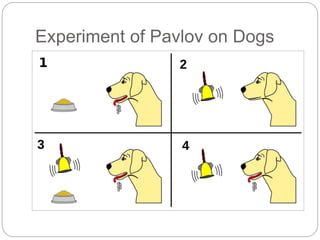
Evan Pavlov was a Russian physiologist who was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1904. He is known for his theory of classical conditioning. Through experiments with dogs, Pavlov observed that dogs learned to associate food with the presence of an external stimulus like a bell or light. When the bell was rung without food, the dogs would still salivate, showing they had learned to associate the bell with food. Pavlov's theory demonstrated that learning can occur through conditioning by linking a neutral stimulus with an unconditioned stimulus to elicit a desired response. His work formed the basis of behaviorism and was influential in psychology.