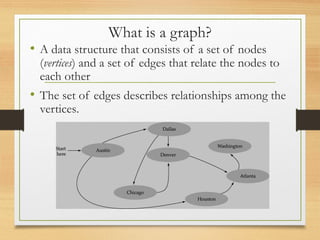
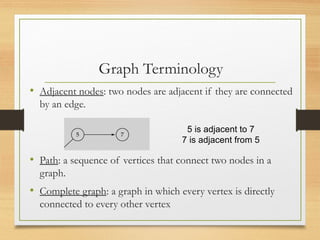
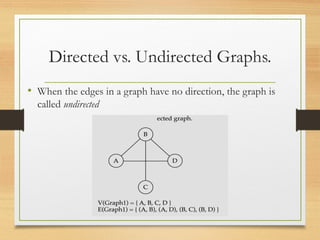
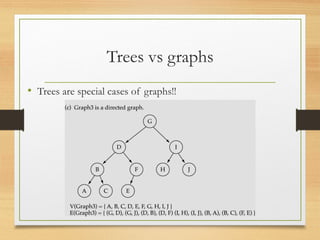
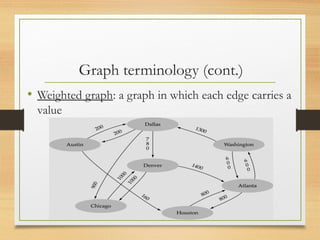
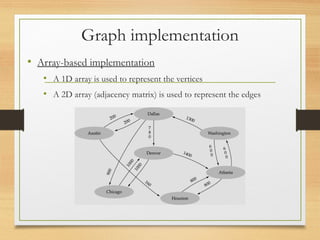
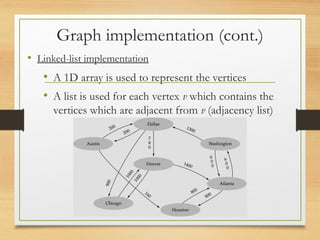
A graph is a data structure consisting of vertices and edges that relate vertices. It can be represented using an adjacency matrix or adjacency list. A graph is defined as G=(V,E) where V is the set of vertices and E is the set of edges. Graphs can be directed or undirected. Depth-first search (DFS) explores paths by going as deep as possible first, while breadth-first search (BFS) explores all neighbors at the current depth before moving deeper.