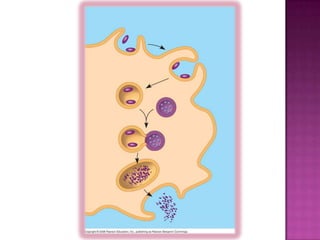
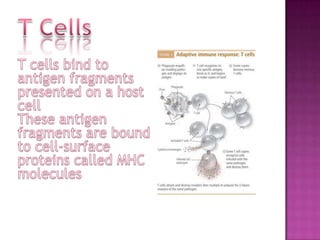
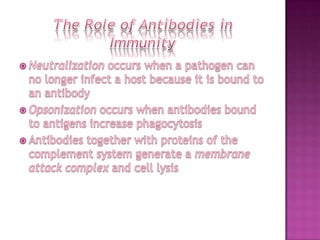
The immune system has both innate and adaptive immunity. Innate immunity provides immediate defenses while adaptive immunity has more specific responses after exposure. The innate system uses white blood cells like neutrophils and macrophages to engulf pathogens. The adaptive system relies on lymphocytes and the lymphatic system. T cells and B cells develop antigen receptors to recognize foreign molecules. T cells help activate other immune cells and cytotoxic T cells destroy infected cells. B cells produce antibodies to neutralize pathogens. Exposure leads to the development of immunological memory through clonal selection. The immune system uses a variety of organs and responses to protect the body.