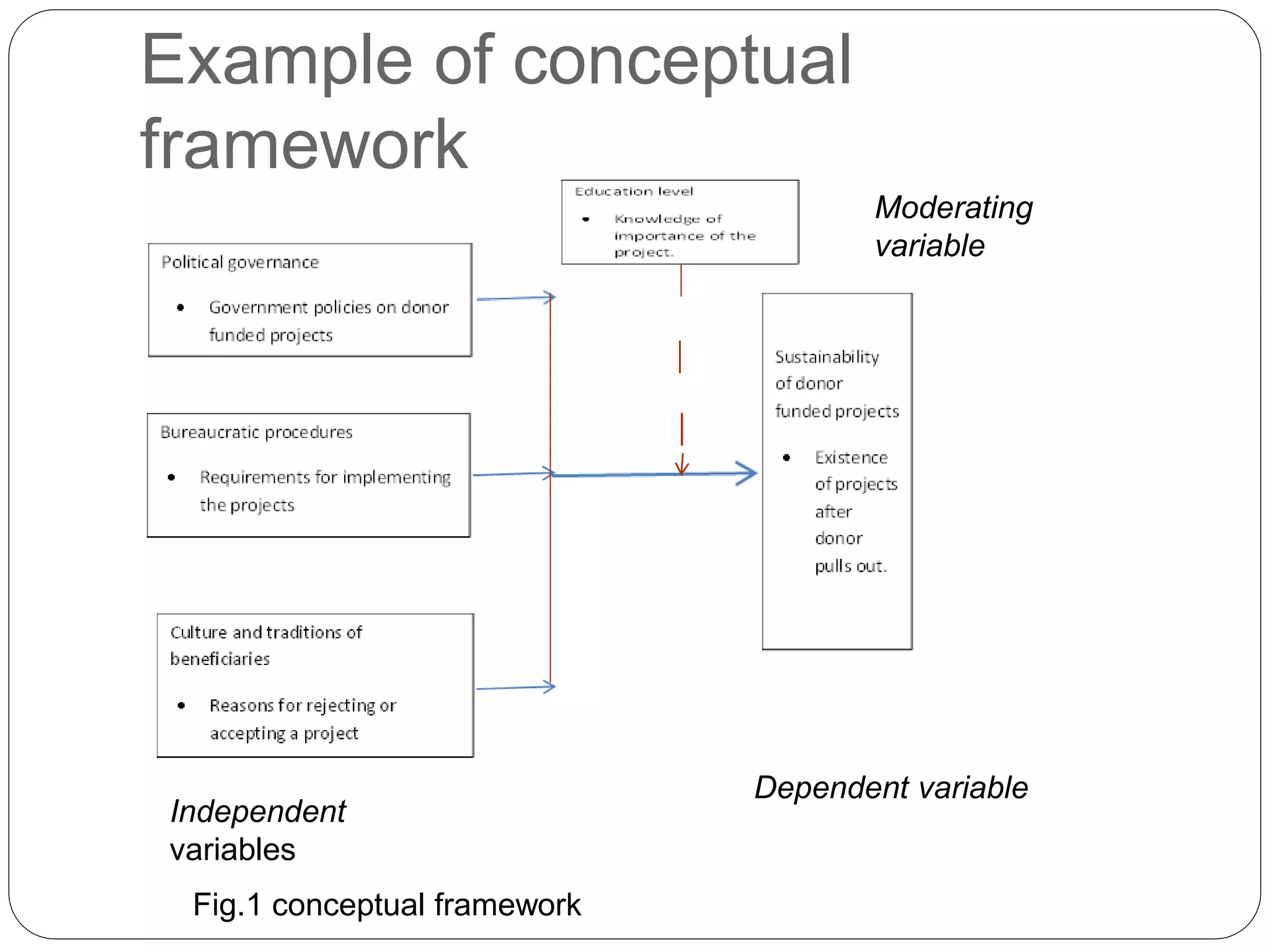
The document discusses theoretical and conceptual frameworks in research. It begins by defining a theoretical framework as a summary of a researcher's theory regarding a problem developed through a literature review. A theoretical framework identifies variables and their relationships. It establishes the structure that guides a research process. A conceptual framework is a hypothesized model that identifies concepts and relationships without existing theory. It provides an outline of preferred approach and relationships between variables. The document distinguishes theoretical frameworks as based on existing literature and theory, while conceptual frameworks are less formal and based on concepts and observations.