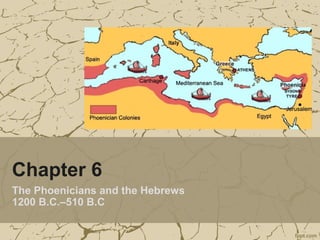
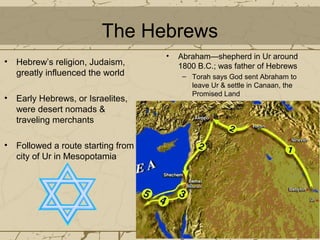
The Phoenicians and Hebrews settled in Canaan between 1200-510 BC. The Phoenicians lived in northern Canaan and were skilled traders and shipbuilders who established an alphabet. Their trading empire extended across the Mediterranean, including the colony of Carthage in North Africa. The Hebrews followed Abraham to Canaan from Mesopotamia and believed in one God, as taught by Moses who led them from Egypt. Under kings Saul, David, and Solomon they established a kingdom in Jerusalem before it fell to neighbors. Both groups contributed ideas of monotheism, morality, justice, and alphabetic writing.