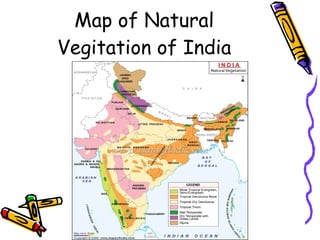
Vegetation in India can be divided into five main types due to varied climatic conditions:
1) Tropical evergreen forests are dense forests found in areas with heavy rainfall that remain green year-round.
2) Tropical deciduous forests are less dense and found in areas with a monsoon climate, shedding leaves at certain times.
3) Tropical thorn forests and scrubs are found in dry areas and have leaves shaped like spines to reduce water loss.
4) Mountain forests vary by height and include coniferous or cone-shaped trees at higher elevations.
5) Mangrove forests can survive in saline water and are mainly found in the Sundarbans and Andaman