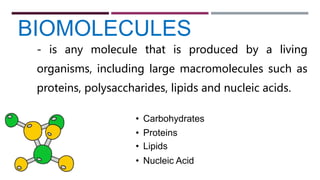
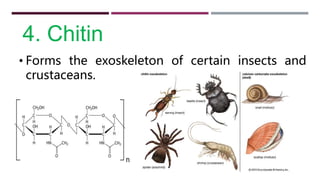
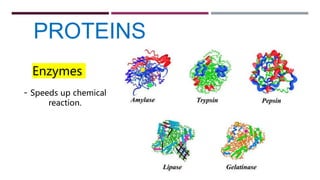
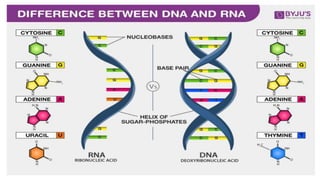
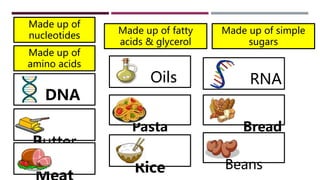
The document discusses the four major categories of biomolecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. It provides details on each category, including their monomers (sugars, fatty acids, amino acids, nucleotides), general formulas, elements, examples, and common tests used to identify each type of biomolecule. Carbohydrates include sugars such as glucose and starch, lipids are made of fatty acids and include fats and oils, proteins comprise amino acids like albumin and enzymes, and nucleic acids involve nucleotides to form structures like DNA and RNA.