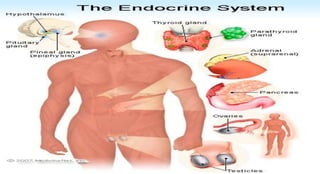
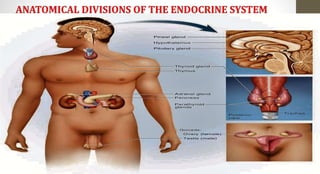
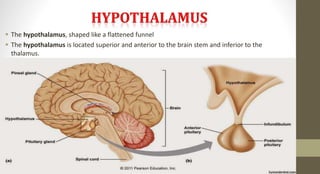
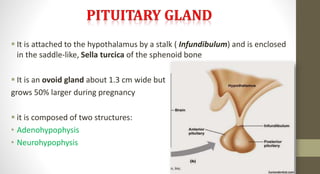
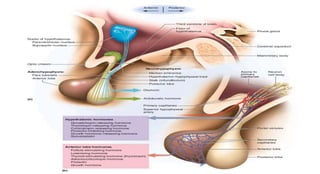
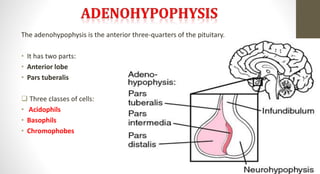
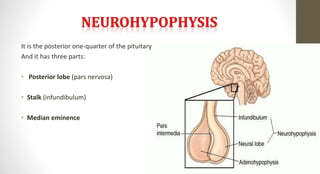
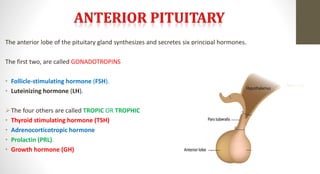
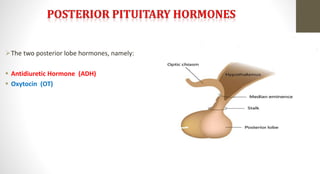
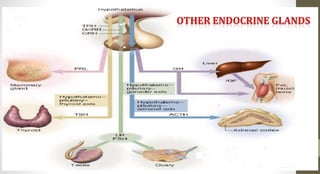
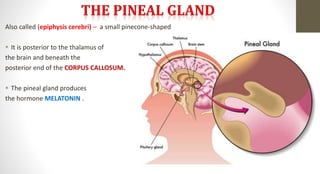
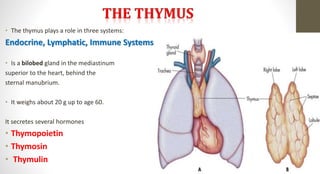
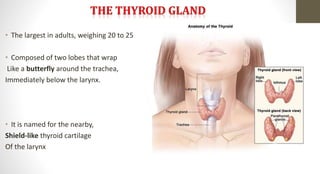
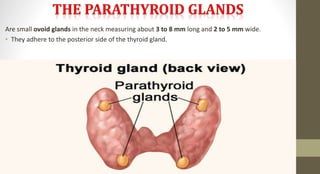
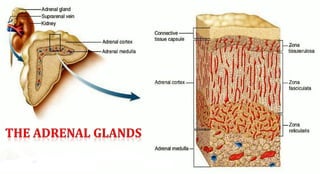
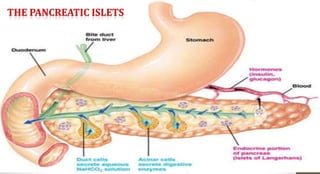
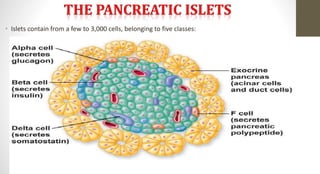
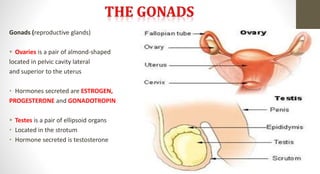
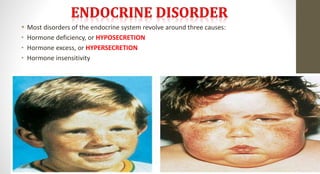
The document discusses the endocrine system, which regulates processes in the body through hormones. It describes the major endocrine glands - the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, adrenal glands, pancreas, gonads, pineal gland, thymus - and the hormones they secrete. The endocrine system maintains homeostasis through feedback loops between the hypothalamus and pituitary gland and target organs. Disorders can arise from hormone deficiencies, excesses, or insensitivities.