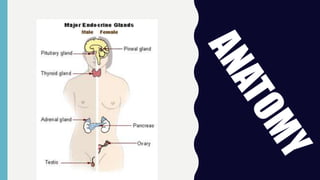
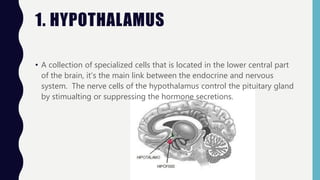
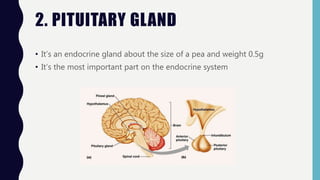
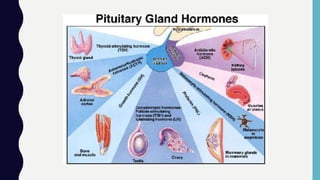
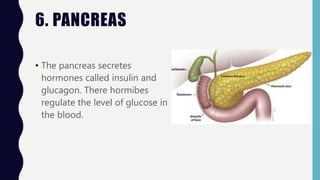
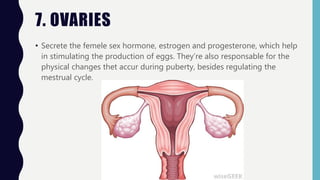
The endocrine system consists of glands that regulate vital functions through the secretion of hormones. The hypothalamus controls the pituitary gland which regulates other glands like the thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, pancreas, ovaries, and testes. These glands work together to control mood, growth, metabolism, and reproductive processes through the production and regulation of hormones like insulin, estrogen, progesterone, testosterone, and cortisol.