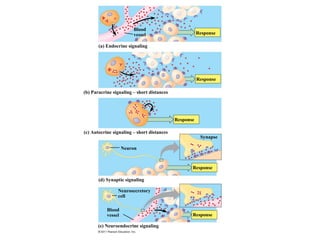
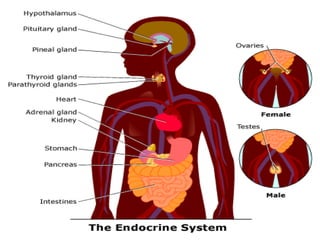
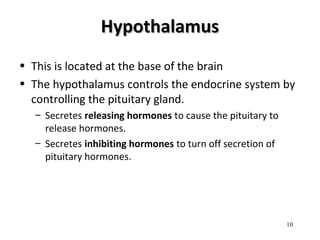
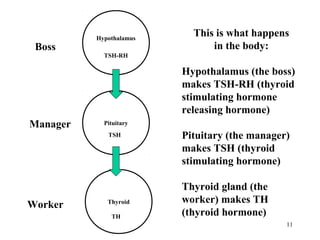
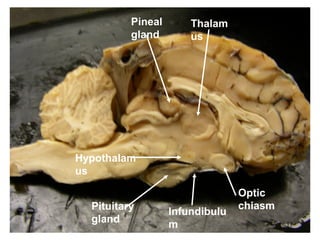
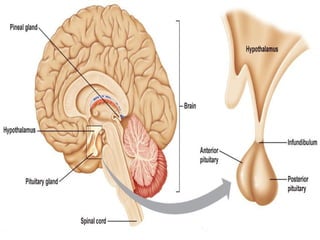
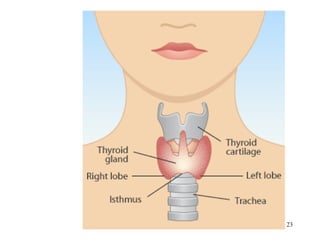
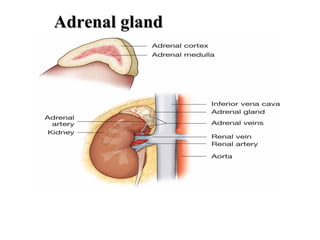
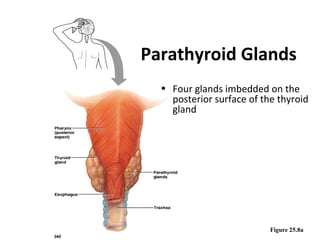
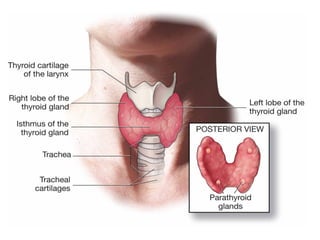
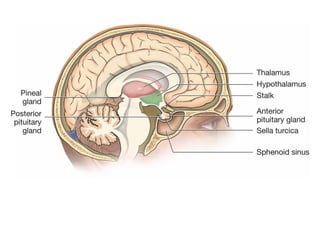
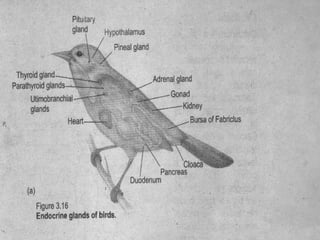
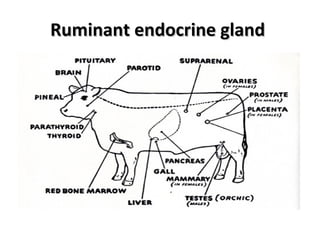
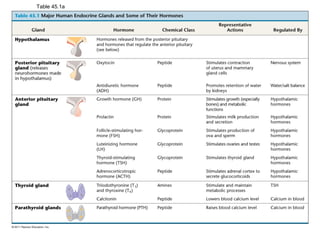
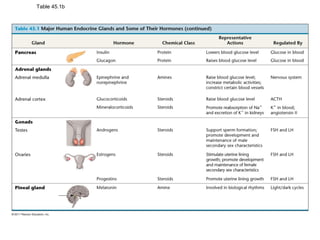
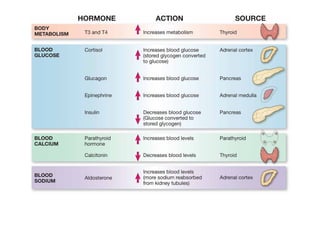
The document discusses the endocrine system in humans and other chordates. It describes the major endocrine glands and hormones, including the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, adrenal glands, gonads, and others. It explains how the hypothalamus controls the pituitary gland to regulate hormone release, and the functions of key hormones like growth hormone, thyroid hormones, insulin, estrogen, and testosterone.