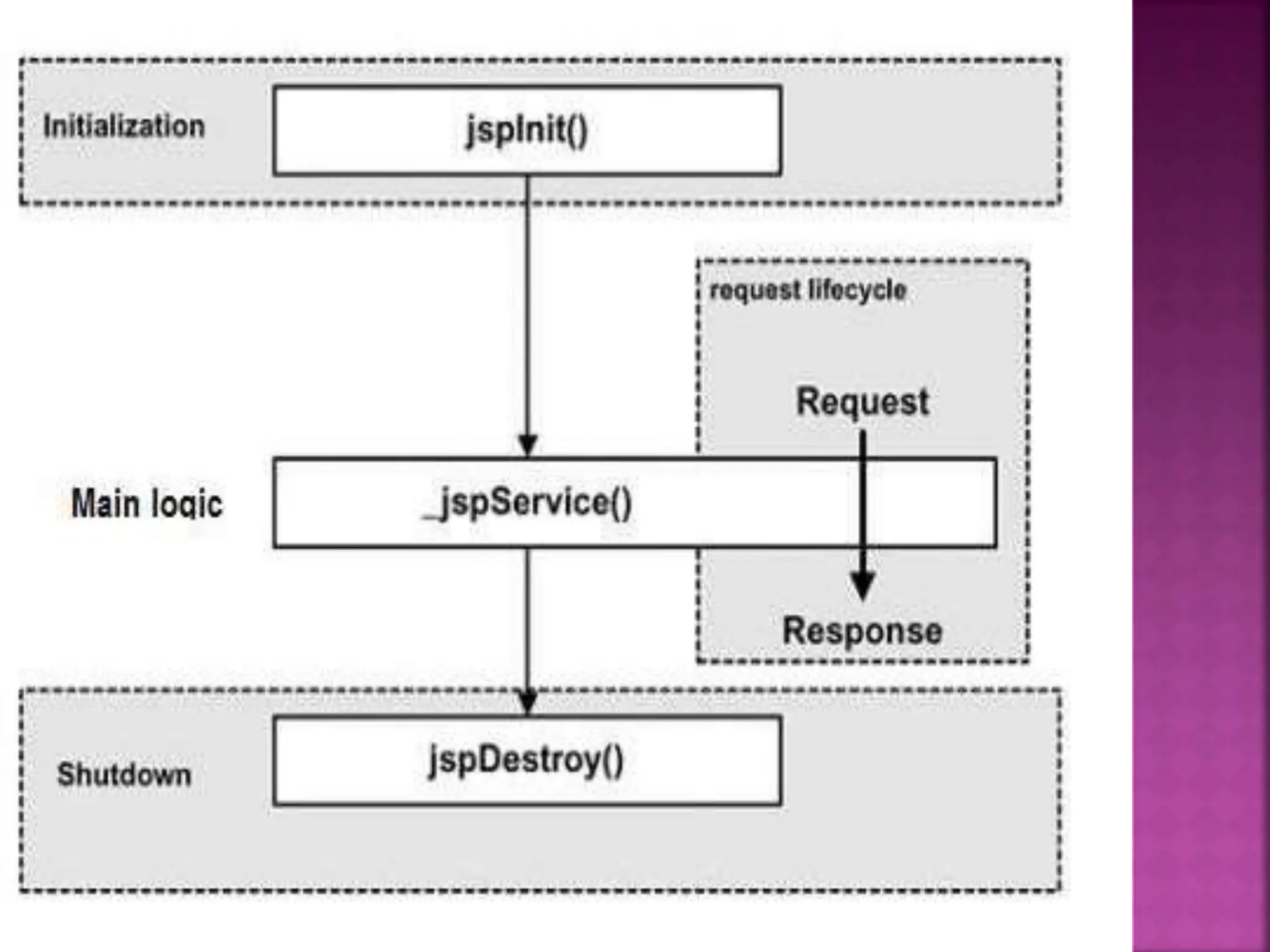
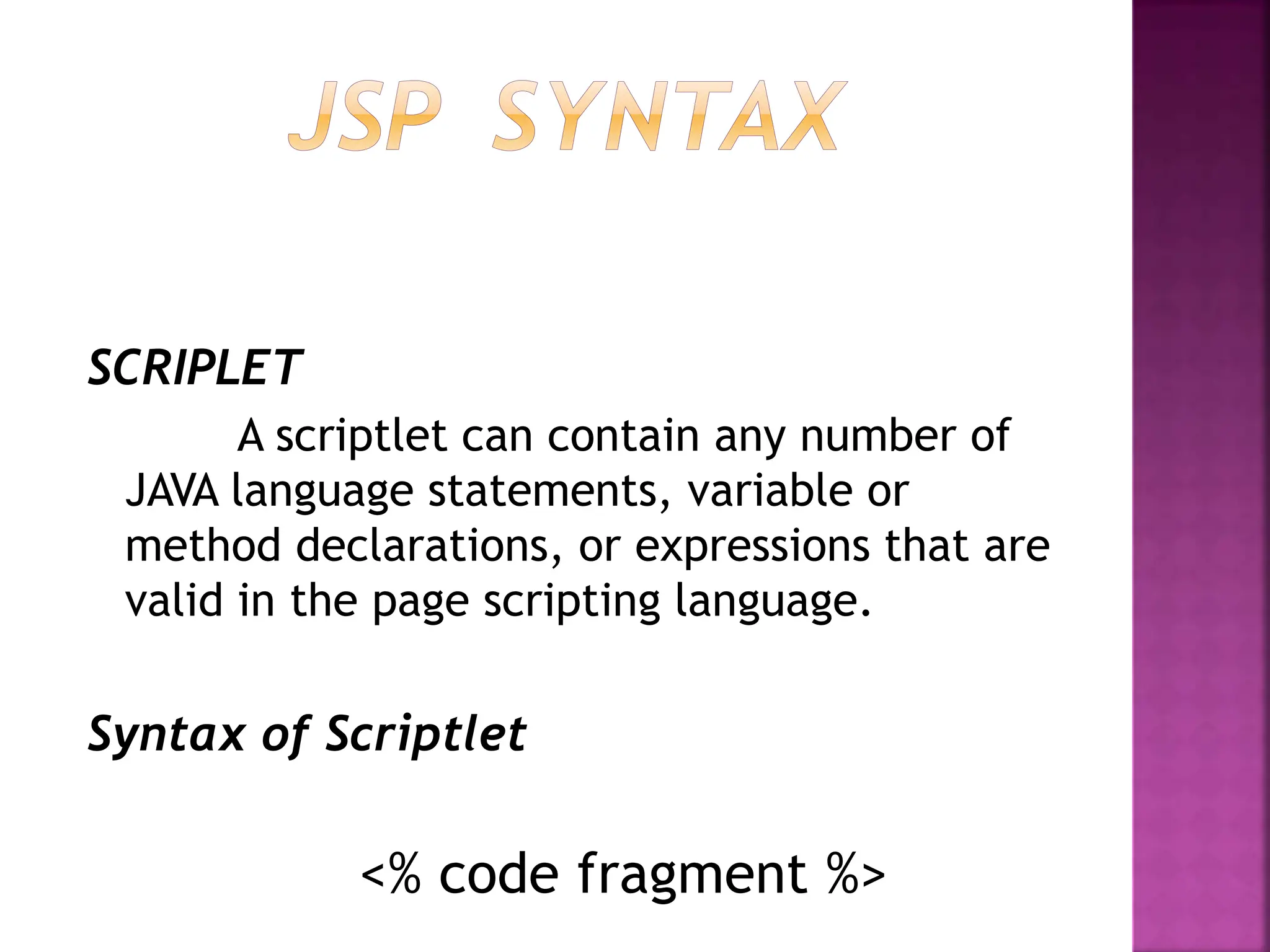
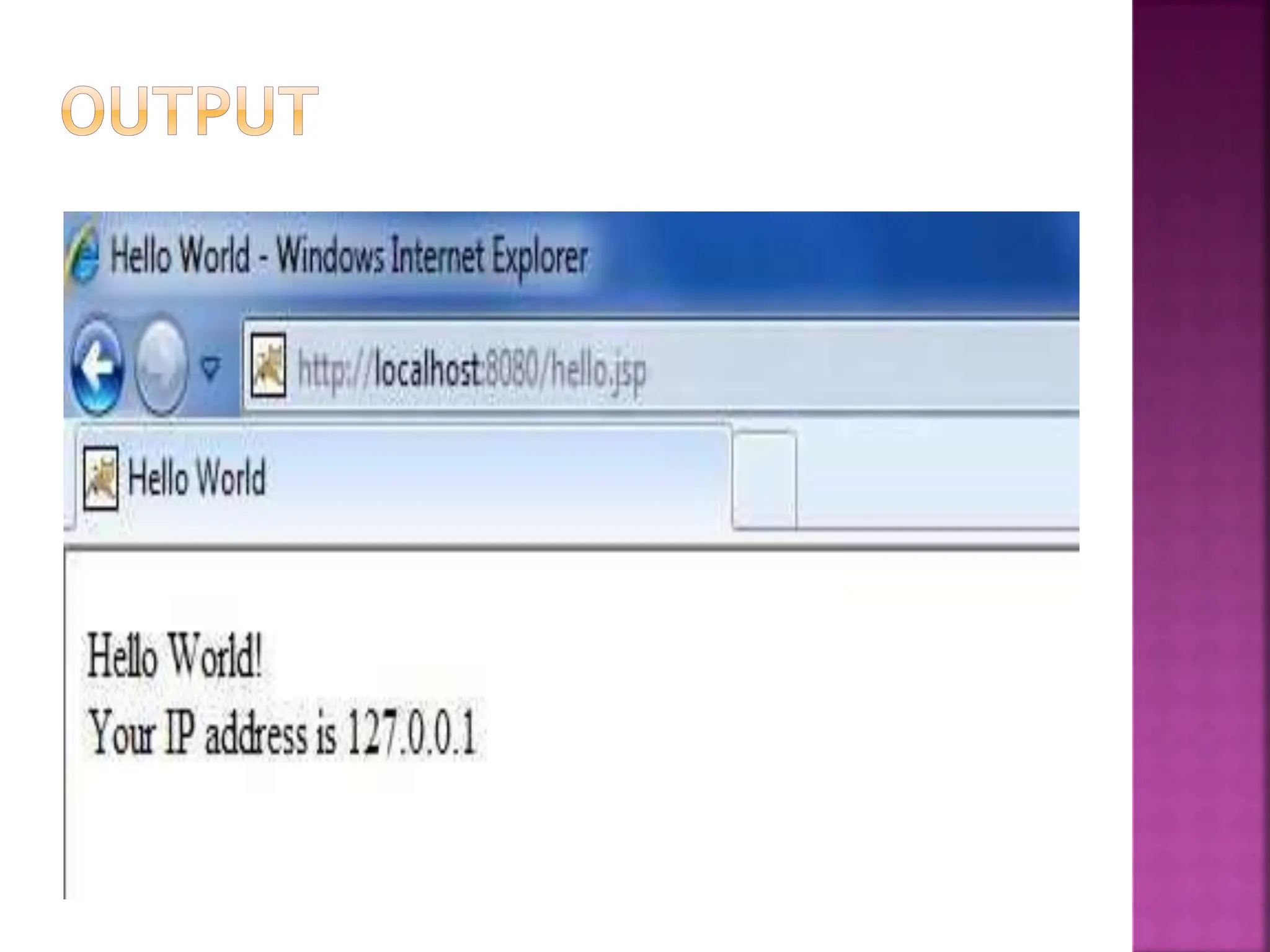
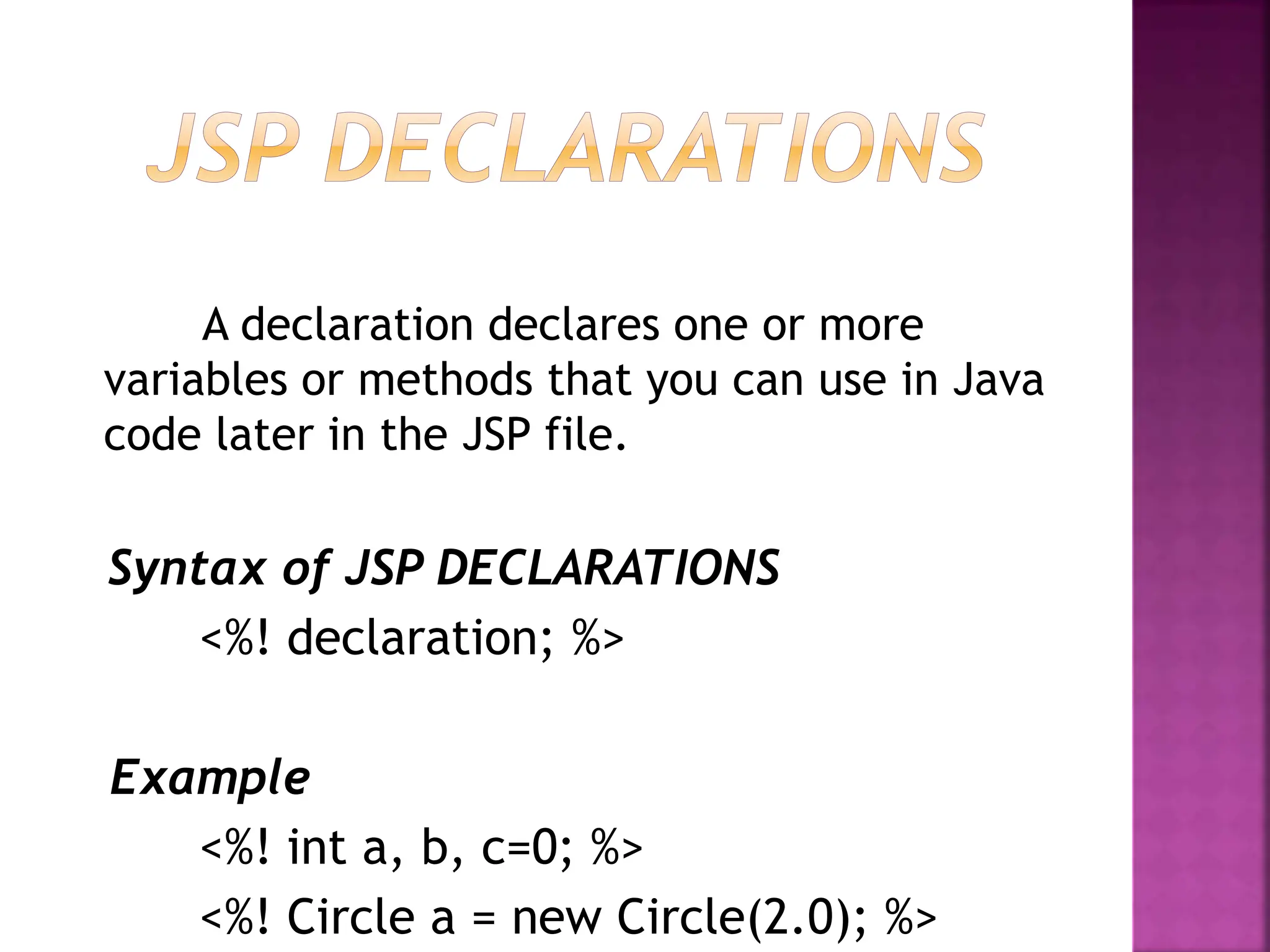
Java Server Pages (JSP) is a technology that helps developers create dynamic web pages by inserting Java code into HTML pages using special JSP tags. JSP was created to provide a more efficient alternative to CGI for developing dynamic web content. JSP pages are compiled into Java servlets, so they benefit from the Java language and portability while also allowing the insertion of scripting code directly into web pages. The JSP lifecycle involves compilation of the JSP into a servlet, initialization, execution to service requests, and cleanup.