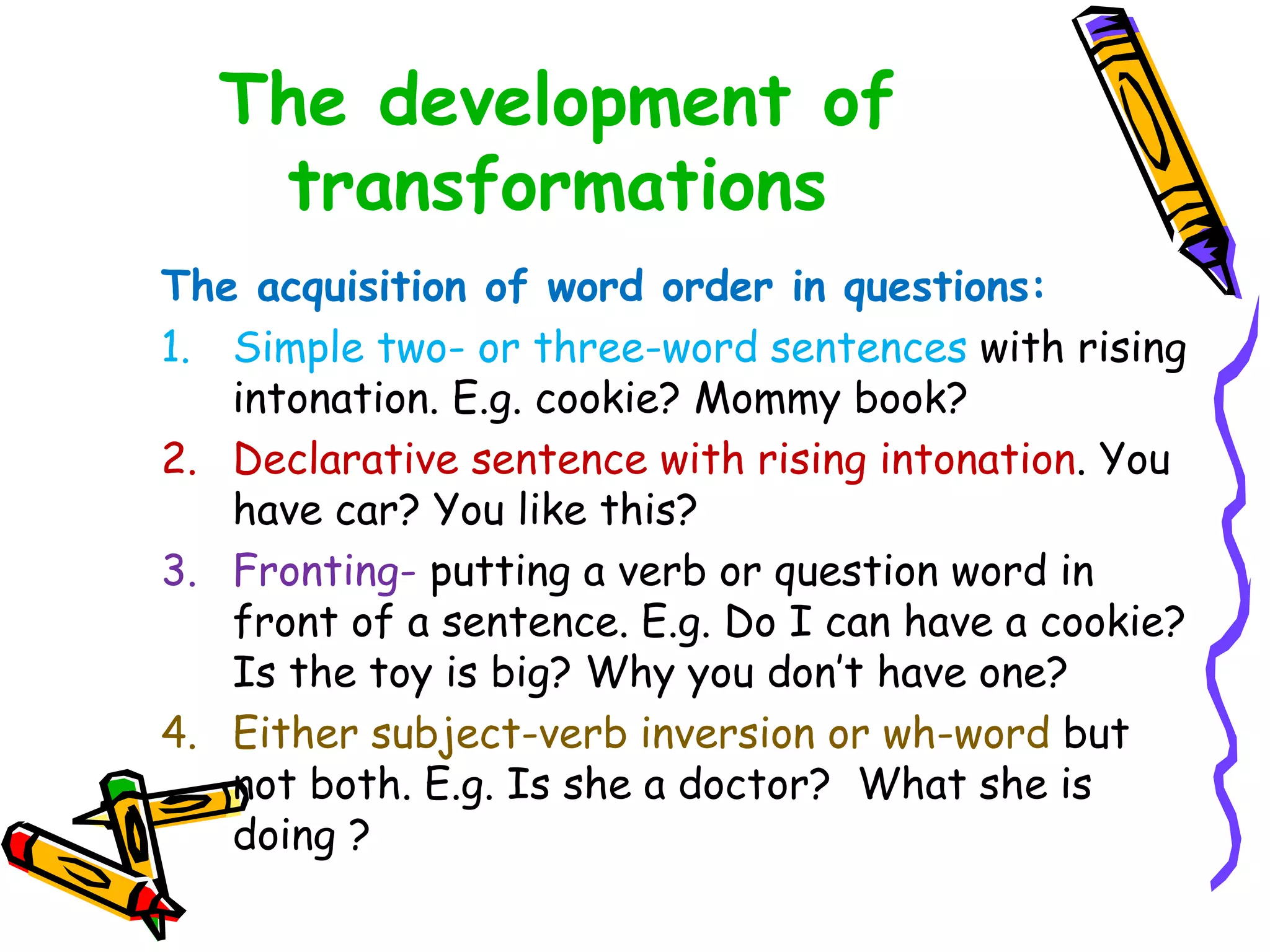
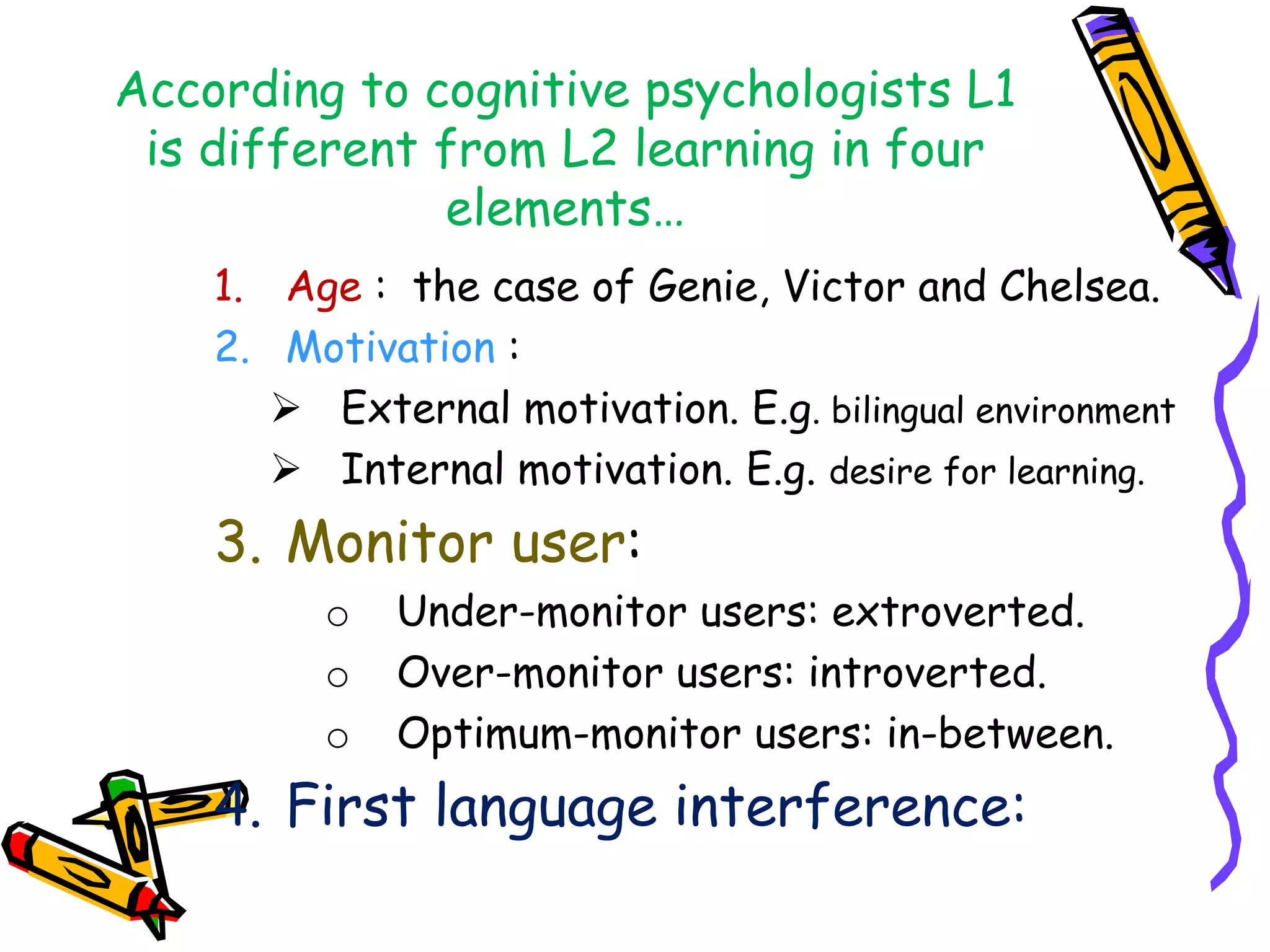
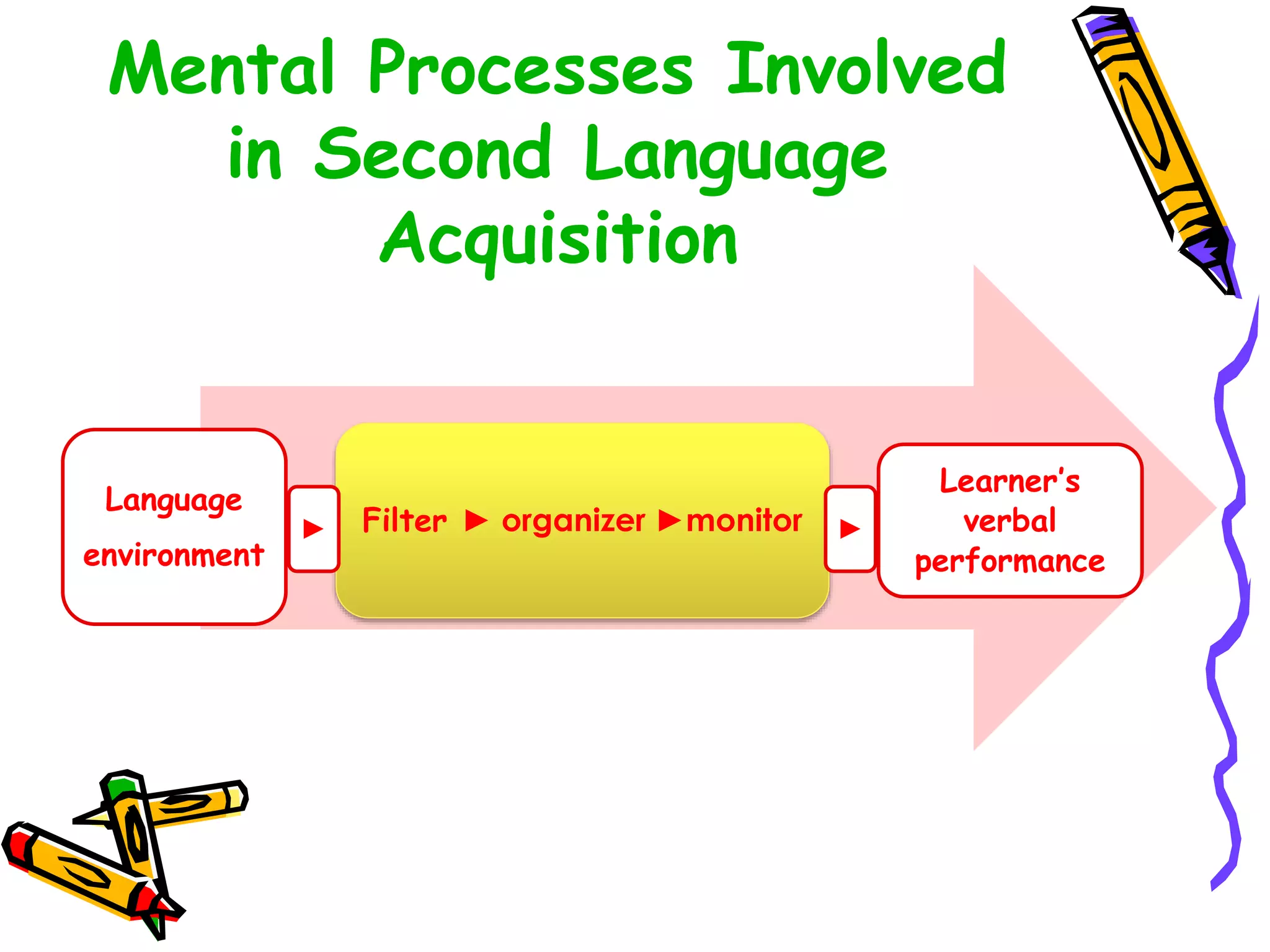
