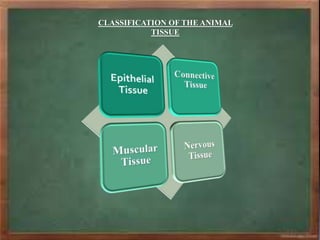
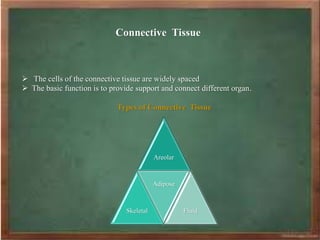
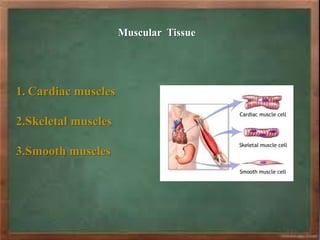
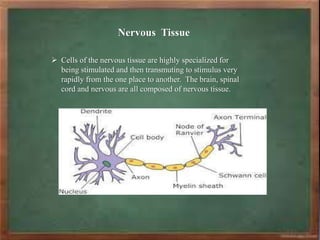
The document discusses the classification and characteristics of plant and animal tissues, detailing various types such as epithelial, connective, muscular, and nervous tissues. Plant tissues are primarily either meristematic or permanent, while animal tissues are categorized into four main types with specific subtypes highlighted. Each tissue type has unique structural features and functions, such as support, protection, and transportation within organisms.