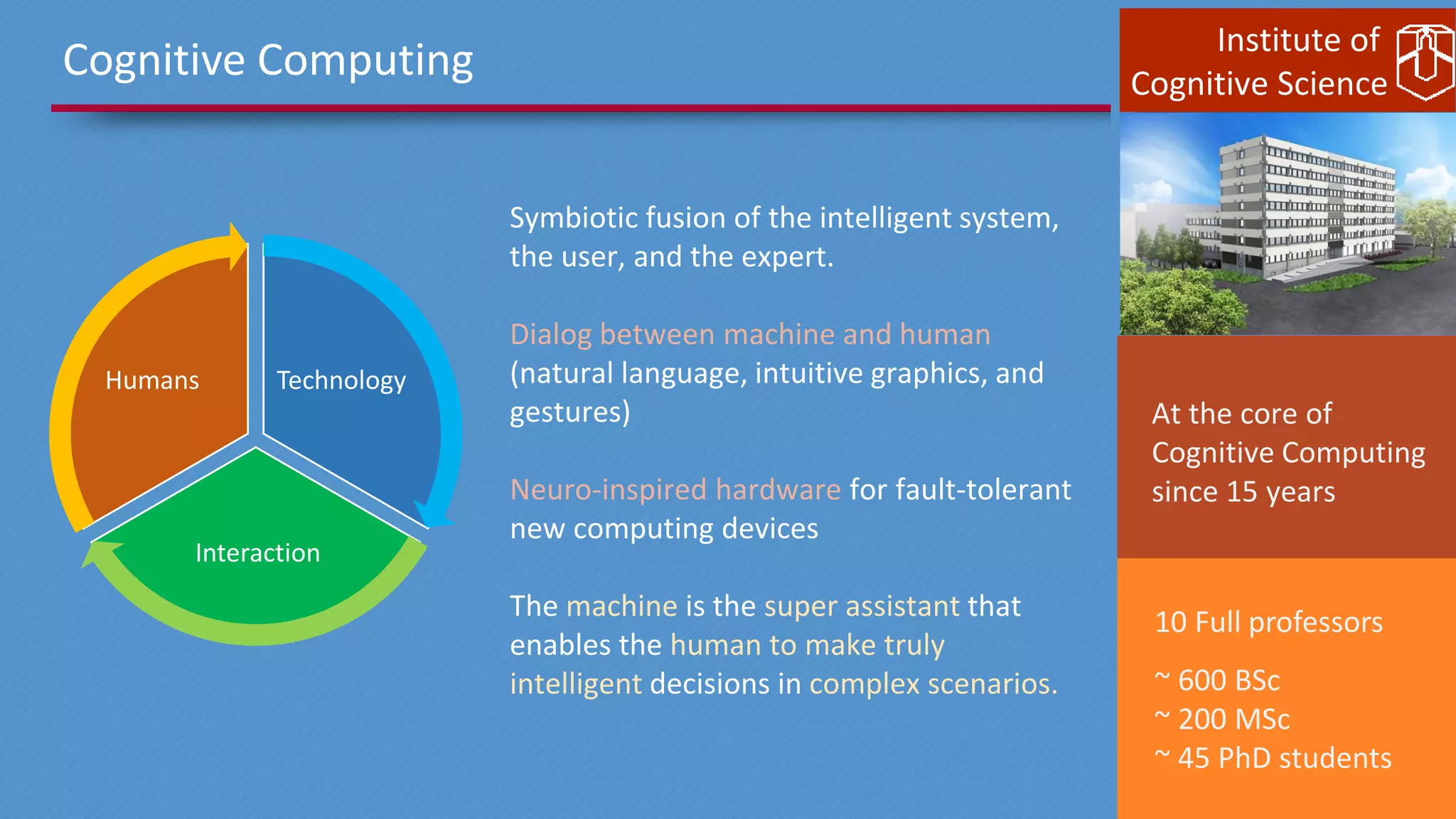
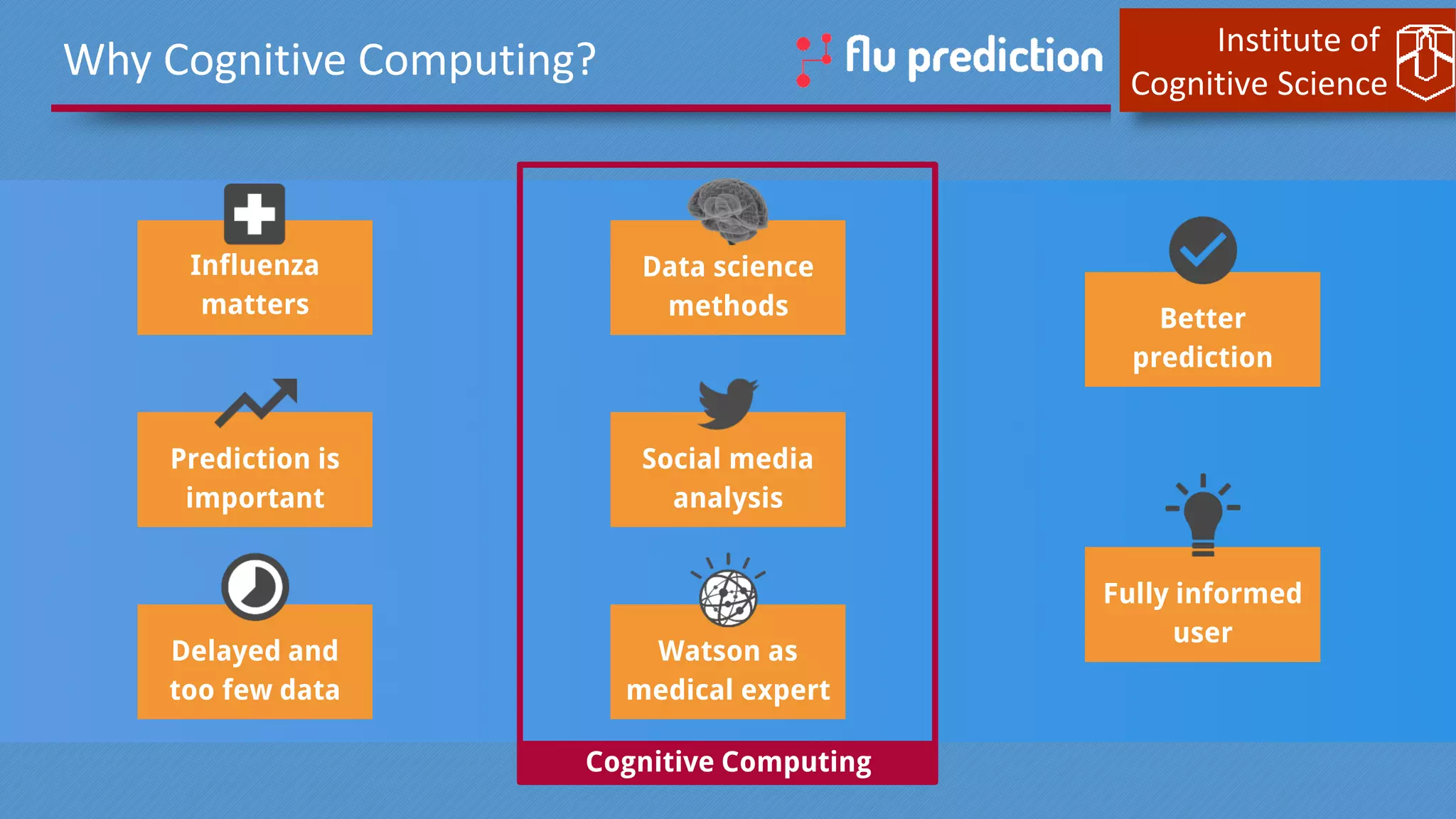
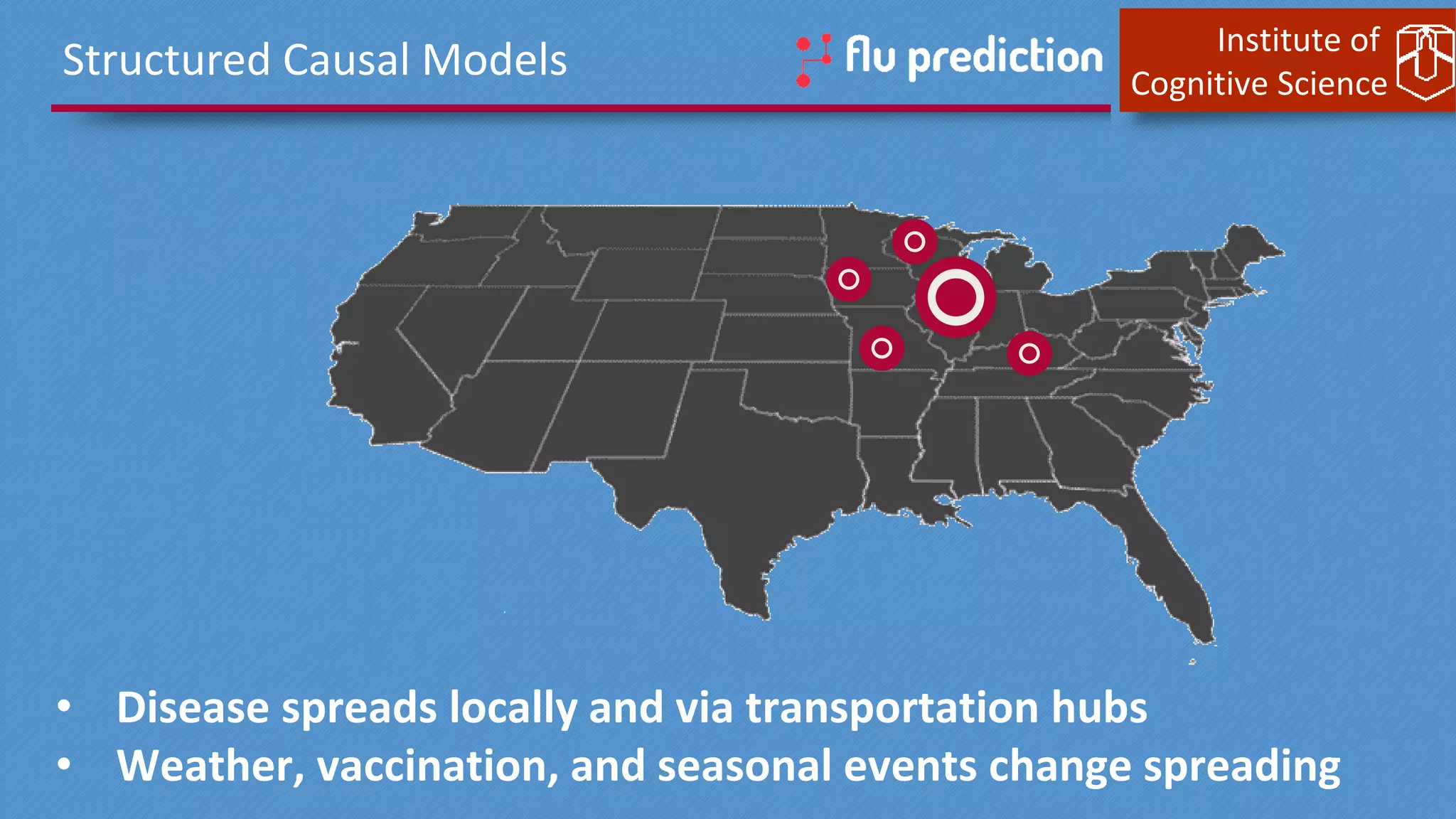
