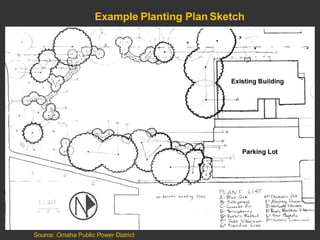
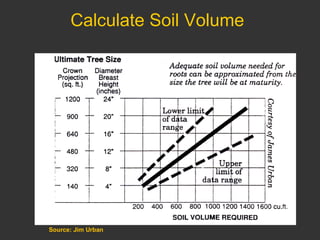
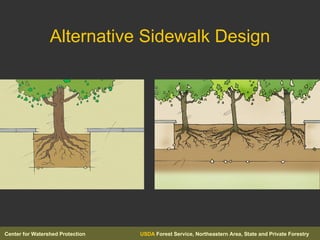
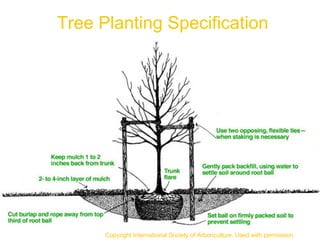
The document discusses site assessment, planting design, and maintenance considerations for urban tree planting. It recommends collecting detailed site information, developing a planting plan that considers species selection and spacing, and calculating soil volume. Special considerations for urban areas include infrastructure conflicts, stormwater management, and protecting trees from human and animal impacts. Maintenance techniques discussed include pruning, watering, weed control, and encouraging natural regeneration.