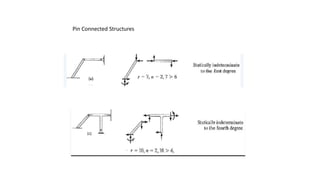
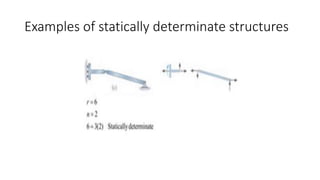
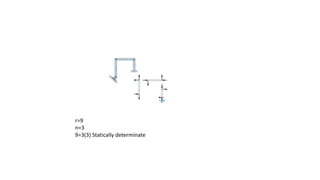
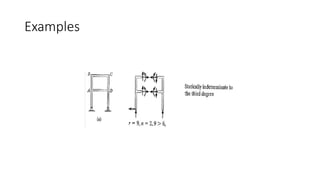
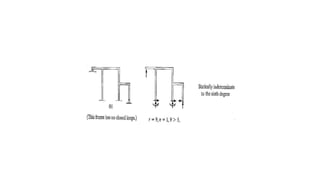
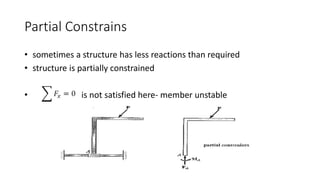
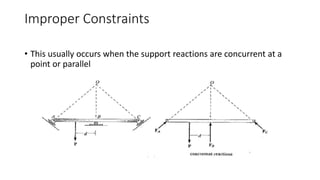
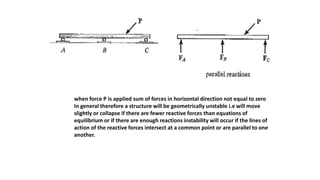
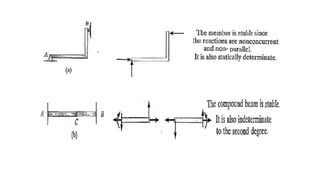
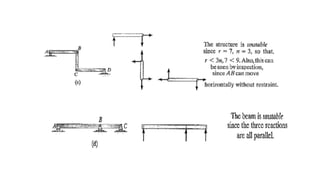
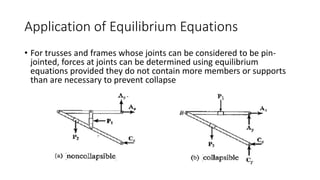
The document discusses statically indeterminate and determinate structures in structural mechanics, emphasizing that indeterminate structures have more unknown forces than equations of equilibrium can solve. It explains methods for analyzing these structures, such as energy methods and the matrix stiffness method. Additionally, it highlights how frames and pin-connected structures are classified based on their stability and determinacy.