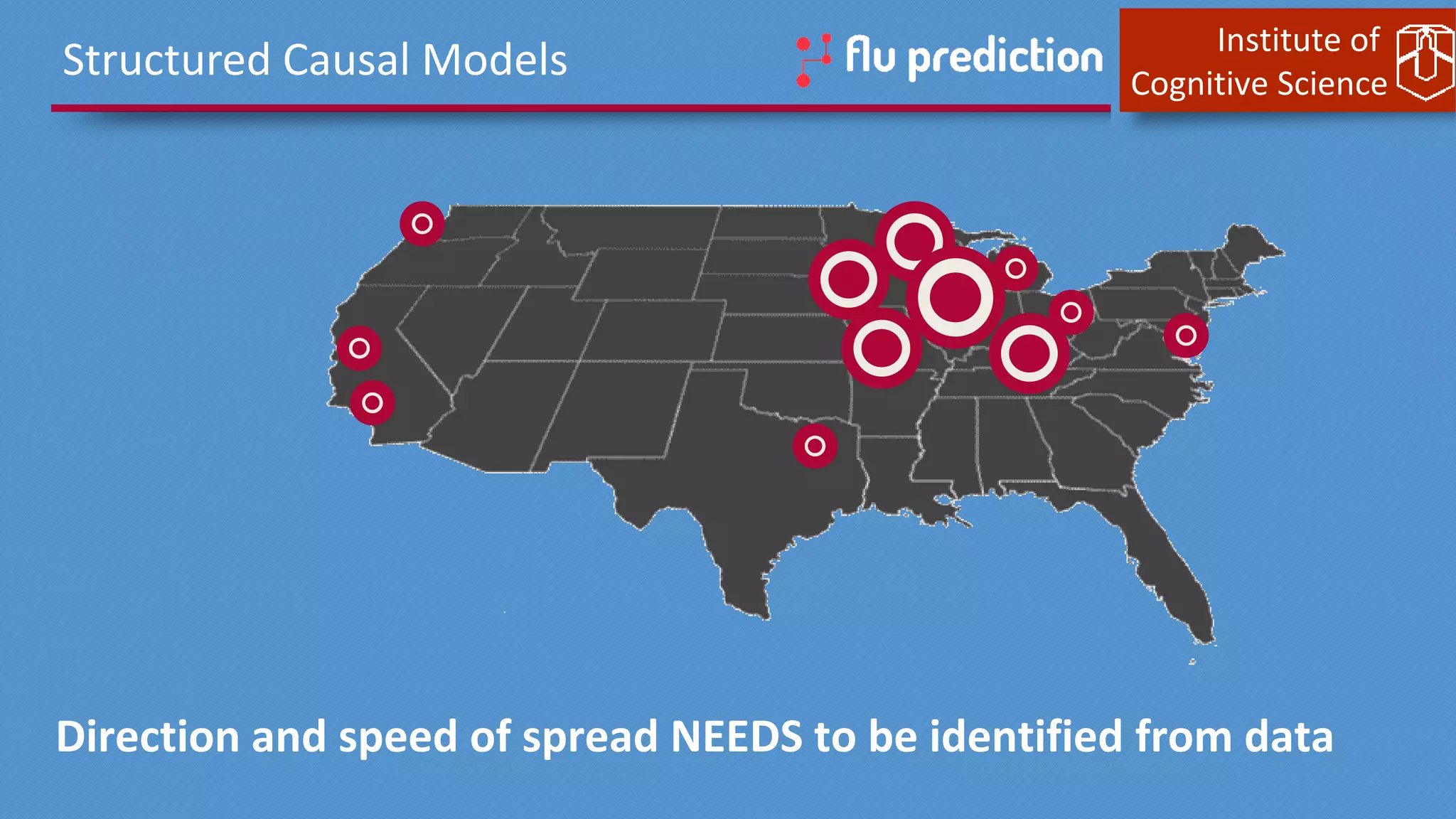
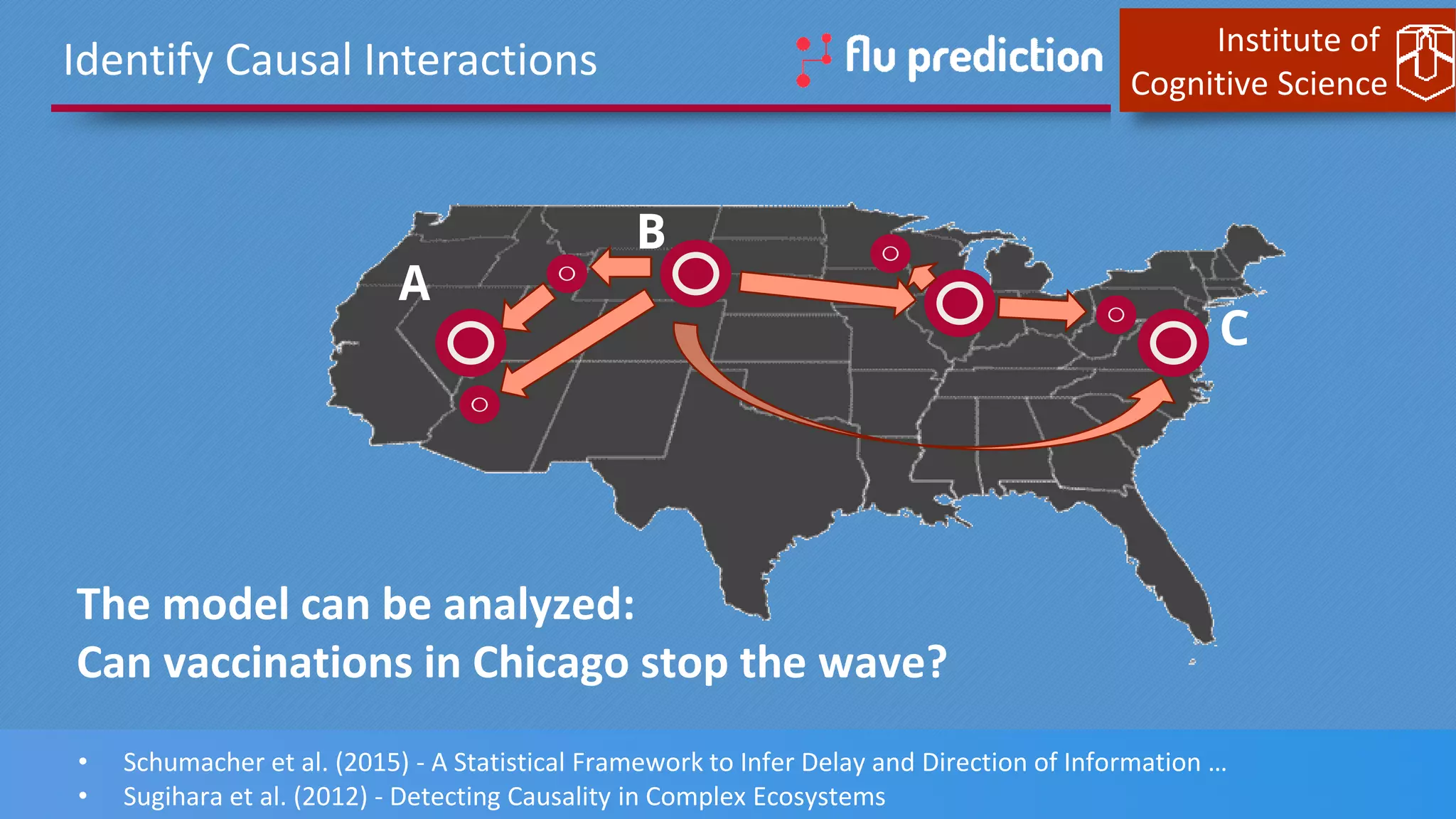
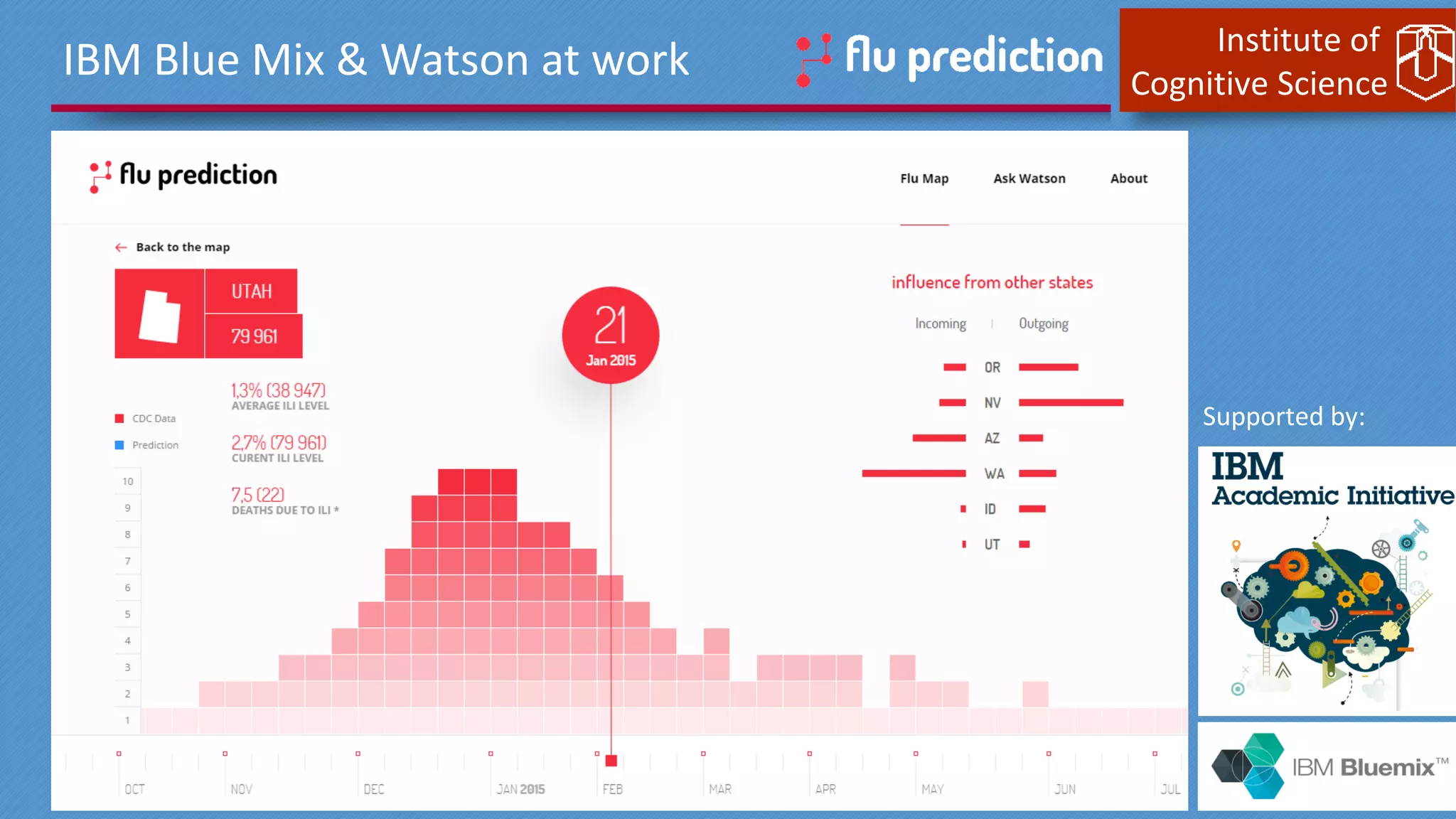
