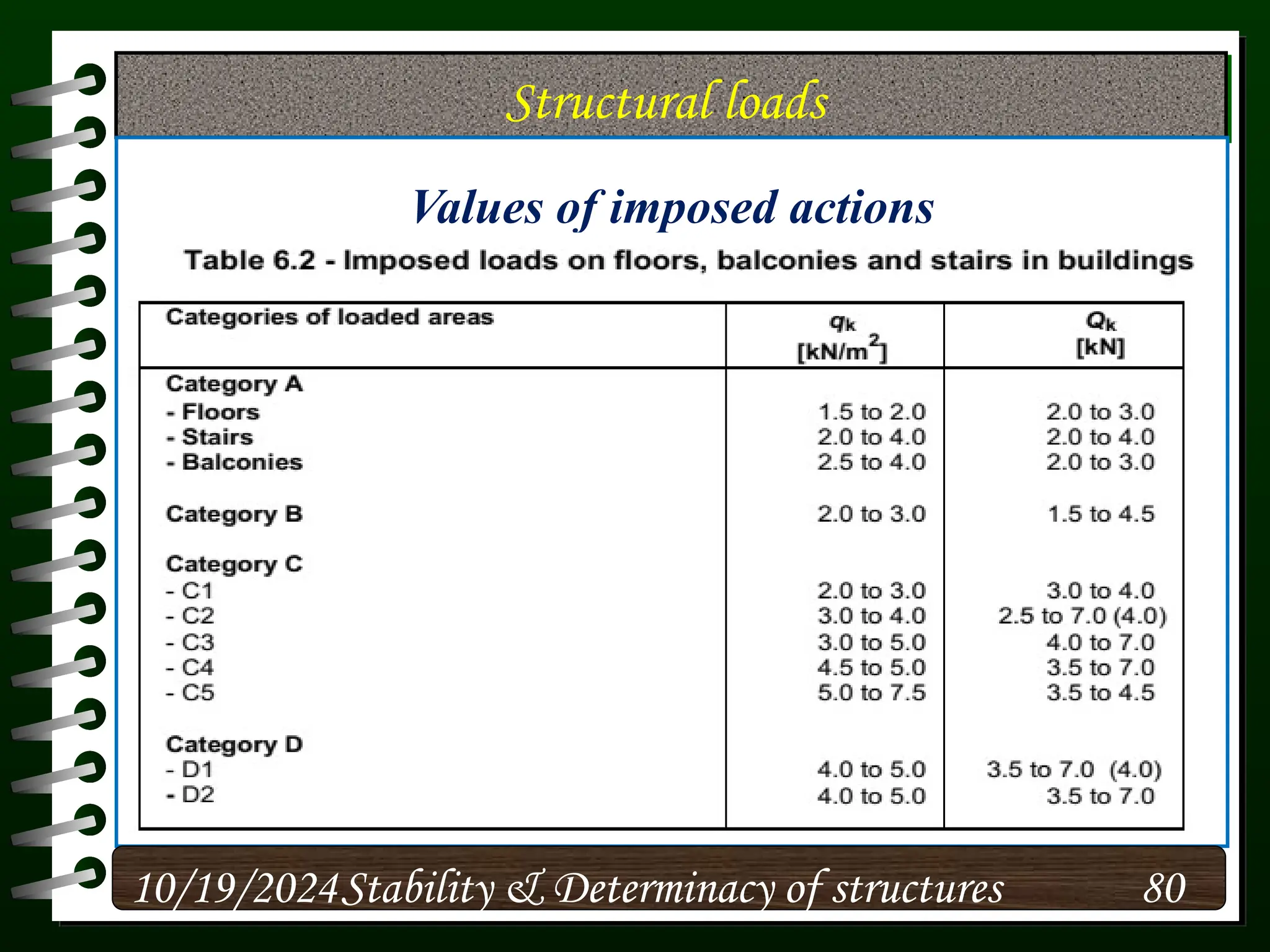
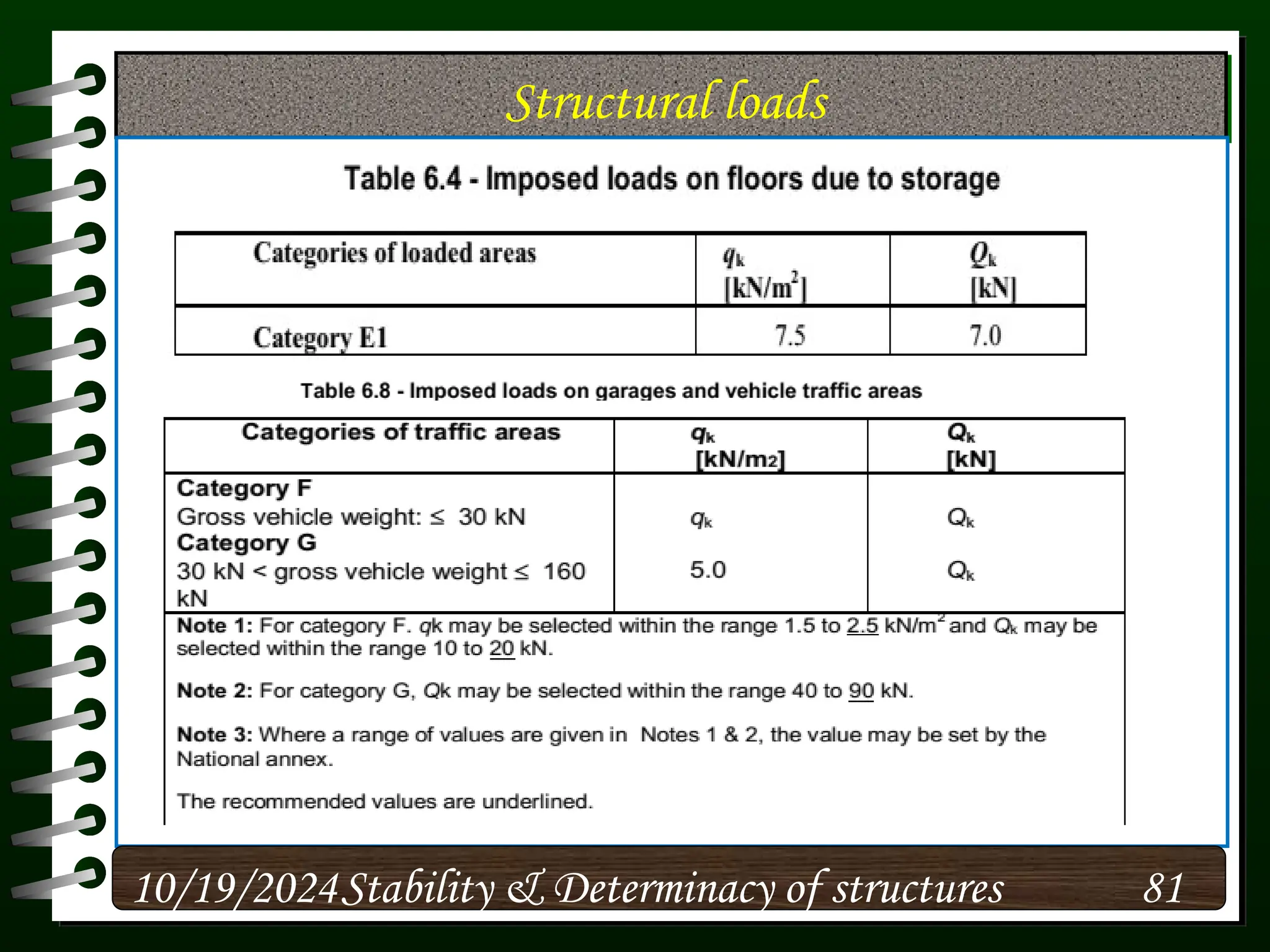
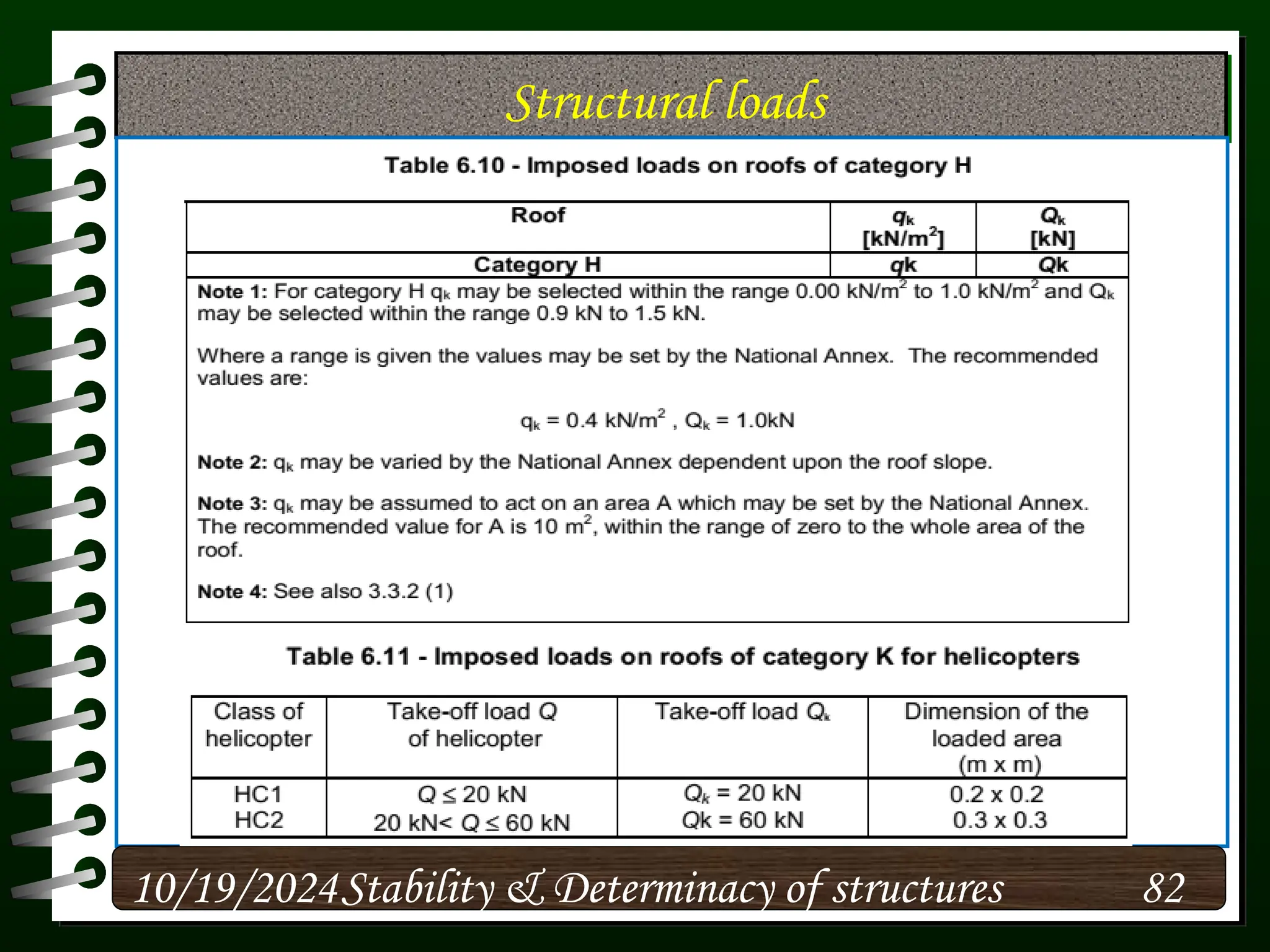
