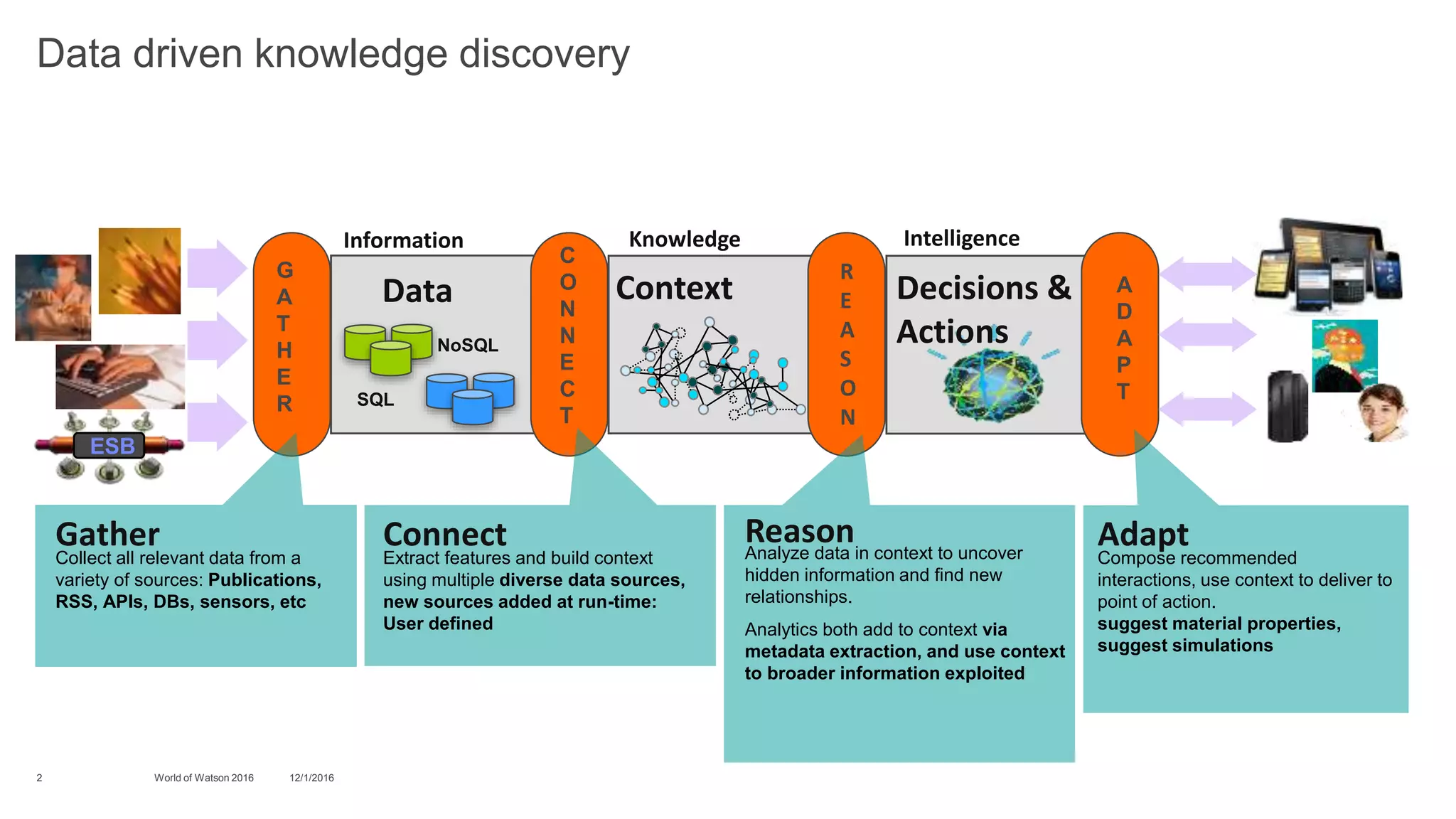
1) The document discusses the power of cognitive computing for the Internet of Things. It describes how cognitive systems can gather data from various sources, extract context and features to discover hidden information, and recommend decisions and actions.
