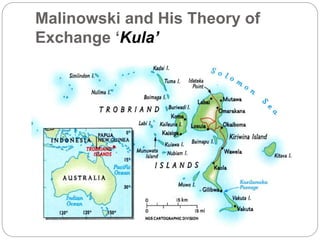
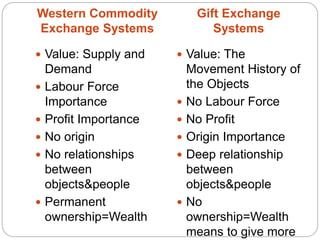
The document discusses the exchange theory in anthropological theory, focusing on the work of Malinowski and Mauss. Malinowski studied the Kula exchange system in western Pacific societies, where ceremonial exchanges of goods like necklaces created social alliances and motivated cultural behaviors. Similarly, Mauss studied the Potlatch system of the Pacific Northwest, where the exchange of goods like canoes brought prestige. Both systems used gift exchanges to reinforce social relationships and hierarchies between communities through moral obligations rather than market exchanges.