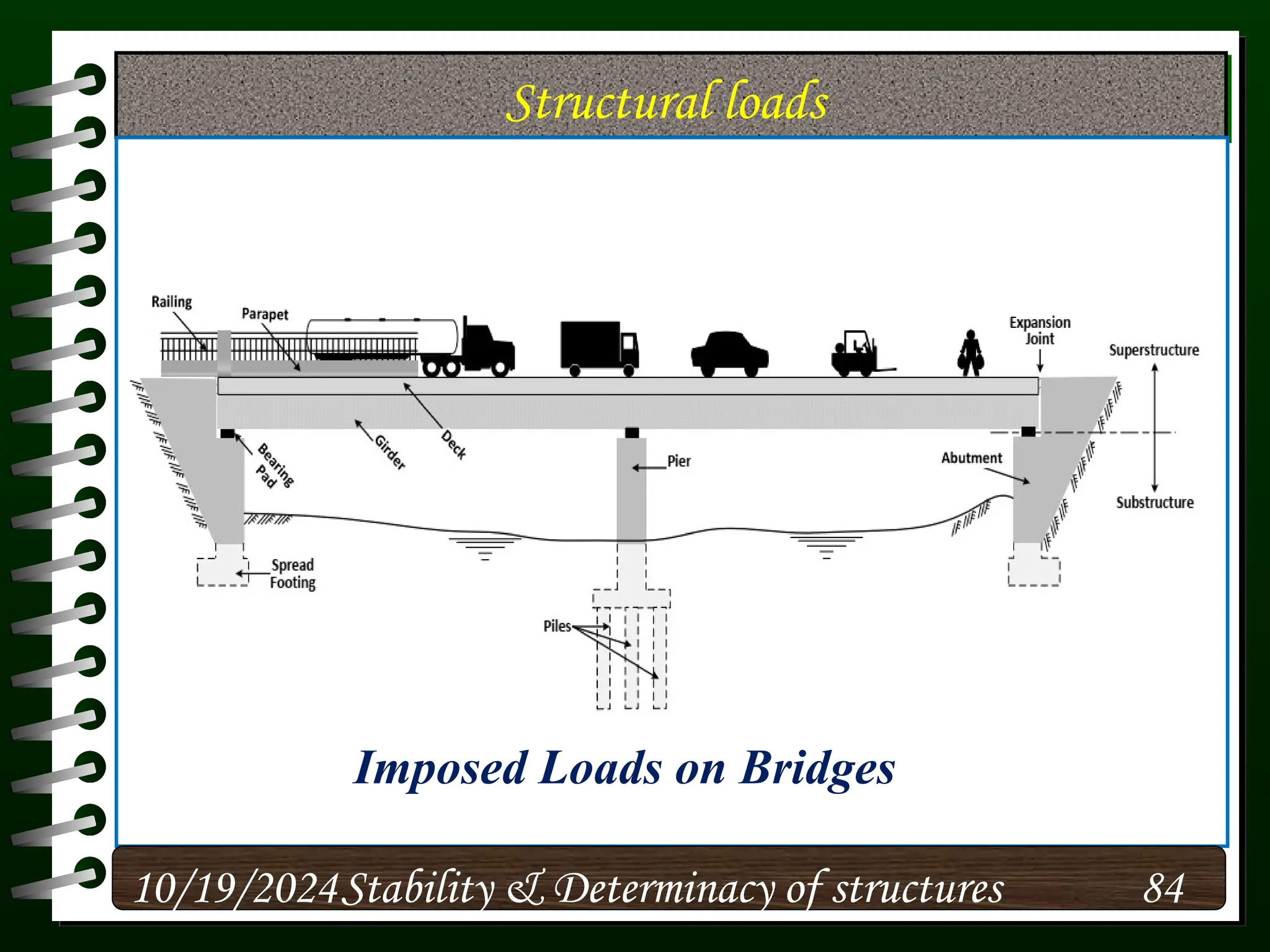
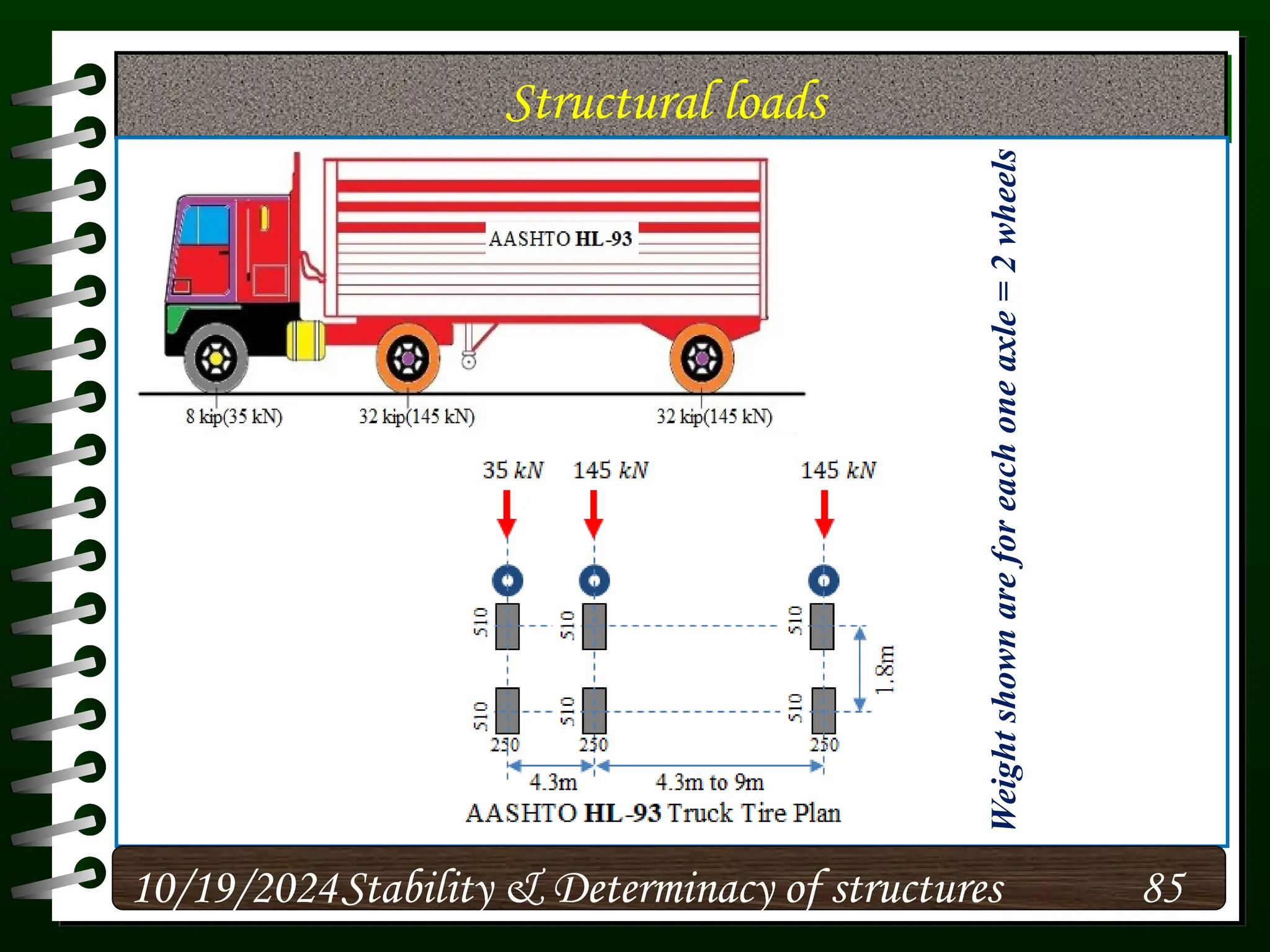
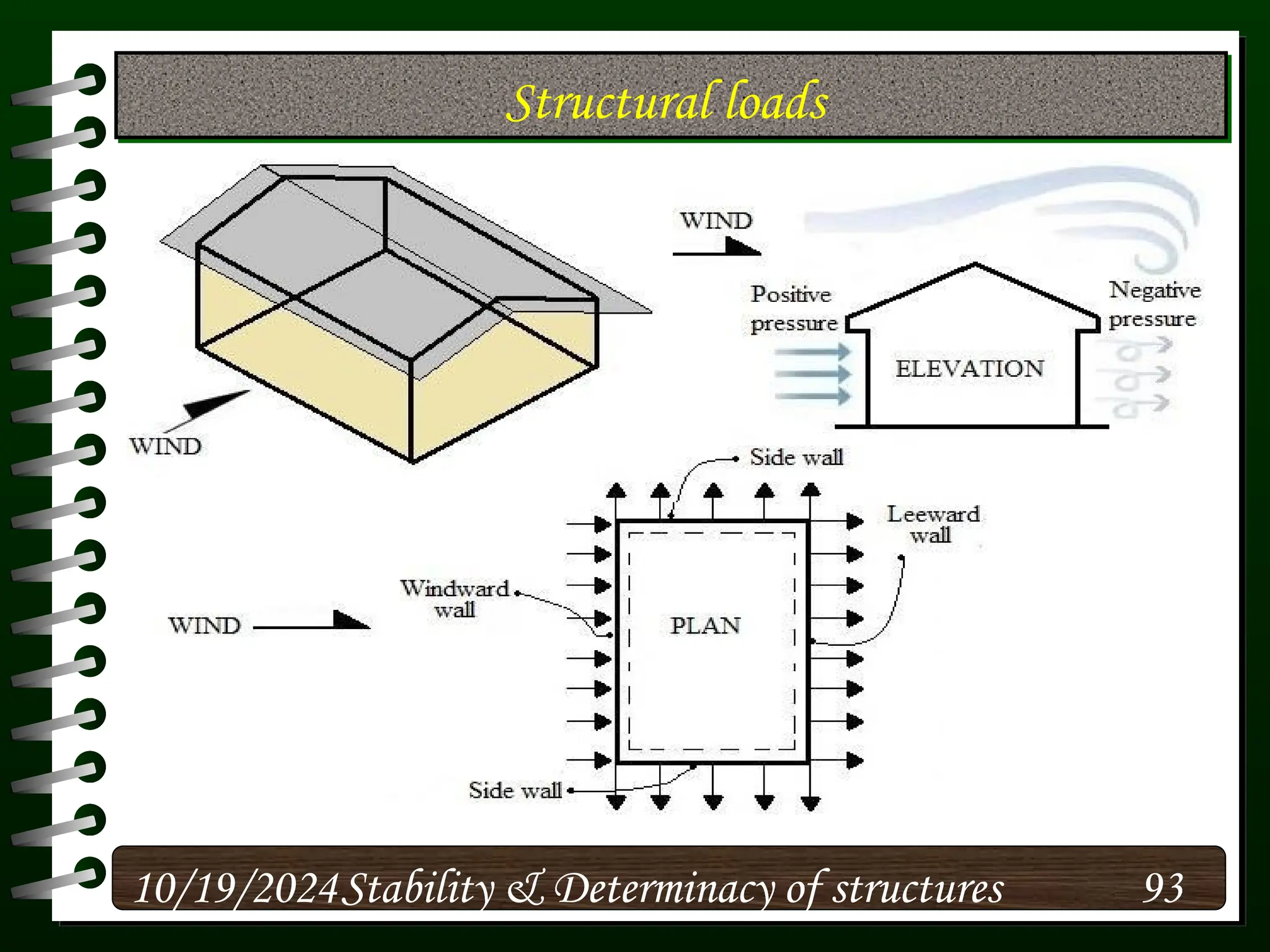