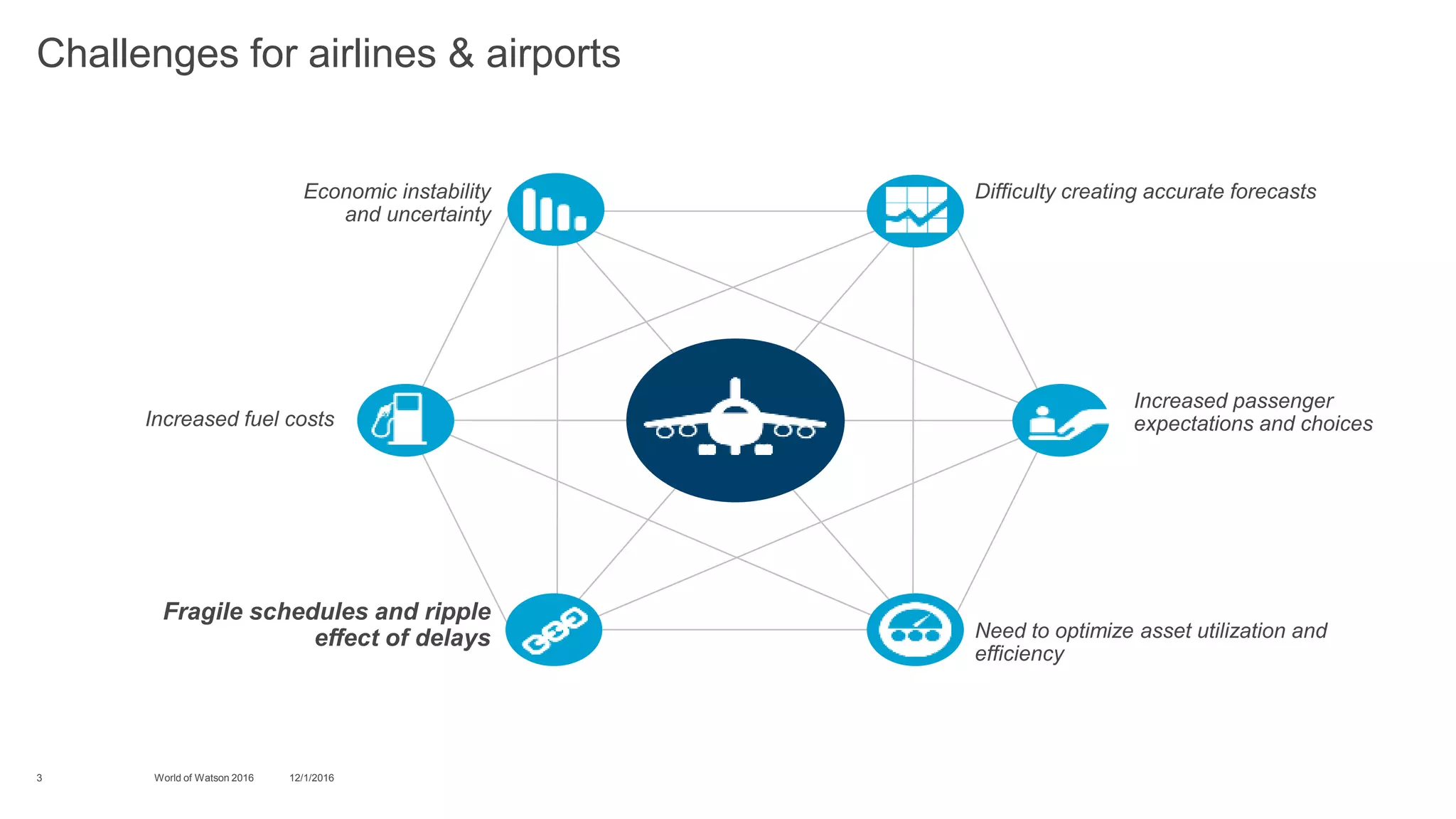
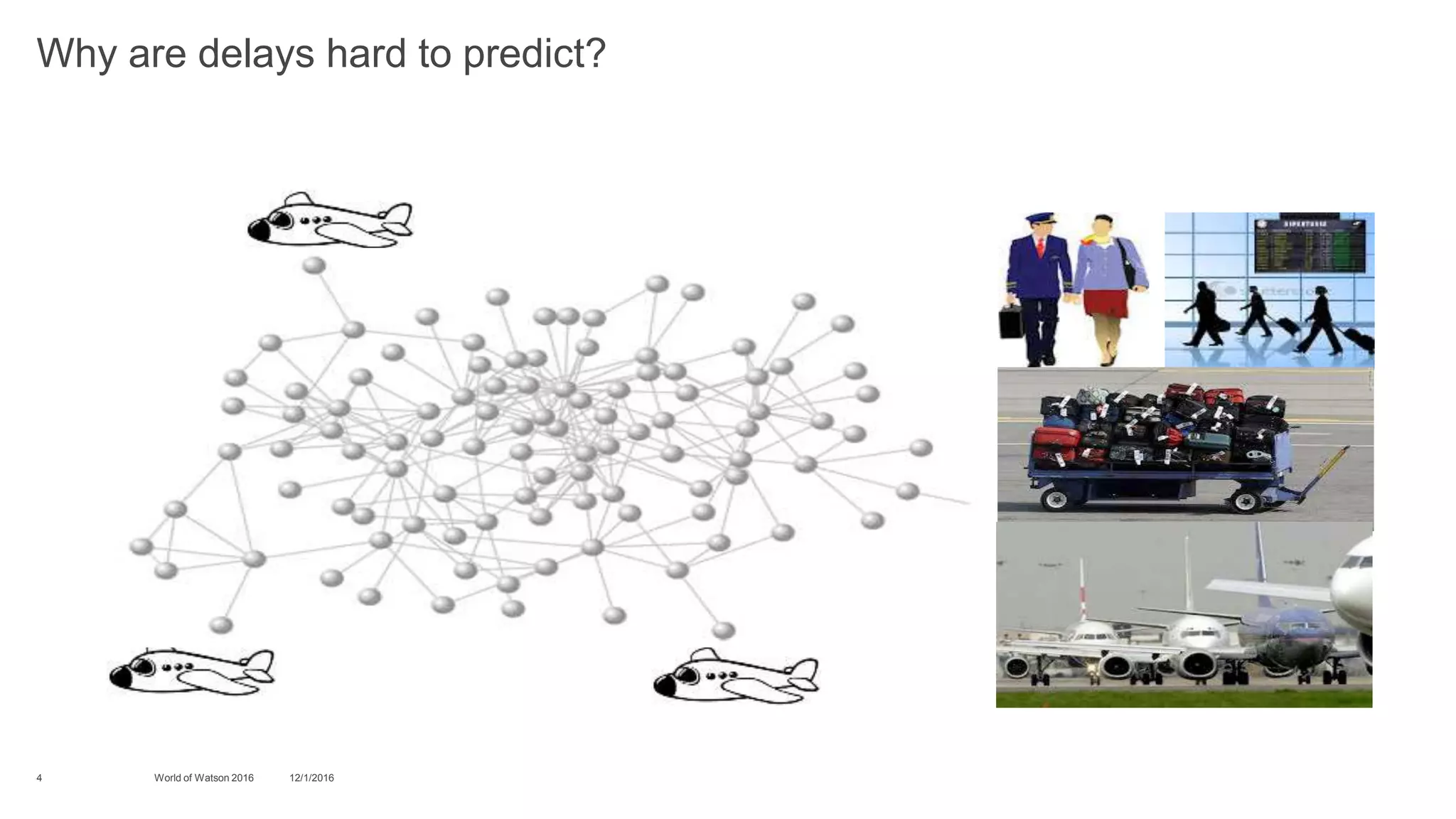
2) It then discusses specific challenges for airlines and airports, such as fragile schedules that can be disrupted by delays, increased passenger expectations, economic instability, and the difficulty of creating accurate delay forecasts.
