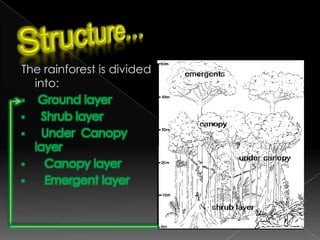
Natural vegetation refers to plants that grow without human assistance. It is an important part of the physical environment and ecosystem, as plants provide food and resources for humans and animals. Natural vegetation can be classified into different types based on location and climate, including forest, grassland, and desert vegetation. The dominant types of forests include tropical rainforests near the equator and temperate coniferous forests at higher latitudes. Forests are important habitats, provide raw materials, help regulate climate, and are used for recreation.