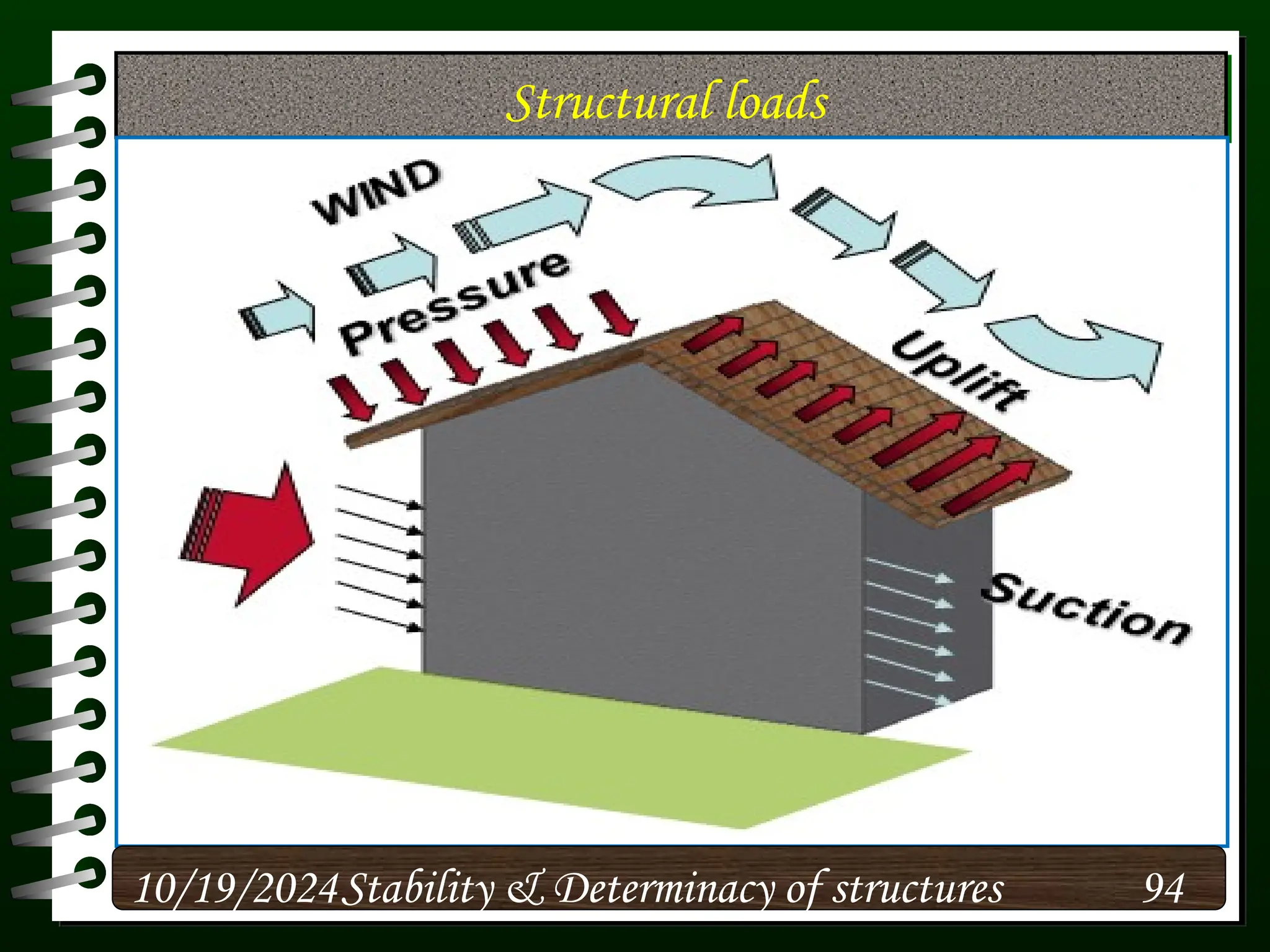
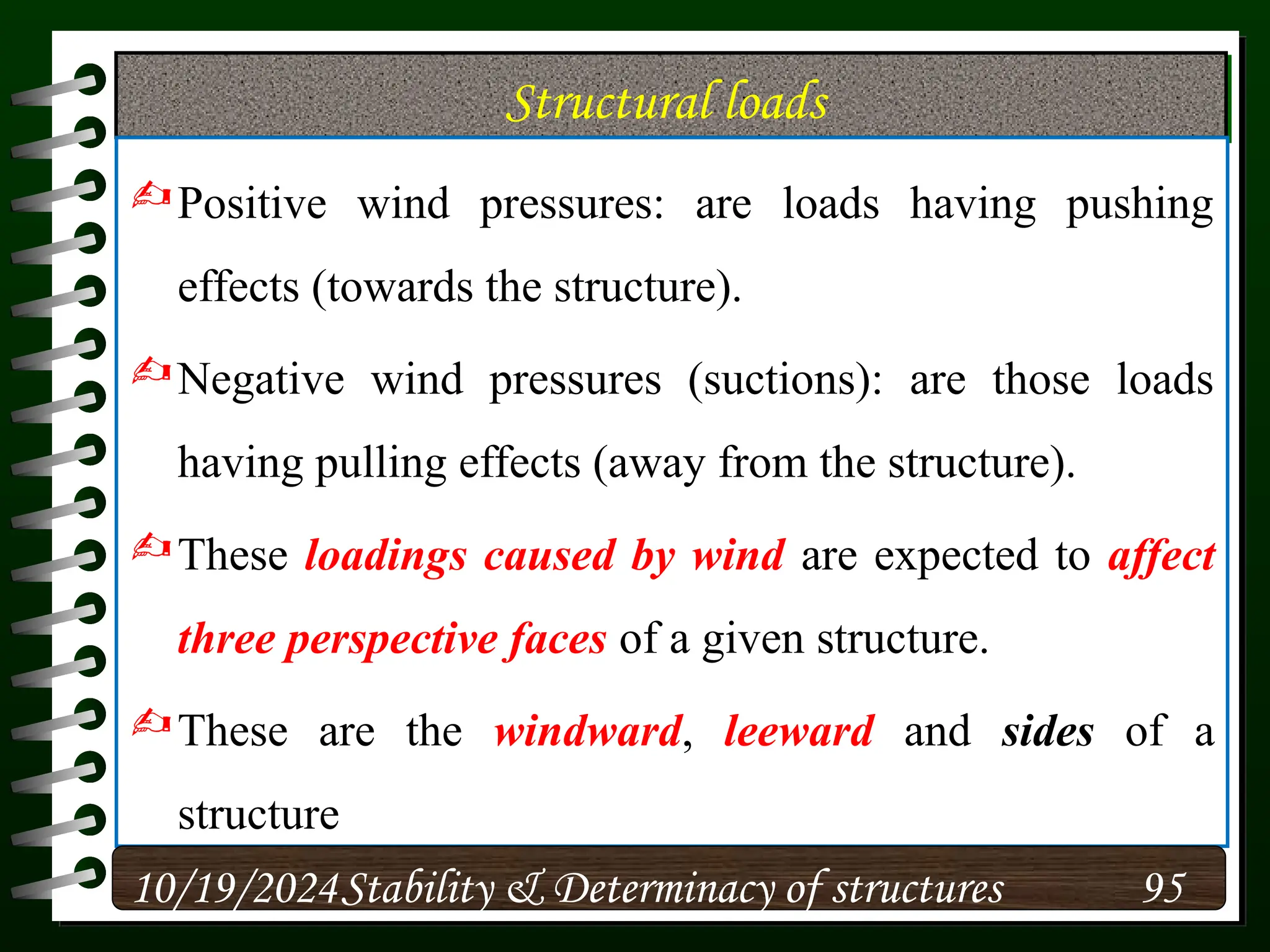
The document discusses the concepts of stability and determinacy in structural engineering, detailing the classification of structures as either determinate or indeterminate based on their response to external loads. It explains the criteria for static indeterminacy, including the distinction between external and internal indeterminacy, and emphasizes the importance of structural analysis methods for accurate assessment. Additionally, it outlines key conditions required to ensure the stability of structures, particularly focusing on support arrangements and the implications of reactant forces.