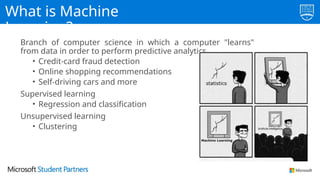
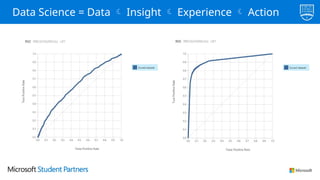
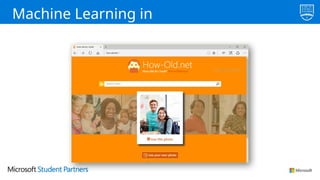
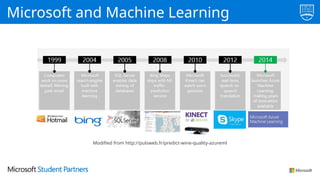
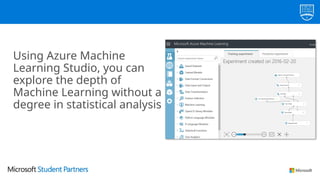
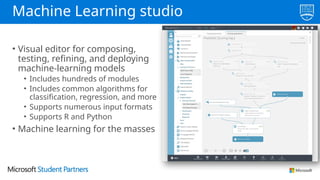
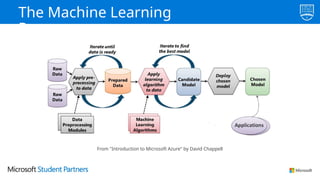
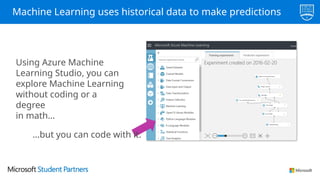
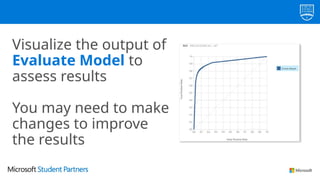
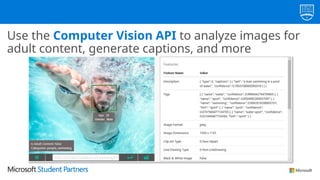
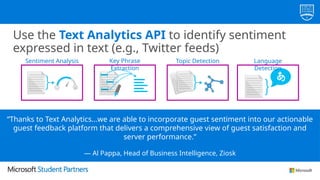
The document discusses the use of Microsoft Azure for applied machine learning, detailing how it enables users to build and deploy predictive models without extensive statistical knowledge. It provides an overview of machine learning concepts, the data preparation process, various algorithms, and emphasizes the importance of clean data for accurate predictions. Additionally, it outlines practical steps for creating and deploying web services based on machine learning models.