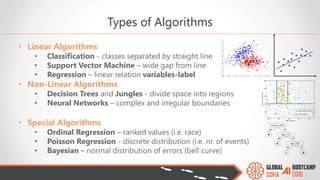
The document outlines the Global AI Bootcamp featuring a presentation on machine learning (ML) and its application within Microsoft Azure's services and tools. Key highlights include the Azure ML integrated platform, various machine learning frameworks, challenges of data preparation, and the importance of iterative processes in ML modeling. The document also discusses artificial intelligence as a service (AIaaS) and the anticipated growth of this market, providing insights into how businesses can leverage these technologies for data science and predictive modeling.














![Data Understanding (Titanic Dataset)
• Mosaic plot
o Categorical distribution
o Visualizes the relation between X and Y
o Strong relation = Y-splits are far apart
o Conclusion: Women have higher survival rate
• Box plot
o Continuous distribution of numeric var
o IQR = middle 50%
o Identify outliers [Q1-1.5 IQR; Q3+1.5 IQR]
o Conclusion: High fares have higher survival rate
• Scatter plot
o How much a variable determines another
o Conclusion: Infants and men 25-45 y
have higher survival rate](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thedatascienceprocess-howtoapplyitwhenweneedit-181217074828/85/The-Data-Science-Process-Do-we-need-it-and-how-to-apply-19-320.jpg)
![• Make features usable
o Numerical
o Categorical (i.e. week day)
o PCA dimensionality reduction
o Dummy variables
• Handle missing data
• Normalize data
o Standard range of numerical scale (i.e. from [-1000;1000] -> [0;1], [-1;1])
o Value range influence the importance of the feature compared to other
Data Preprocessing](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thedatascienceprocess-howtoapplyitwhenweneedit-181217074828/85/The-Data-Science-Process-Do-we-need-it-and-how-to-apply-20-320.jpg)




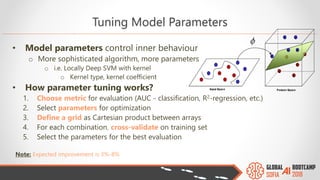


![Performance Metrics
• Regression model
o Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE)
o Coefficient of Determination, R2 ϵ [0;1]
• Multi-class classification model
o Confusion matrix
• Binary classification model
o Accuracy based on correct answers
o Area under ROC curve (AUC)
o Threshold
o Precision = TP / (TP + FP)
o Recall = TP / (TP + FN)
o Cost-Balanced (F1)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thedatascienceprocess-howtoapplyitwhenweneedit-181217074828/85/The-Data-Science-Process-Do-we-need-it-and-how-to-apply-29-320.jpg)