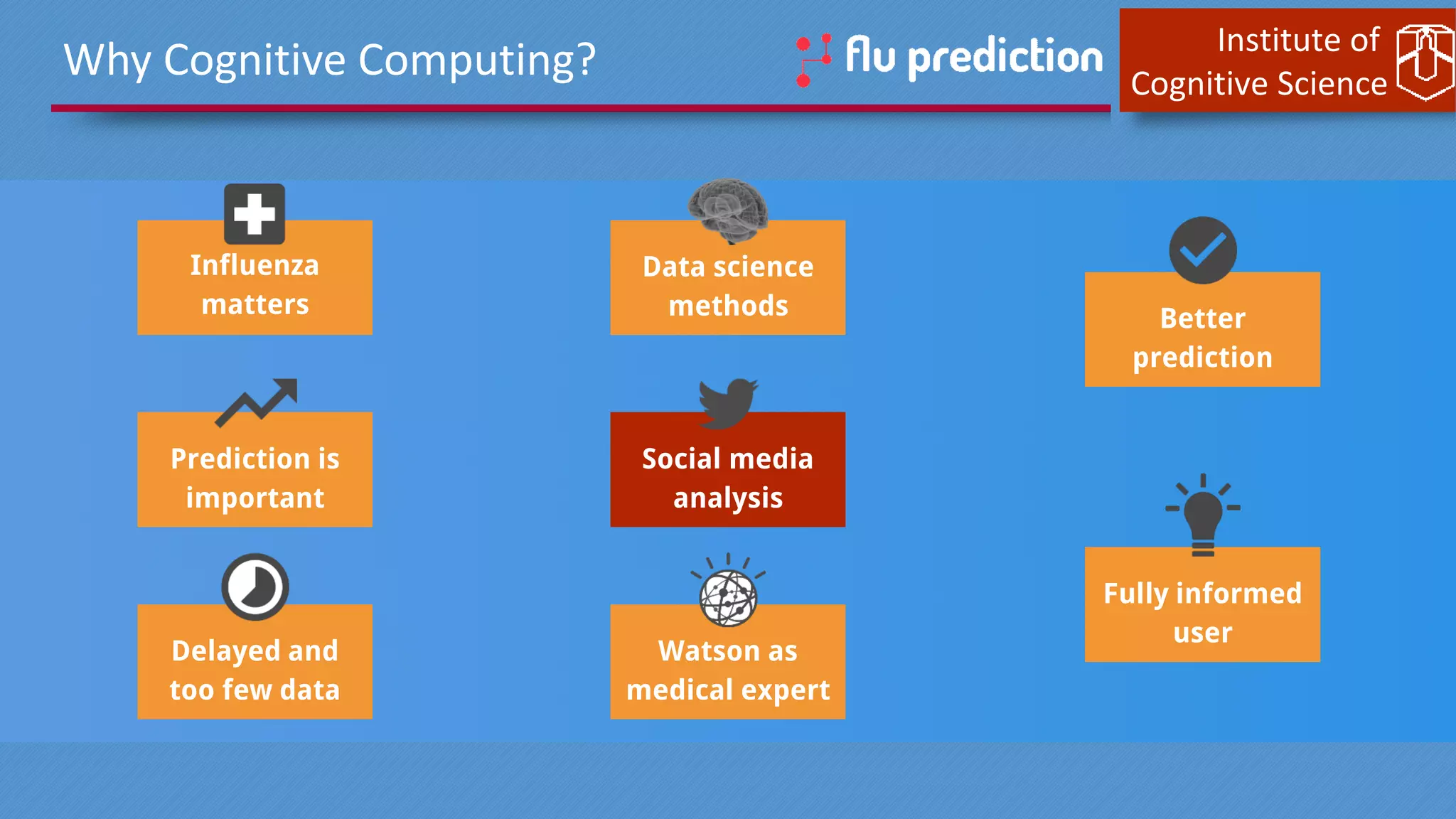
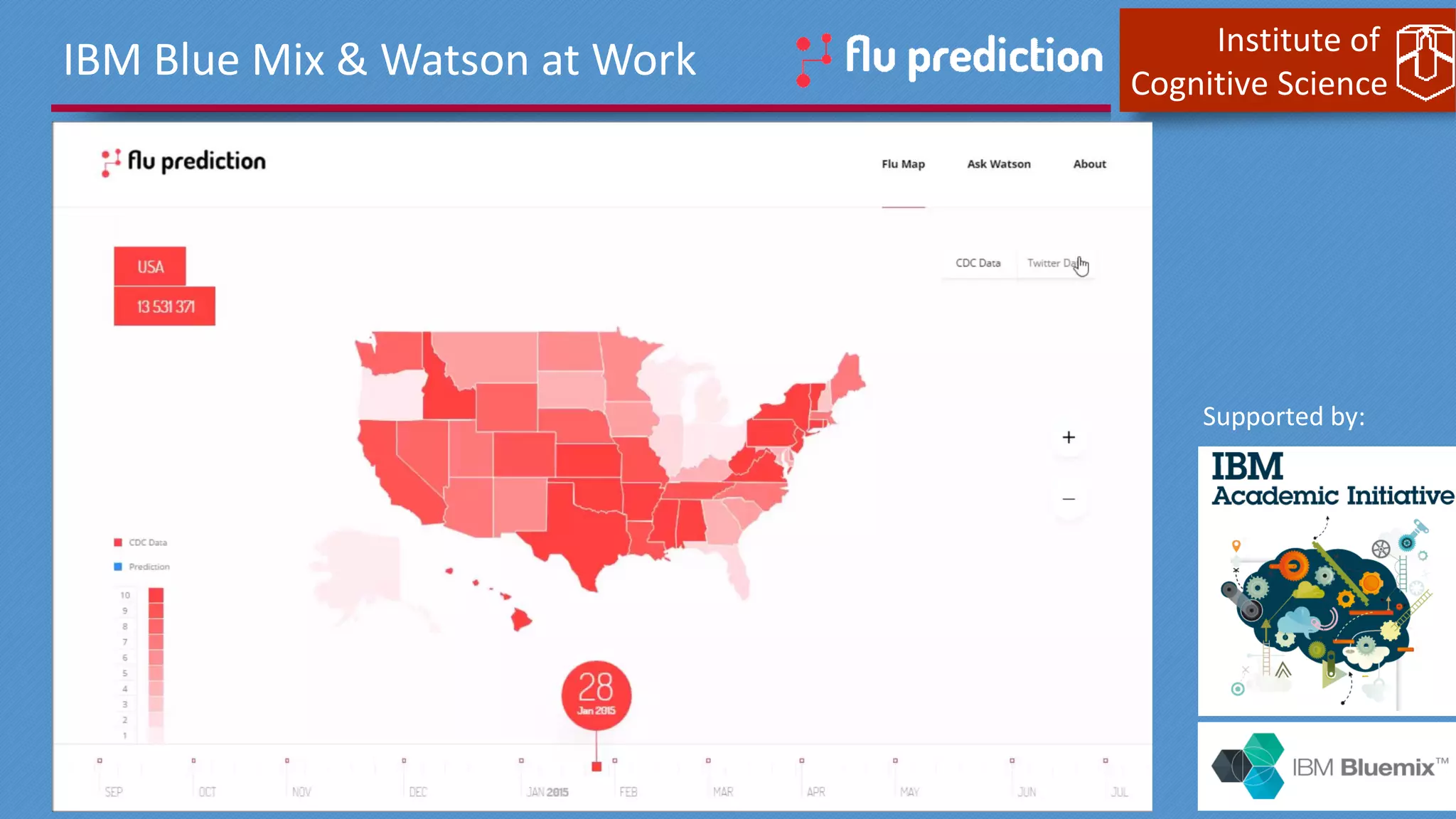
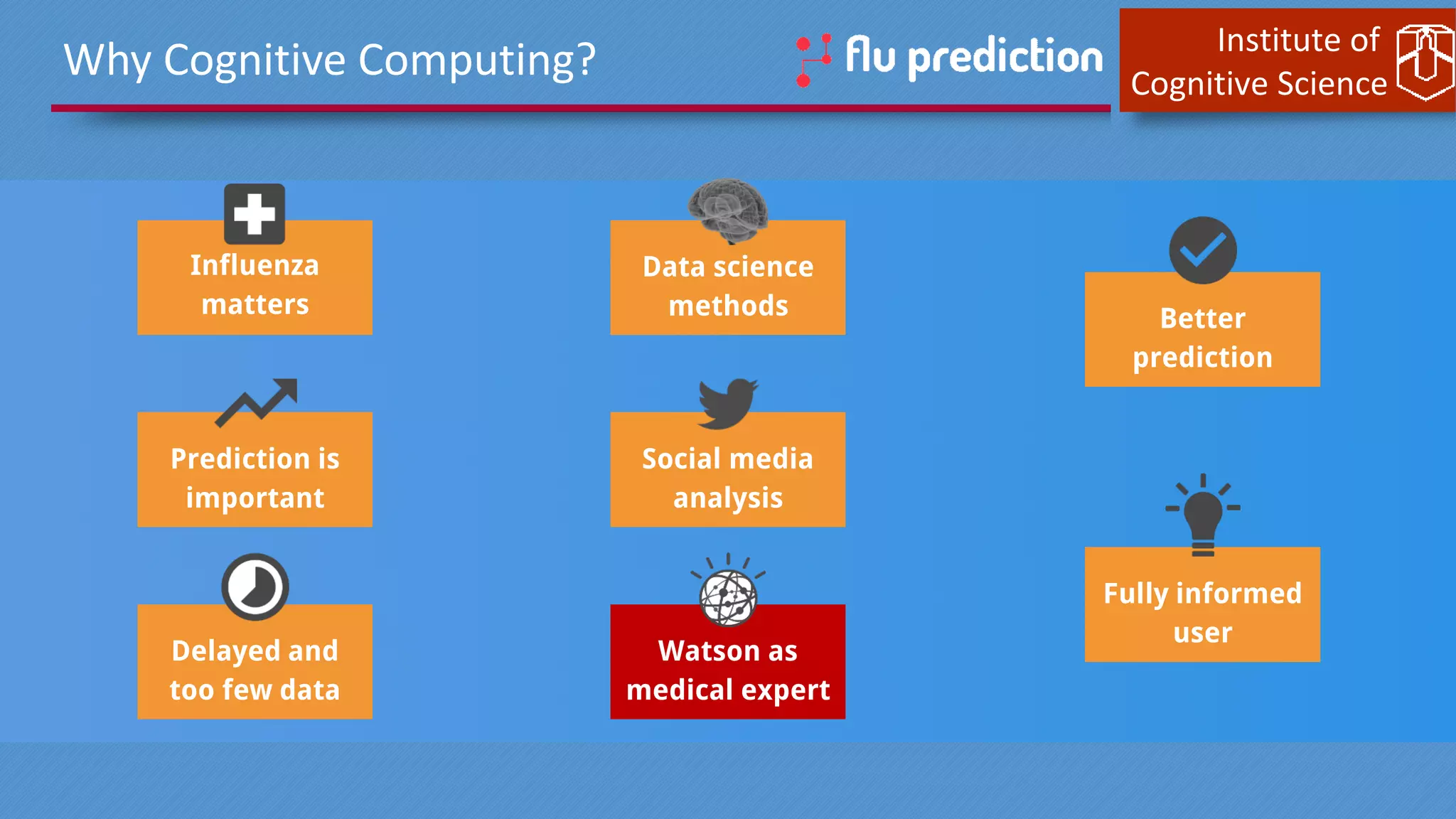
