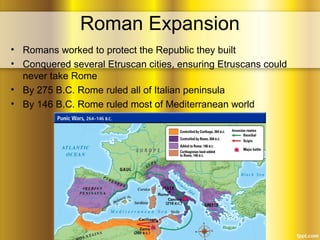
The Roman Republic was established in 509 B.C. after the overthrow of the Etruscan king Tarquin, featuring a government where citizens elected rulers, though patricians held significant power over plebeians. Rome expanded its territory through military conquests, defeating rivals such as Carthage in the Punic Wars, which transformed it into a dominant Mediterranean power but also led to economic and social disparities. Key figures like Julius Caesar emerged during a time of political strife, ultimately leading to the end of the Republic and the rise of the Roman Empire under Octavian in 31 B.C.