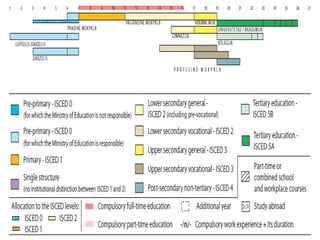
The education system in Lithuania is governed by laws on education passed in 1991 and amended in 2003. The system includes pre-school, primary, basic, secondary, vocational, and higher education. Education is compulsory between ages 7-16 and provided by state schools as well as private and municipal institutions. The Ministry of Education and Science oversees the system and defines funding criteria.