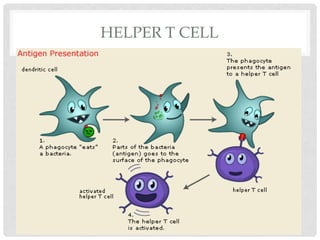
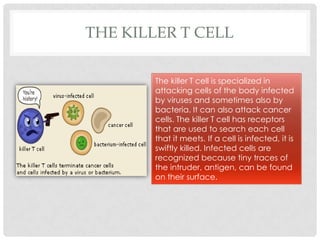
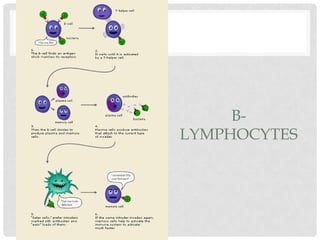
The immune system is made up of organs and tissues that work to destroy pathogens. There are two main types of immune cells: phagocytes and lymphocytes. Phagocytes such as granulocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells find and digest bacteria, viruses, and dead cells. Lymphocytes include B cells and T cells that recognize and respond to specific pathogens. B cells produce antibodies that help destroy pathogens, while T cells include helper cells that activate other immune cells and killer cells that attack infected cells. Memory cells provide long-term immunity against previously encountered pathogens.