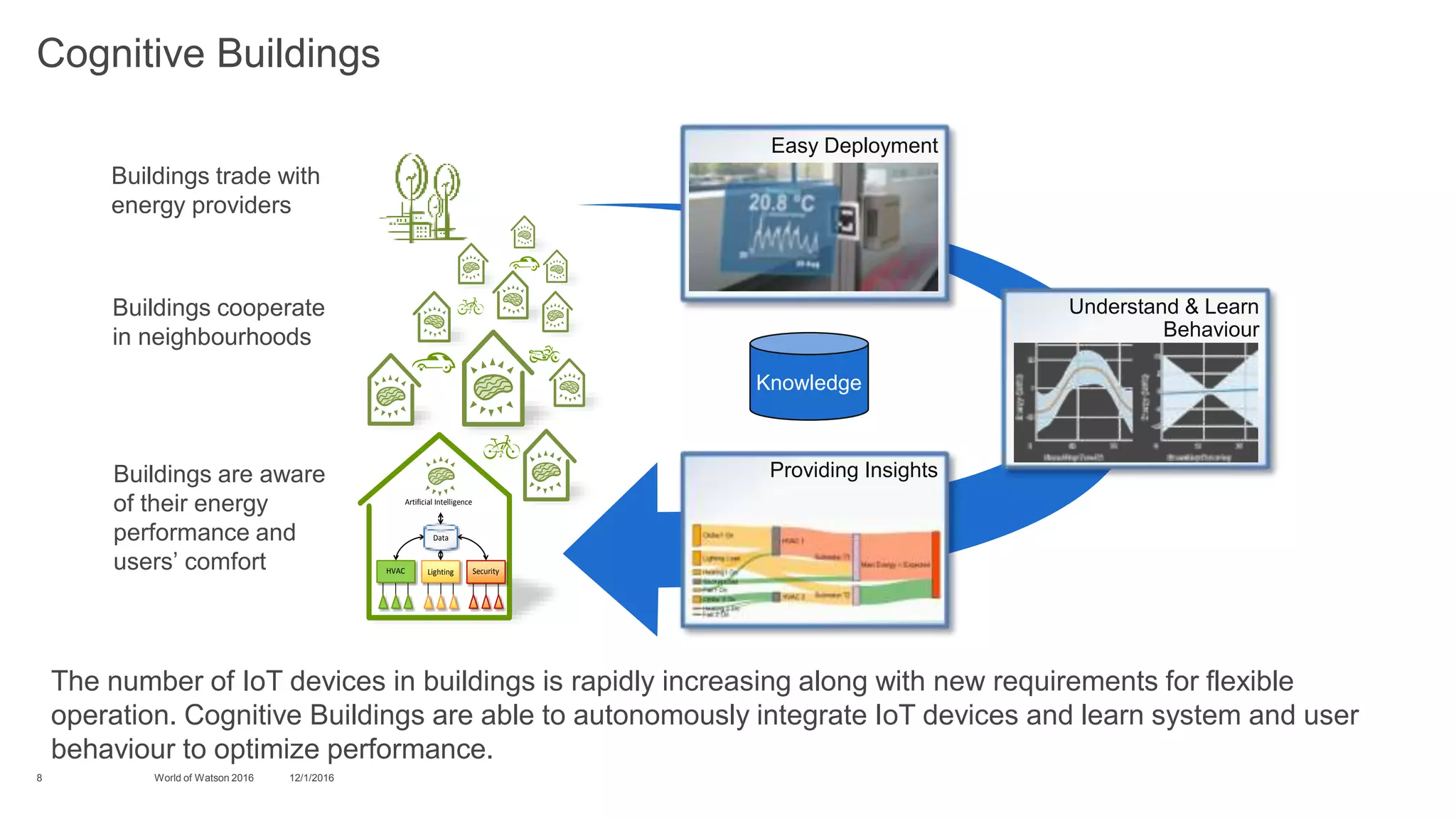
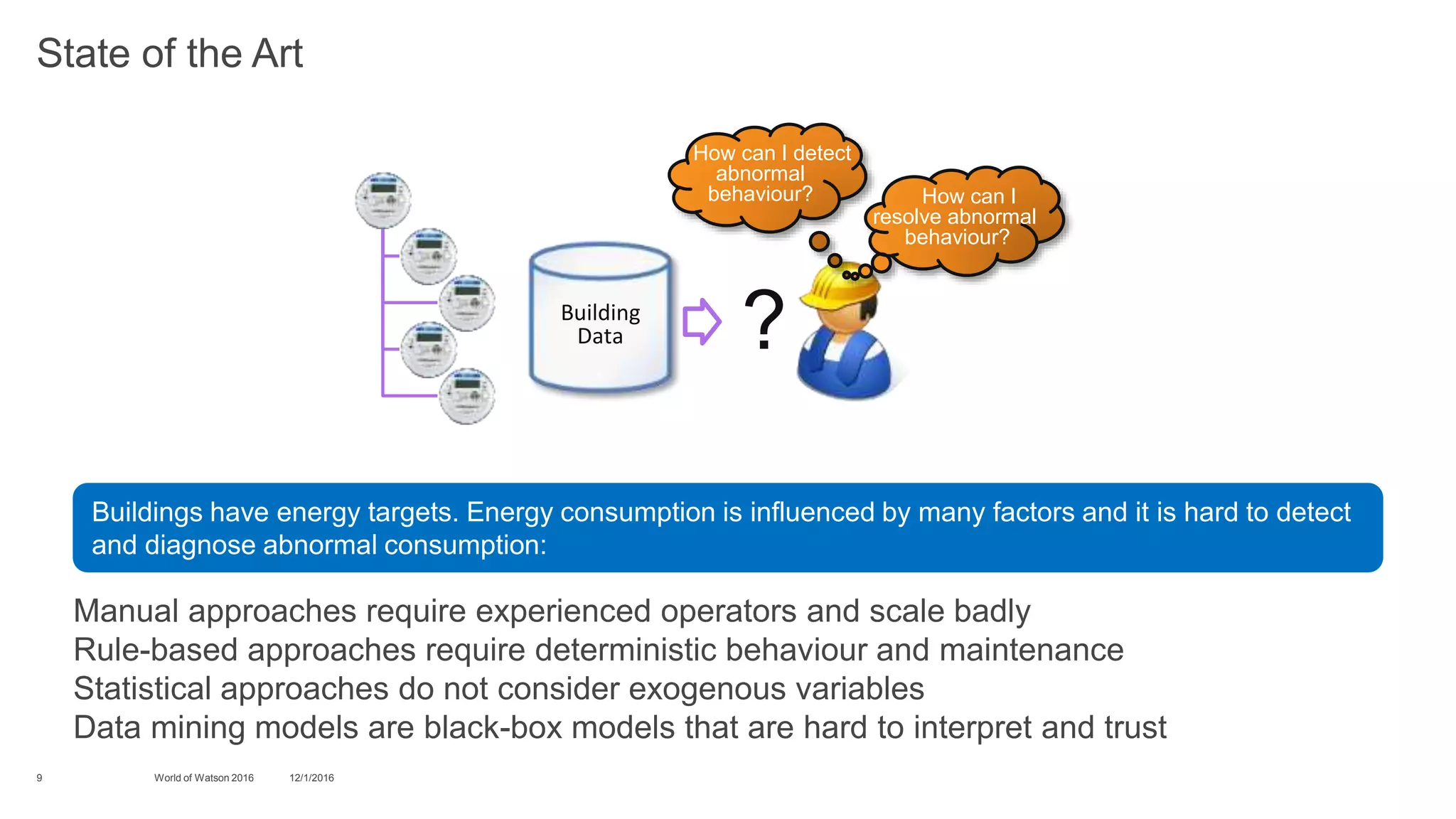
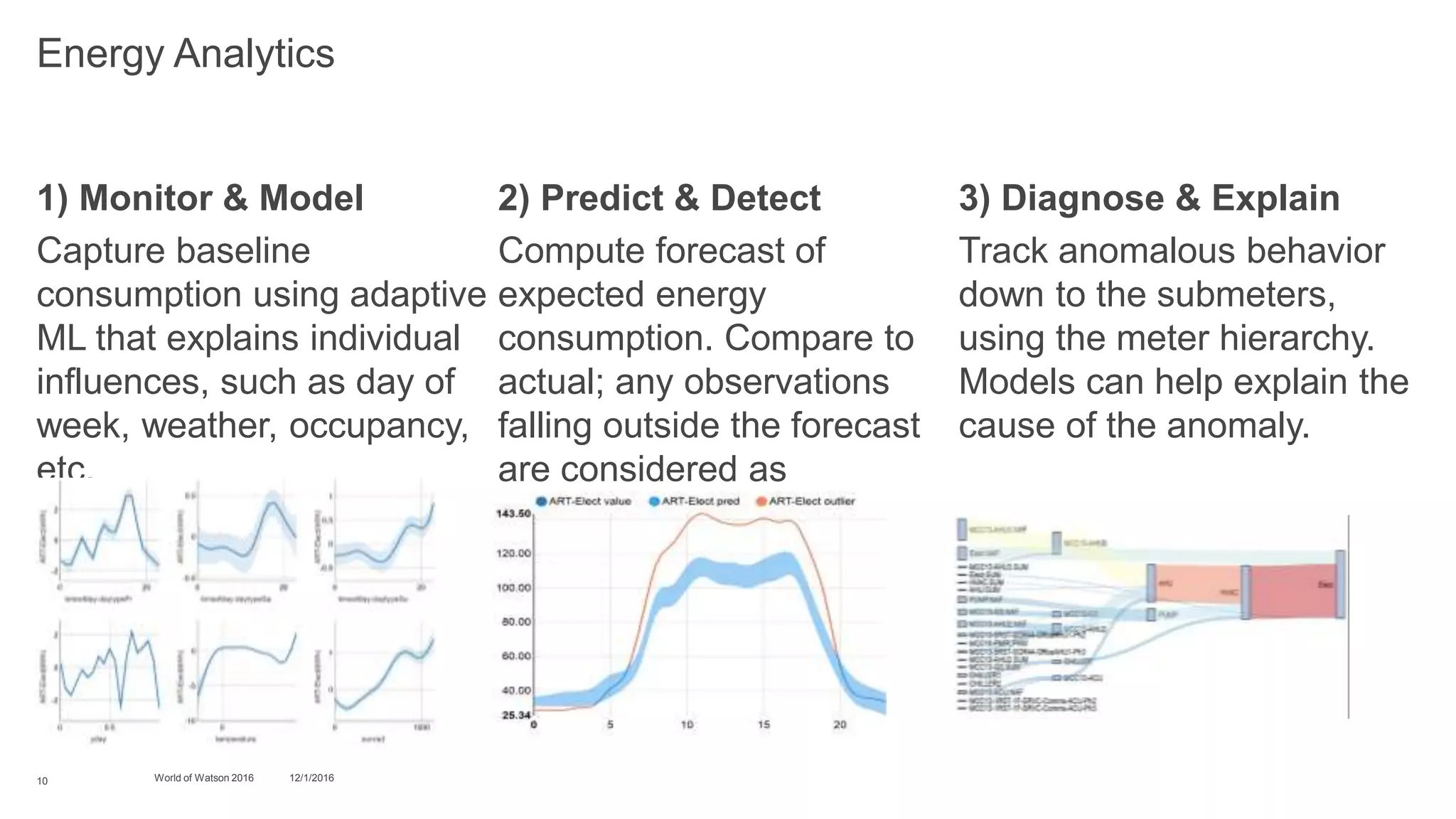
3) Finally, it discusses challenges for optimizing energy usage in "cognitive buildings" using IoT devices, including detecting and diagnosing abnormal energy consumption patterns across various subsystems in a building. It describes how cognitive approaches can help monitor usage, detect anomalies, and explain their causes.