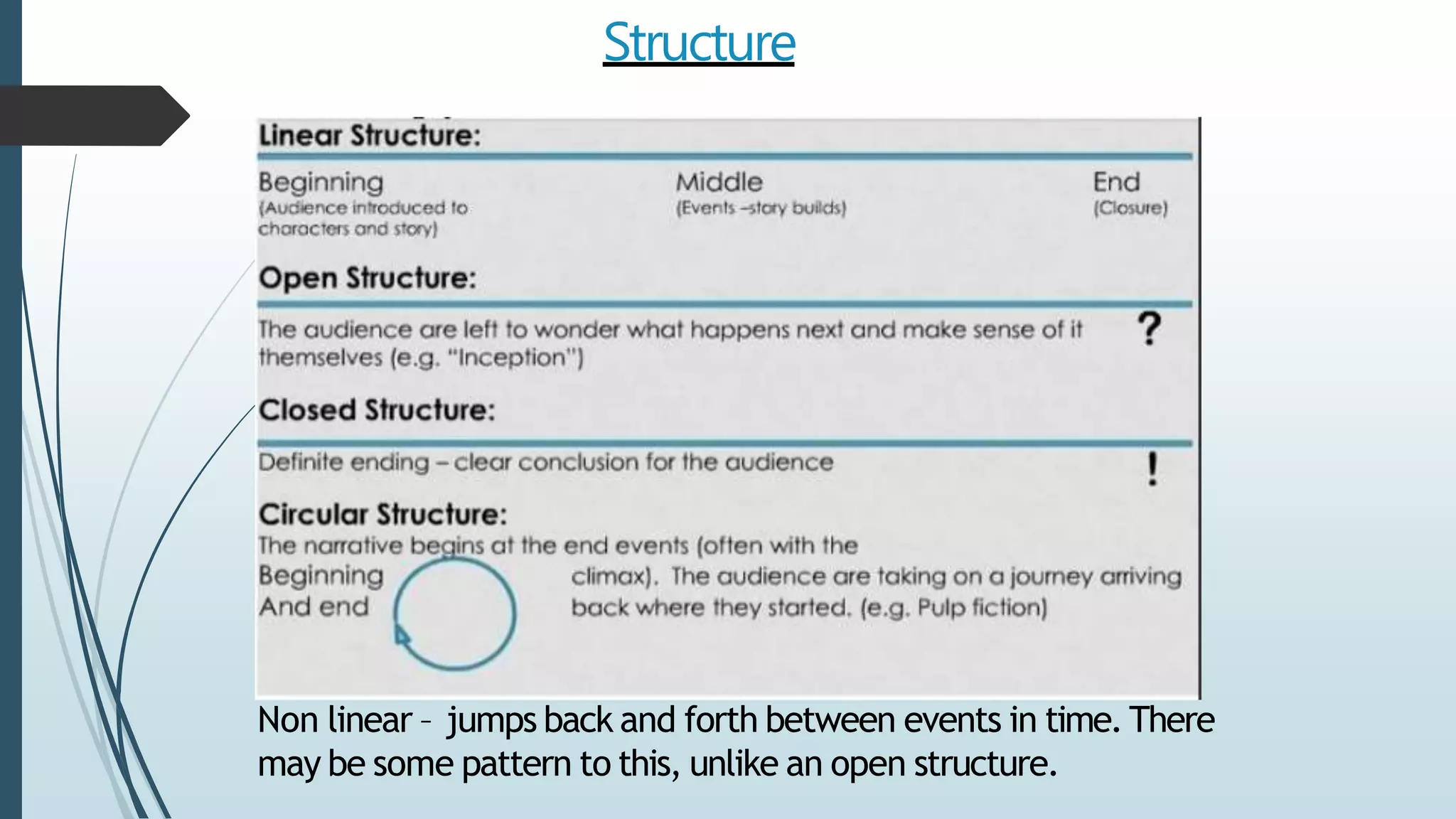
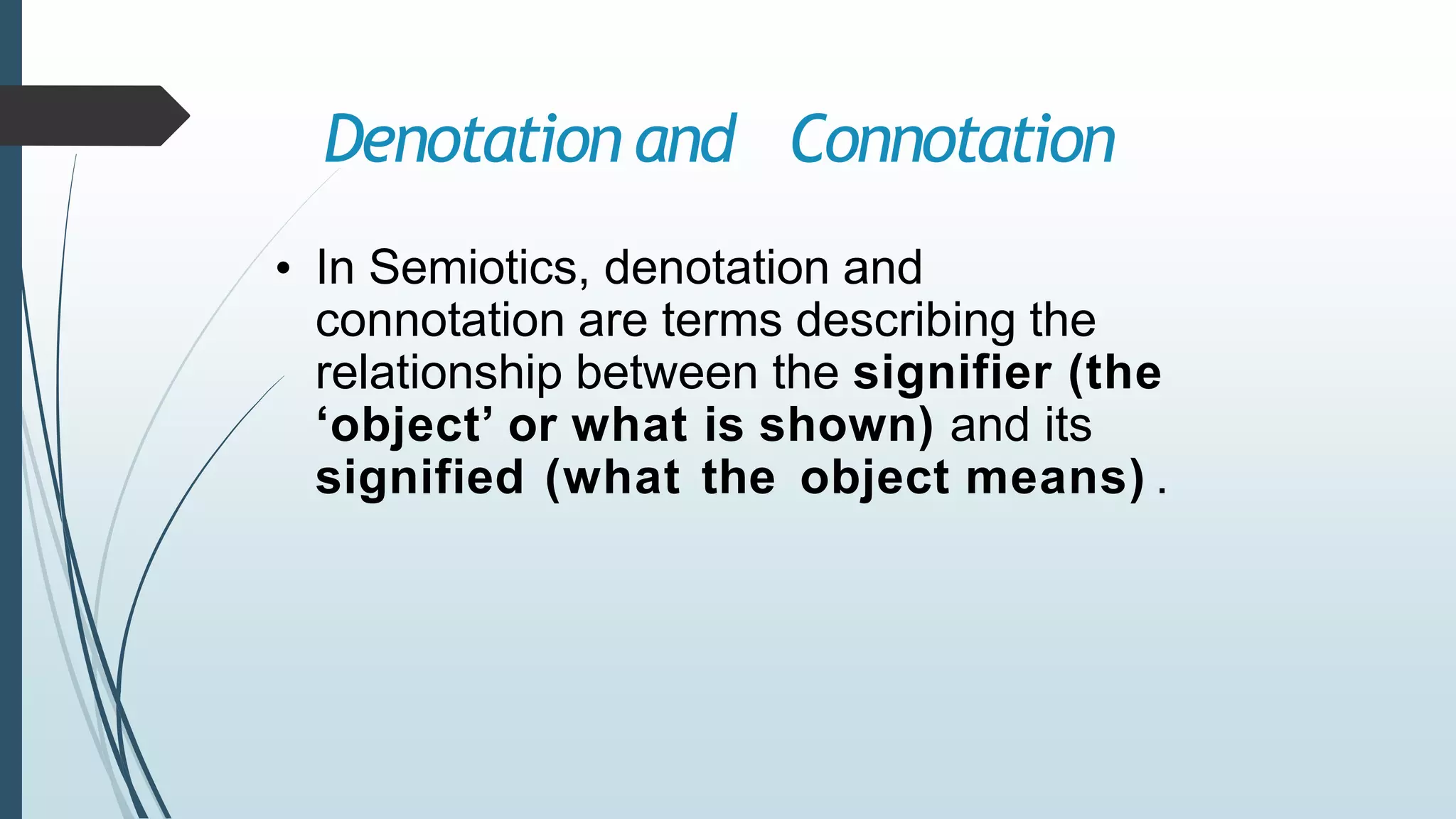
This document provides information on various media theorists that can be used for a 1B media analysis. It discusses theorists related to genre, narrative, representation, audience and media language. Specifically, it outlines key concepts from theorists such as Levi-Strauss on binary oppositions, Mulvey on the male gaze, Propp's narrative roles, and Hall's encoding/decoding model of audiences. It also provides guidance on applying these theories to analyze representations, audience positioning and genre in media texts.