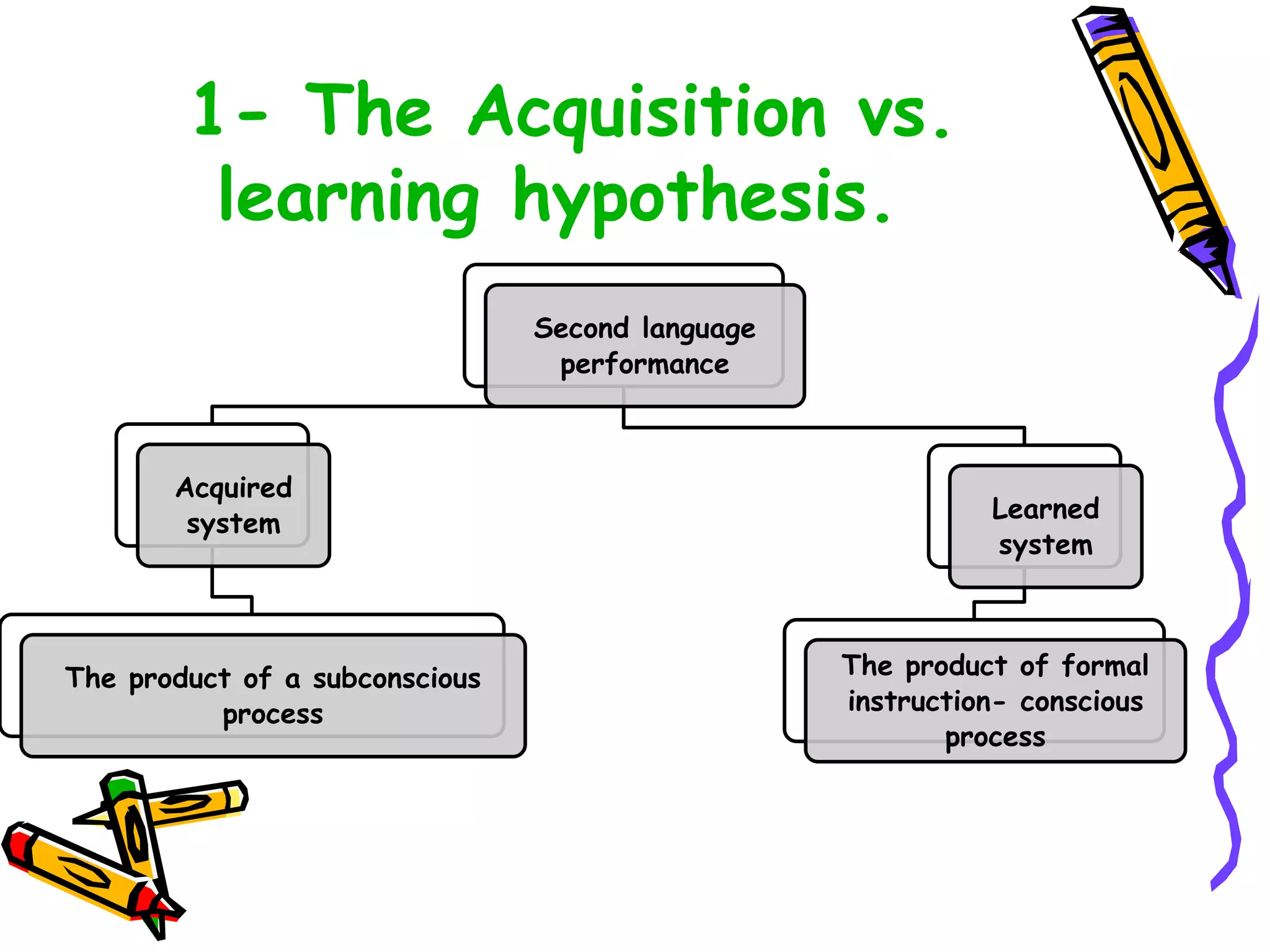
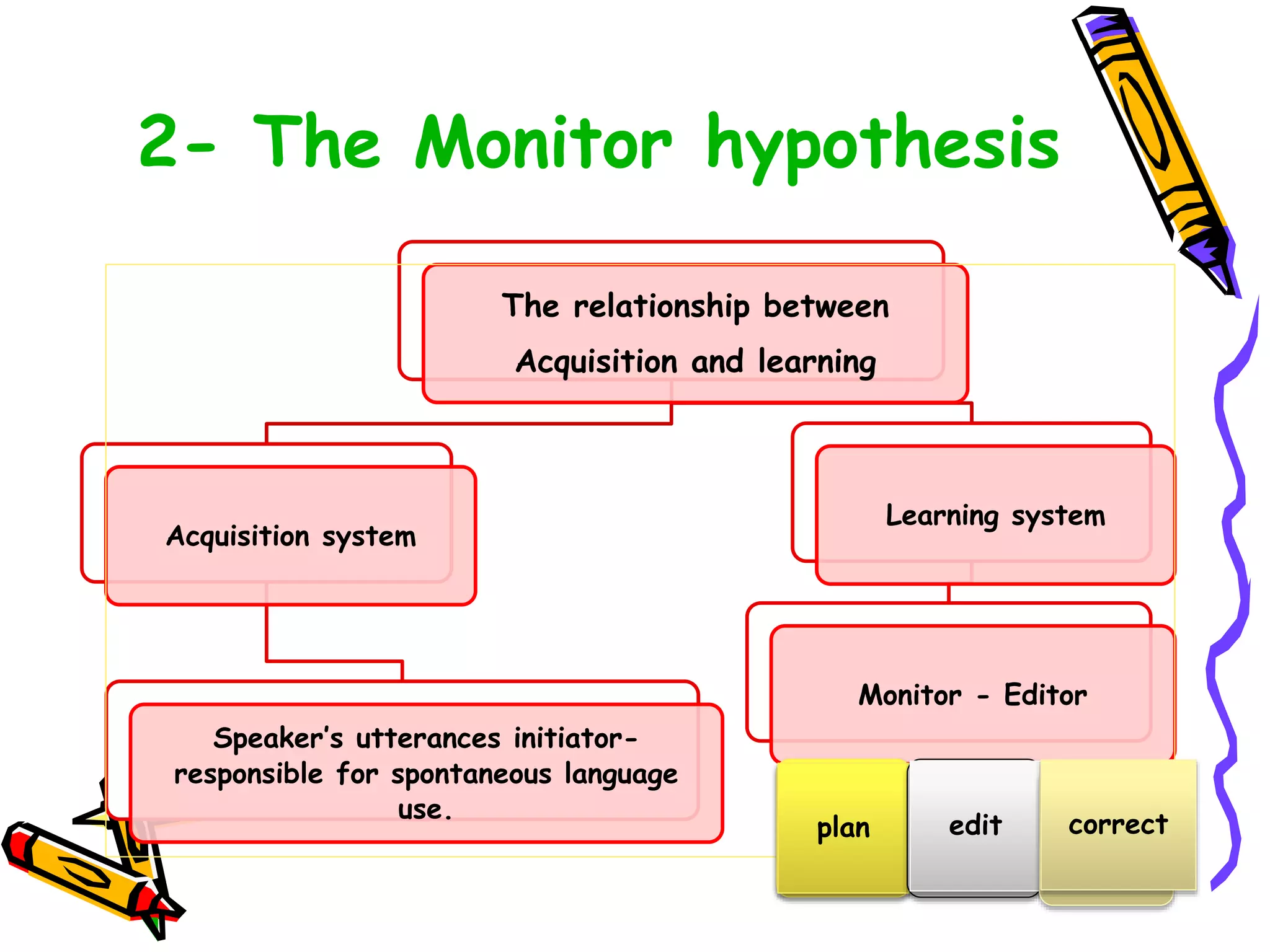
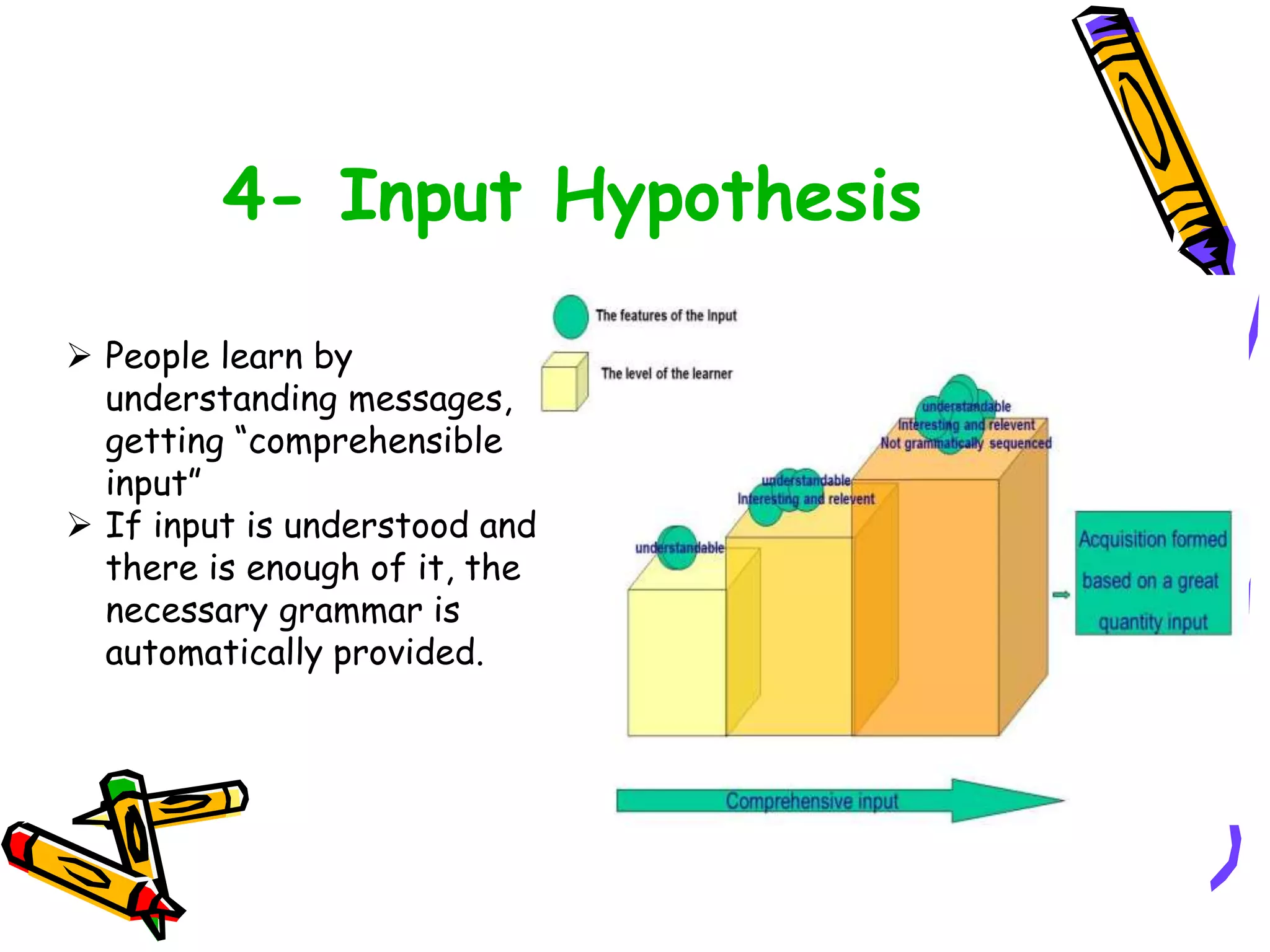
