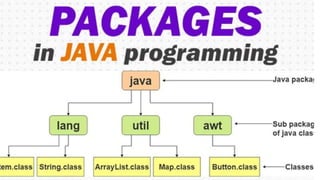
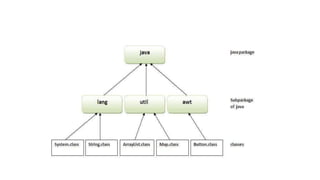
- A Java package is a group of similar types of classes, interfaces and sub-packages that are organized to avoid naming collisions and increase accessibility.
- Packages are categorized into built-in packages provided by Java and user-defined packages. Common built-in packages include java, lang, awt, and io.
- There are several ways to access classes from other packages including using import statements and fully qualified names. This allows separation and reuse of code across packages.


![Simple example of java package:
The package keyword is used to create a package in java.
//save as Simple.java
package mypack;
public class Simple
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
System.out.println("Welcome to package");
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/packagesinjava-240227052117-dbbdb136/85/THE-PACKAGES-CONCEPT-IN-JAVA-PROGRAMMING-pptx-5-320.jpg)

![Example of package that import the packagename.*
//save by A.java
package pack;
public class A
{
public void msg()
{
System.out.println("Hello");
}
}
//save by B.java
package mypack;
import pack.*;
class B
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
A obj = new A();
obj.msg();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/packagesinjava-240227052117-dbbdb136/85/THE-PACKAGES-CONCEPT-IN-JAVA-PROGRAMMING-pptx-7-320.jpg)

![//save by B.java
package mypack;
import pack.A;
class B
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
A obj = new A();
obj.msg();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/packagesinjava-240227052117-dbbdb136/85/THE-PACKAGES-CONCEPT-IN-JAVA-PROGRAMMING-pptx-9-320.jpg)
![• 3) Using fully qualified name
• If you use fully qualified name then only declared class of this package will be
accessible. Now there is no need to import. But you need to use fully qualified
name every time when you are accessing the class or interface.
• It is generally used when two packages have same class name e.g. java.util
and java.sql packages contain Date class.
• Example of package by import fully qualified name
1.//save by A.java
2.package pack;
3.public class A{
4. public void msg(){System.out.println("Hello");}
5.}
6.//save by B.java
7.package mypack;
8.class B{
9. public static void main(String args[]){
10. pack.A obj = new pack.A();//using fully qualified name
11. obj.msg();
12. }
13.}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/packagesinjava-240227052117-dbbdb136/85/THE-PACKAGES-CONCEPT-IN-JAVA-PROGRAMMING-pptx-10-320.jpg)


![Example of Subpackage:
package com.javatpoint.core;
class Simple
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
System.out.println("Hello subpackage");
}
}
To Compile: javac -d . Simple.java
To Run: java com.javatpoint.core.Simple
Output:Hello subpackage](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/packagesinjava-240227052117-dbbdb136/85/THE-PACKAGES-CONCEPT-IN-JAVA-PROGRAMMING-pptx-13-320.jpg)

![//save as Simple.java
package mypack;
public class Simple
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
System.out.println("Welcome to package");
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/packagesinjava-240227052117-dbbdb136/85/THE-PACKAGES-CONCEPT-IN-JAVA-PROGRAMMING-pptx-15-320.jpg)


