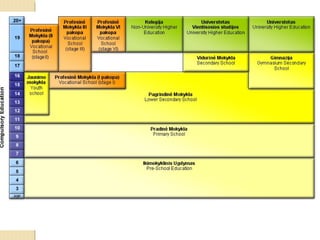
Lithuania's education system includes pre-school, primary and lower secondary school, upper secondary school, vocational education, and higher education. There are 22 universities and 28 colleges that provide higher education. Primary and lower secondary school is compulsory from ages 6-7 and lasts 10 years, followed by optional upper secondary school or vocational education. Vocational education includes 4 types of programs that can lead to certification or allow students to continue their education. Higher education is provided at universities and non-academic colleges, and typically involves 4 years of study to earn a Bachelor's degree.