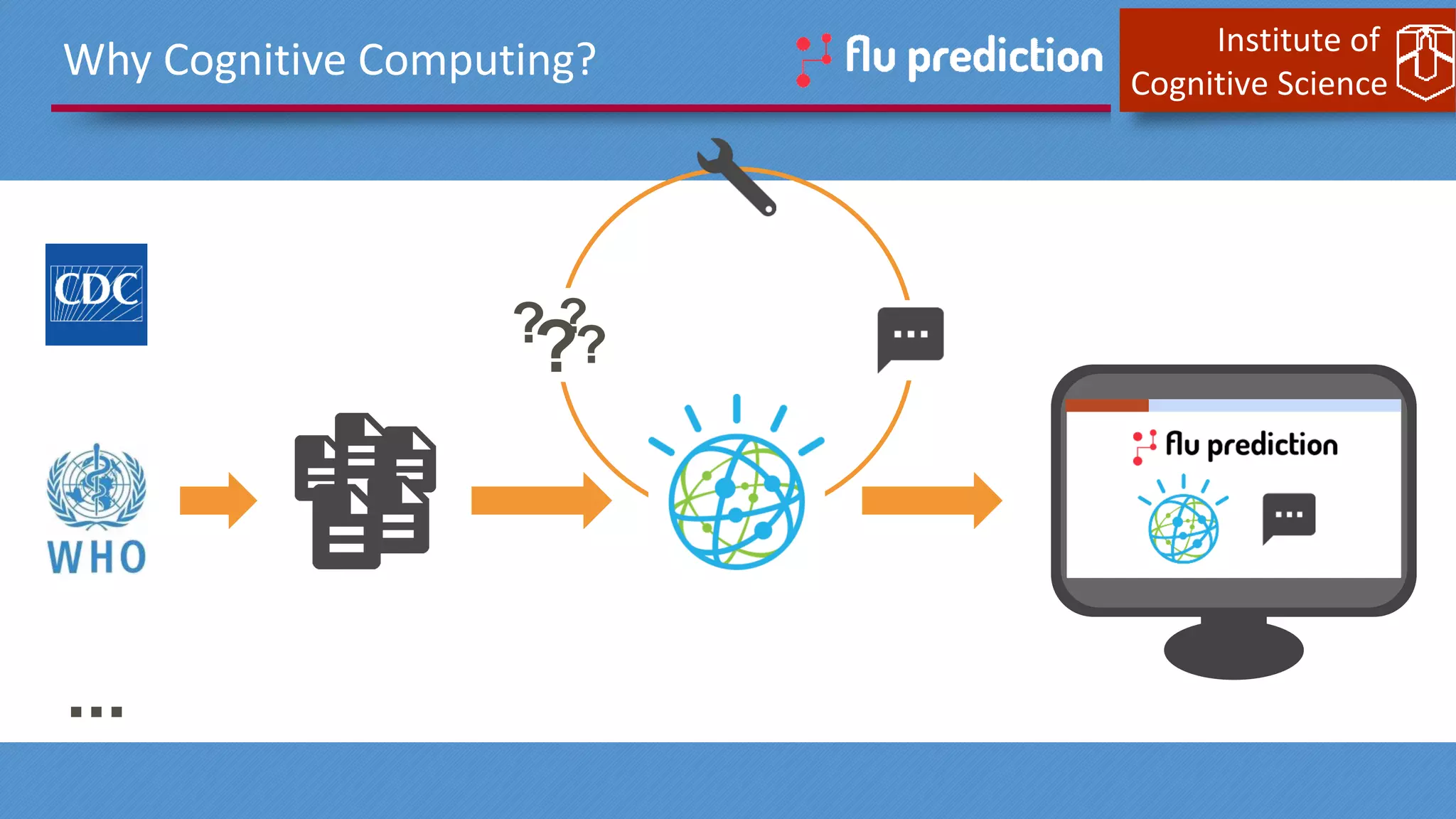
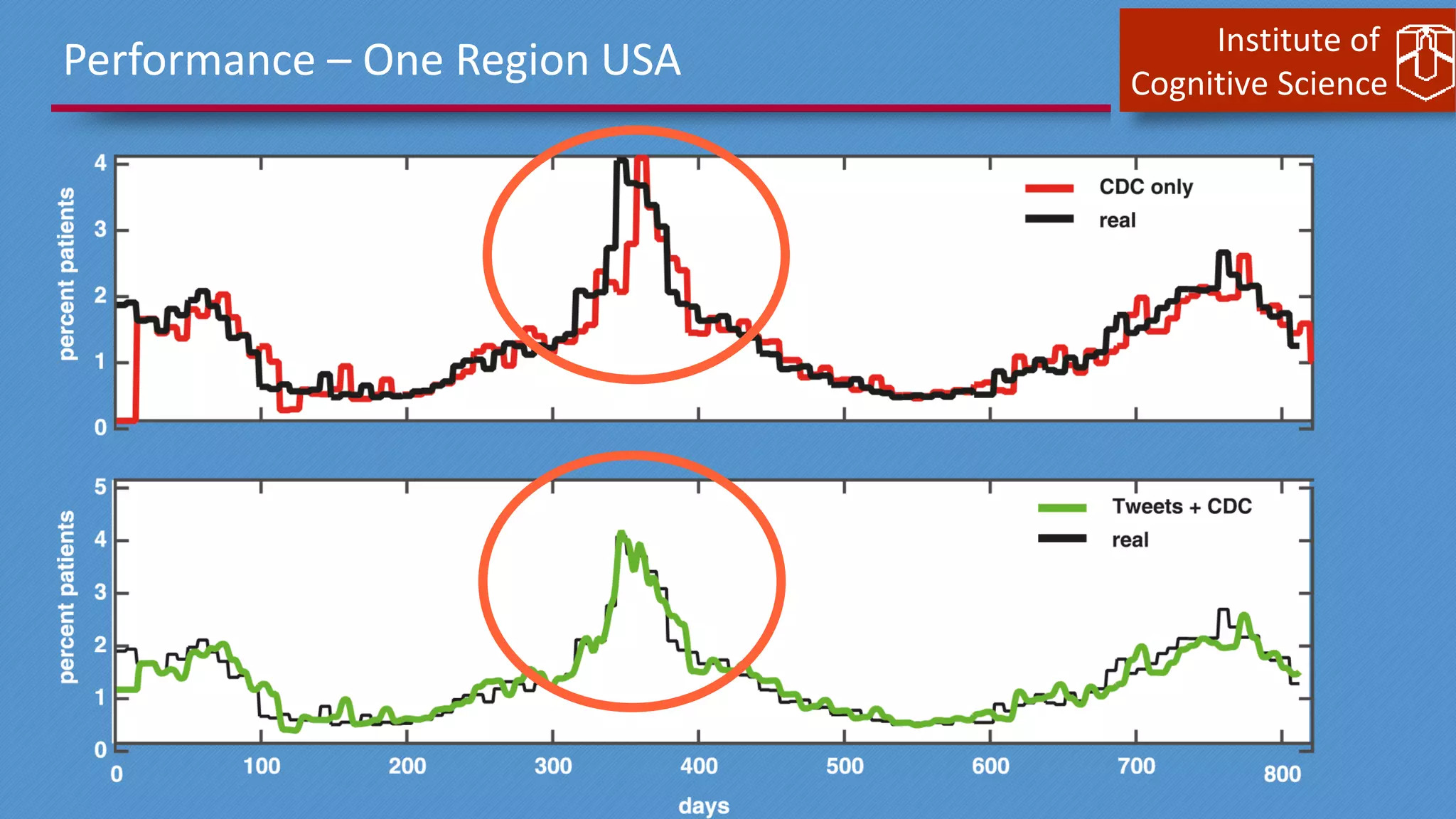
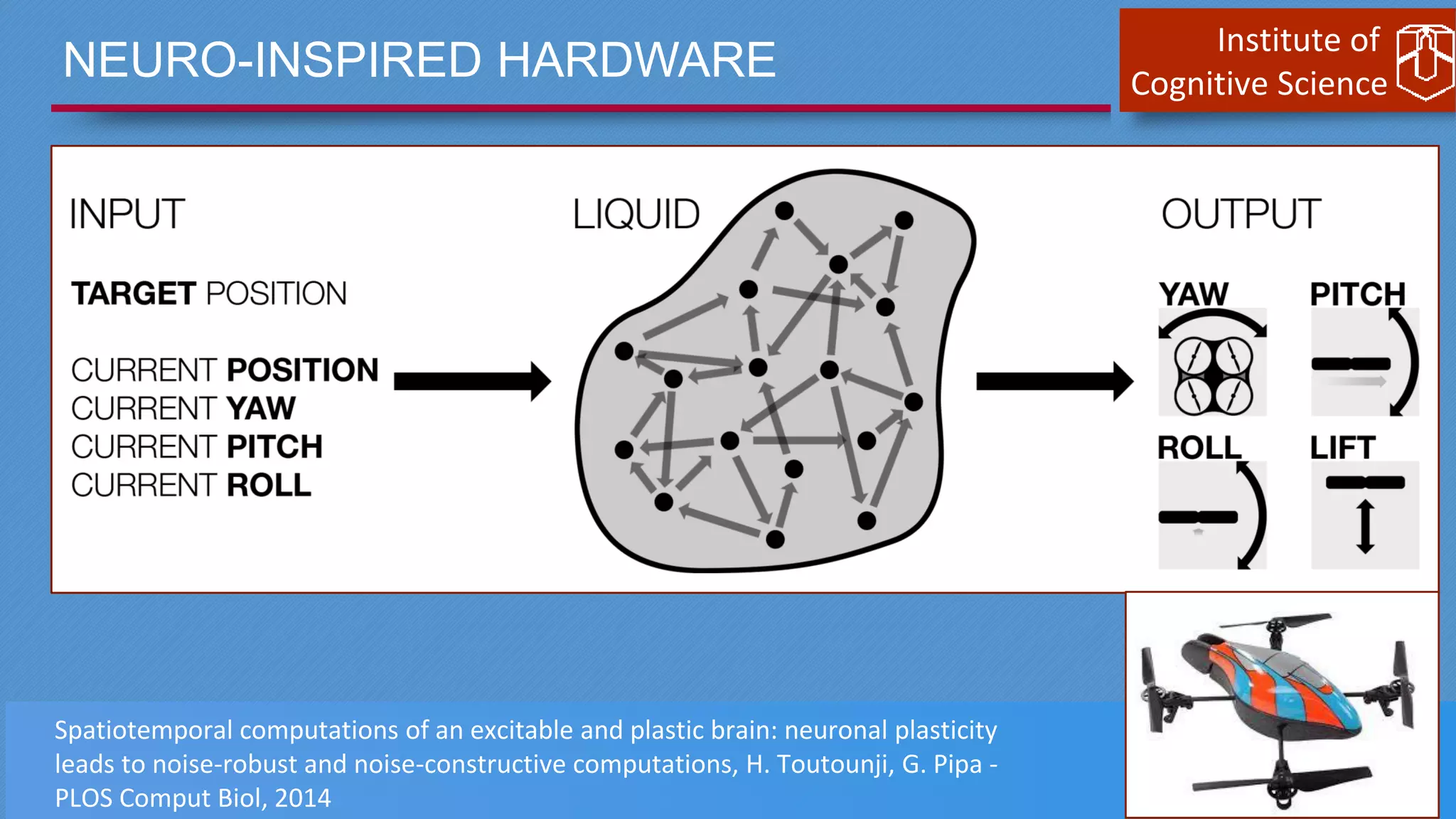
This document discusses cognitive computing from the Institute of Cognitive Science. It describes how cognitive computing uses social media analysis, data science methods, and IBM's Watson AI to better predict disease spread, such as influenza. By fusing real-time social media data with slower but more reliable CDC data, cognitive systems can improve predictions. The institute also researches neuromorphic hardware and reservoir computing techniques inspired by the brain to enable new kinds of fault-tolerant computing.