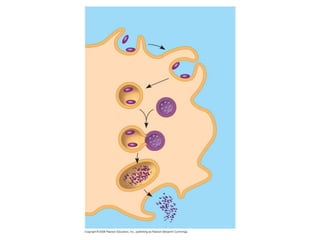
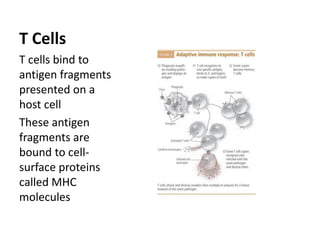
The immune system has two main types of defenses - innate immunity which is always present and provides immediate response, and acquired immunity which develops after exposure and provides specific long-term responses. The innate system uses white blood cells like neutrophils, macrophages, and eosinophils to engulf and destroy pathogens. The adaptive system uses lymphocytes and the lymphatic system, including B cells which produce antibodies and T cells which identify infected cells. Together these defenses provide active immunity from infection and immunization, while passive immunity provides short-term protection from antibodies.