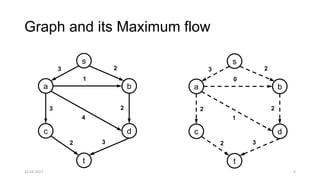
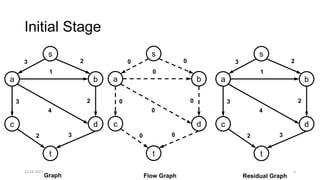
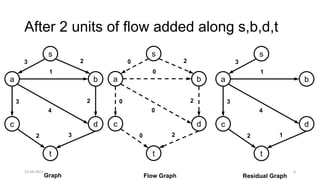
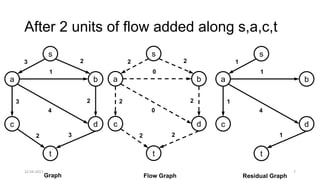
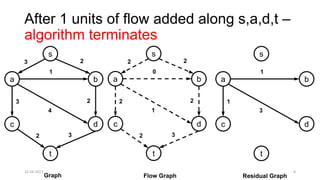
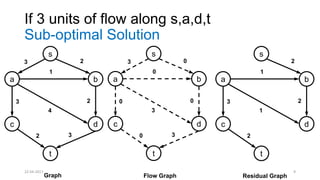
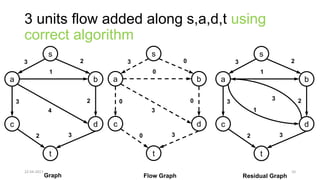
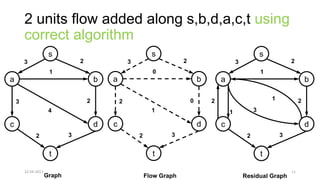
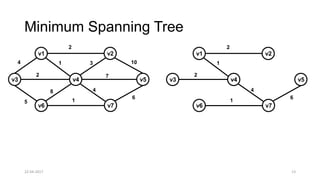
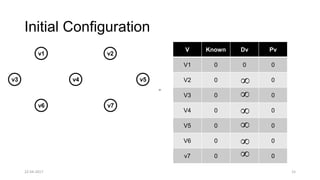
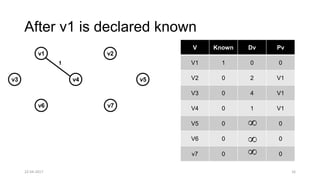
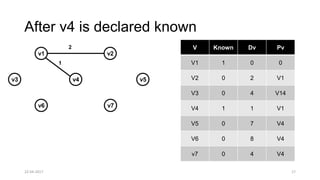
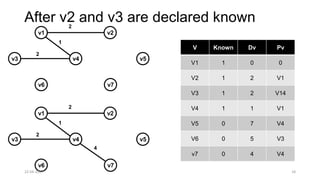
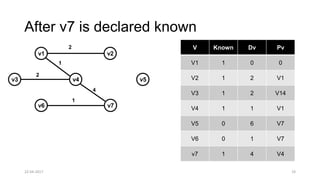
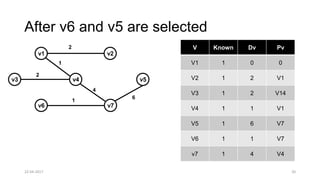
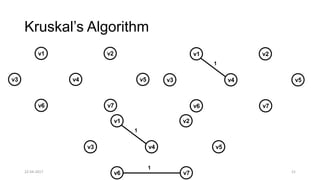
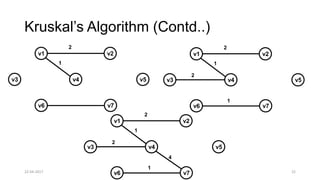
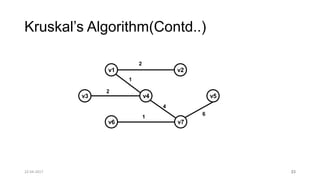
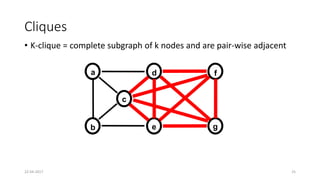
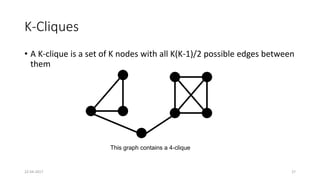
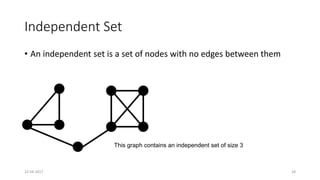
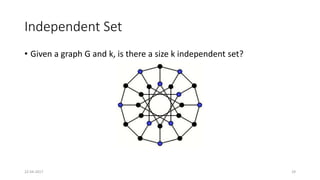
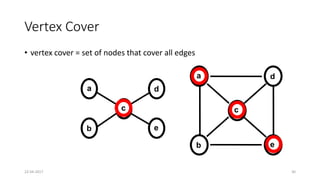
The document discusses theoretical foundations of computer science with a focus on graph algorithms, including network flow problems and spanning trees. It introduces algorithms such as Prim's and Kruskal's for finding minimum spanning trees and highlights applications in real-time scenarios like traffic flow and GPS navigation. It also covers NP-complete problems in graphs, such as k-clique and vertex cover, illustrating their complexities and applications in various fields.