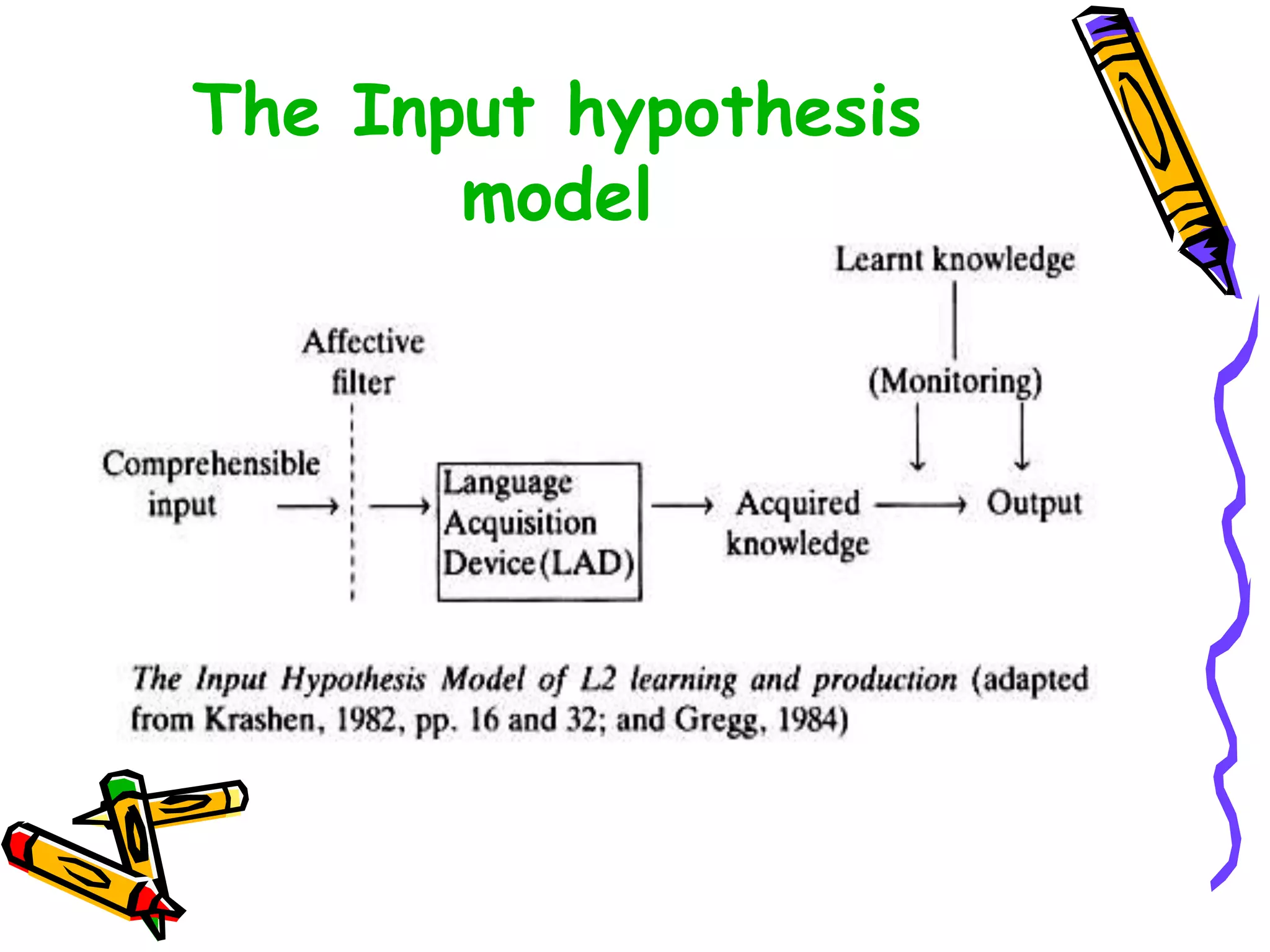
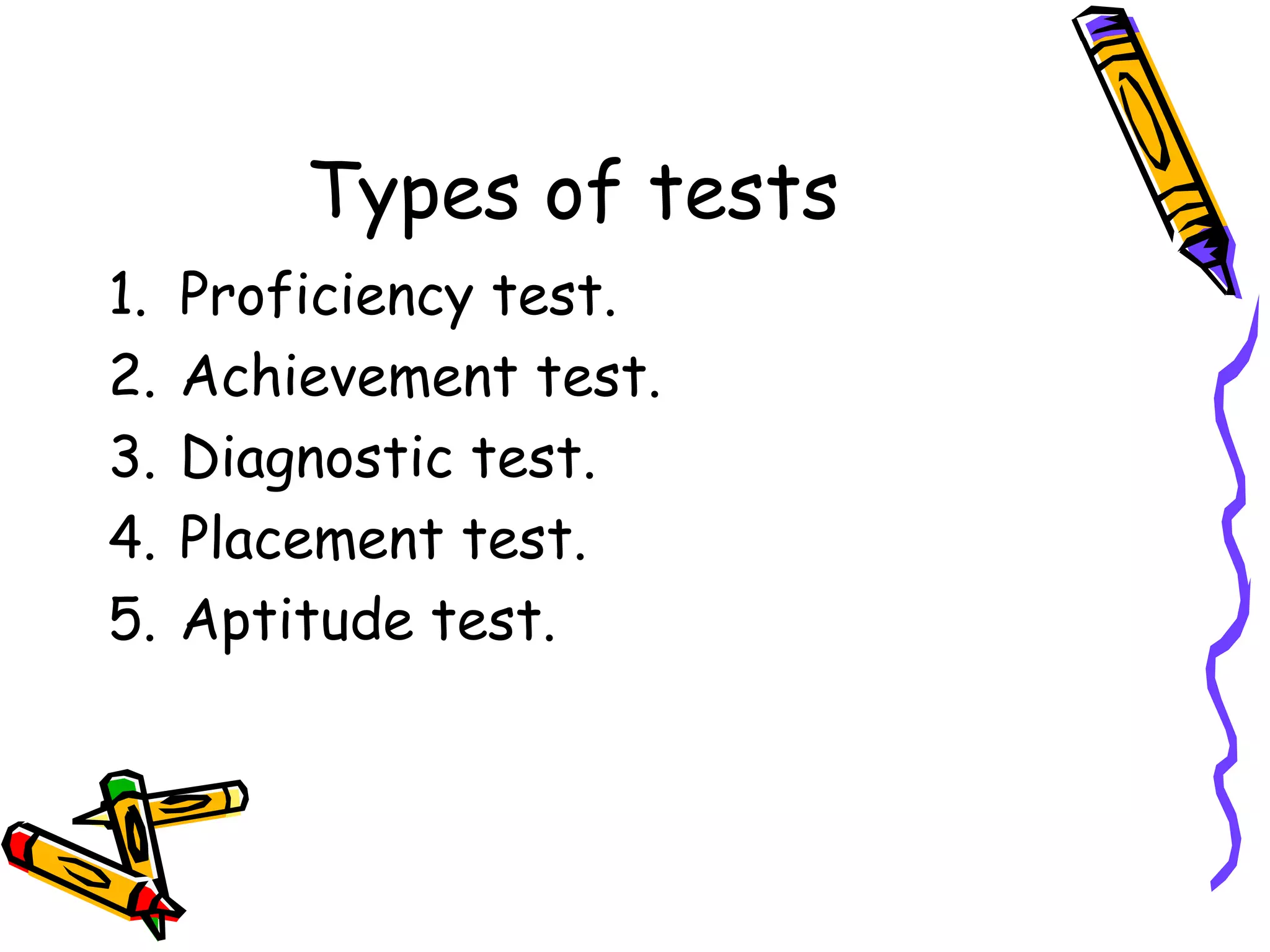
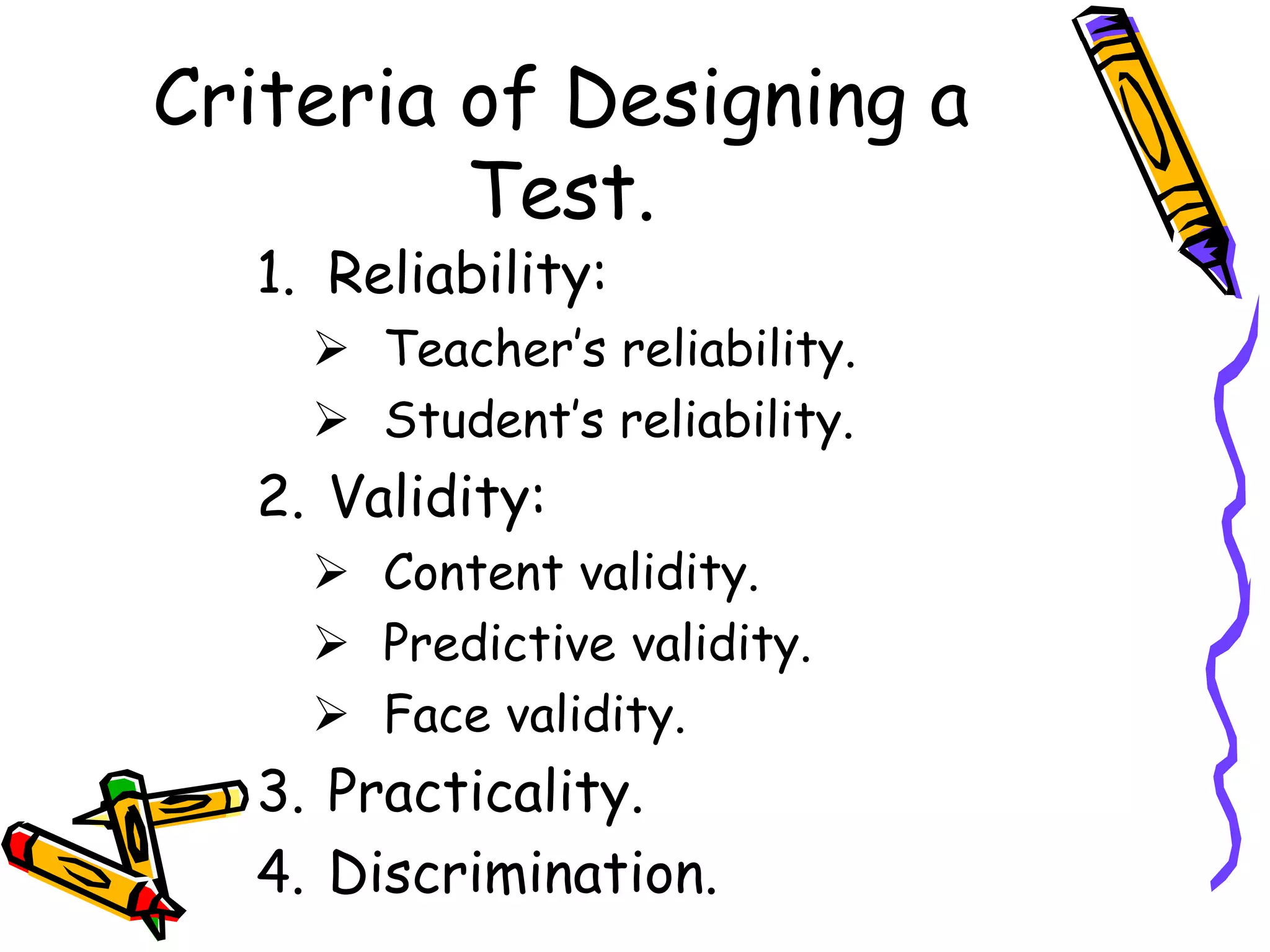
This document discusses various topics related to language acquisition and testing. It begins by comparing first and second language acquisition, and the cognitive vs behaviorist views. It then outlines Roger Brown's stages of grammatical morpheme development in children. Next, it discusses the development of transformations like negatives and questions. Stephen Krashen's theory of second language acquisition is then summarized, including the acquisition-learning distinction and the input, monitor, natural order, and affective filter hypotheses. Finally, the document discusses types of language tests and criteria for designing effective tests.