Embed presentation
Download to read offline


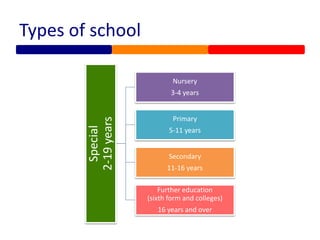



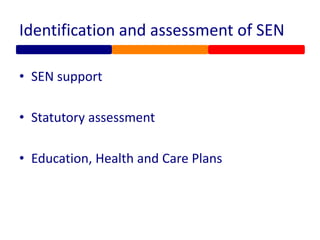

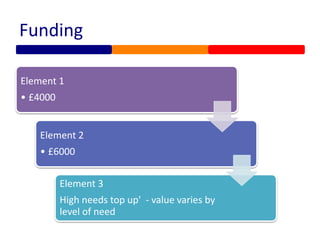


Special educational needs in England are overseen by the Department for Education. Students receive compulsory education from ages 5 to 18 and are generally expected to achieve a grade C or higher in core subjects by age 16. The legal framework is established by the Children and Families Act of 2014 and focuses on early identification, multi-agency support, and considering students' and families' views. Students may have needs related to communication, cognition, social/emotional/mental health, or physical/sensory issues. Formal plans and funding levels are determined through assessment and may include education, health, and care plans to support outcomes.










