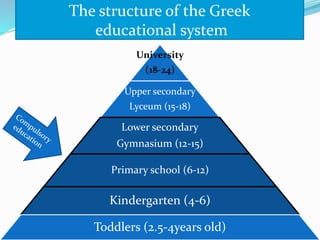
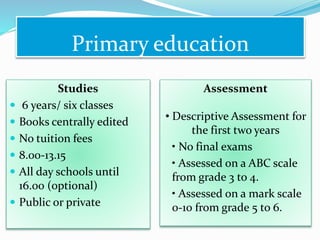
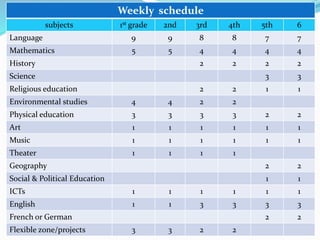
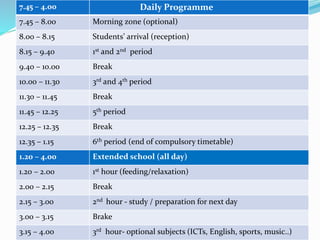
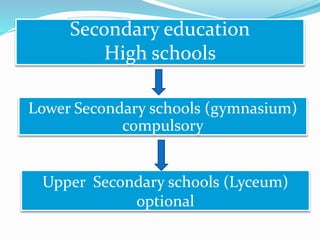
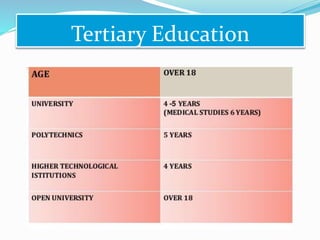
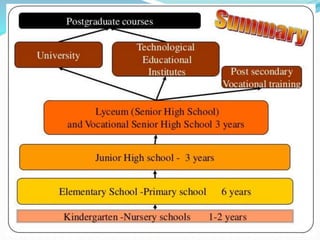
The document summarizes the structure of the Greek educational system. It begins with pre-school education at ages 2.5-6 years old, then compulsory primary education from ages 6-12. Lower secondary education is from ages 12-15, followed by optional upper secondary (lyceum) from ages 15-18. Tertiary education includes universities from ages 18-24. The document provides details on assessment, subject schedules, school calendars, and administration of the different education levels in Greece.