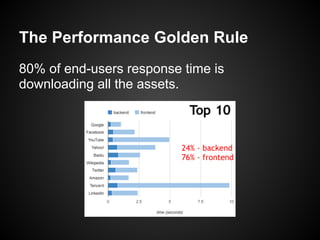
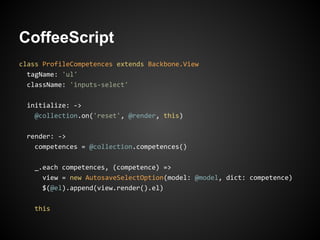
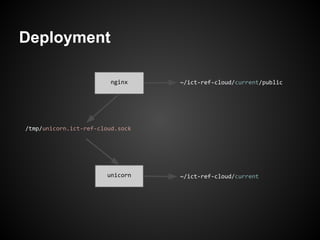
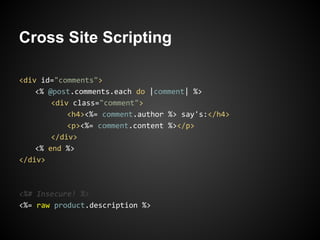
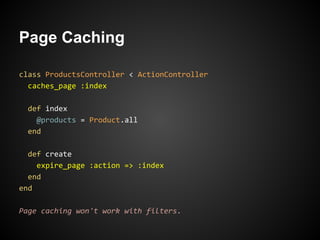
The document discusses best practices for building web applications using the Ruby on Rails framework. It covers topics like asset pipeline for concatenating and minifying assets, CoffeeScript and SASS for high-level languages, content negotiation for different formats, partials for view components, AJAX, caching, and solving the N+1 query problem through includes and batch loading.












![Non-Resourceful Routes
match 'photos/show' => 'photos#show', :via => [:get, :post]
match 'photos/:id' => 'photos#show', :constraints => { :id => /
[A-Z]d{5}/ }
match "photos", :constraints => { :subdomain => "admin" }
match "/stories/:name" => redirect("/posts/%{name}")
match 'books/*section/:title' => 'books#show'
root :to => 'pages#main'](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/092012-the-rails-way-120927164615-phpapp02/85/The-Rails-Way-17-320.jpg)



![SEO Friendy URL's
<%= link_to product.name, product %>
Will generate
/products/14-foo-bar
/products/14-foo-bar "/products/:id" => "products#show"
{ :id => "14-foo-bar" }
class Product < ActiveRecord::Base
def to_param
"#{id}-#{name.parametrize}"
end Product.find(params[:id])
end
Will call to_i
Product.find(14)
Example from: http://www.codeschool.com/courses/rails-best-practices](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/092012-the-rails-way-120927164615-phpapp02/85/The-Rails-Way-21-320.jpg)


![Response Rendering
class UsersController < ApplicationController
def new
@user = User.new new.html.erb
end
def create
@user = User.new(params[:user])
if @user.save
redirect_to :action => :show show.html.erb
else
render :new new.html.erb
end
end
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/092012-the-rails-way-120927164615-phpapp02/85/The-Rails-Way-24-320.jpg)



![Content Negotiation
class ProductsController < ApplicationController
respond_to :html, :json, :js
def edit
respond_with Product.find(params[:id])
end
def update
respond_with Product.update(params[:id], params[:product])
end
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/092012-the-rails-way-120927164615-phpapp02/85/The-Rails-Way-28-320.jpg)













![AJAX
/app/controllers/products_controller.rb
class ProductsController < ApplicationController
def create
@product = Product.new(params[:product])
respond_to do |format|
if @product.save
format.html { redirect_to @product }
else
format.html { render :action => 'new' }
format.js
end
end
end
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/092012-the-rails-way-120927164615-phpapp02/85/The-Rails-Way-42-320.jpg)






![Conditional GET support
class ProductsController < ApplicationController
def show
@product = Product.find(params[:id])
if stale?(:last_modified => @product.updated_at.utc, :etag => @product)
respond_to do |format|
# ... normal response processing
end
end
end
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/092012-the-rails-way-120927164615-phpapp02/85/The-Rails-Way-50-320.jpg)






