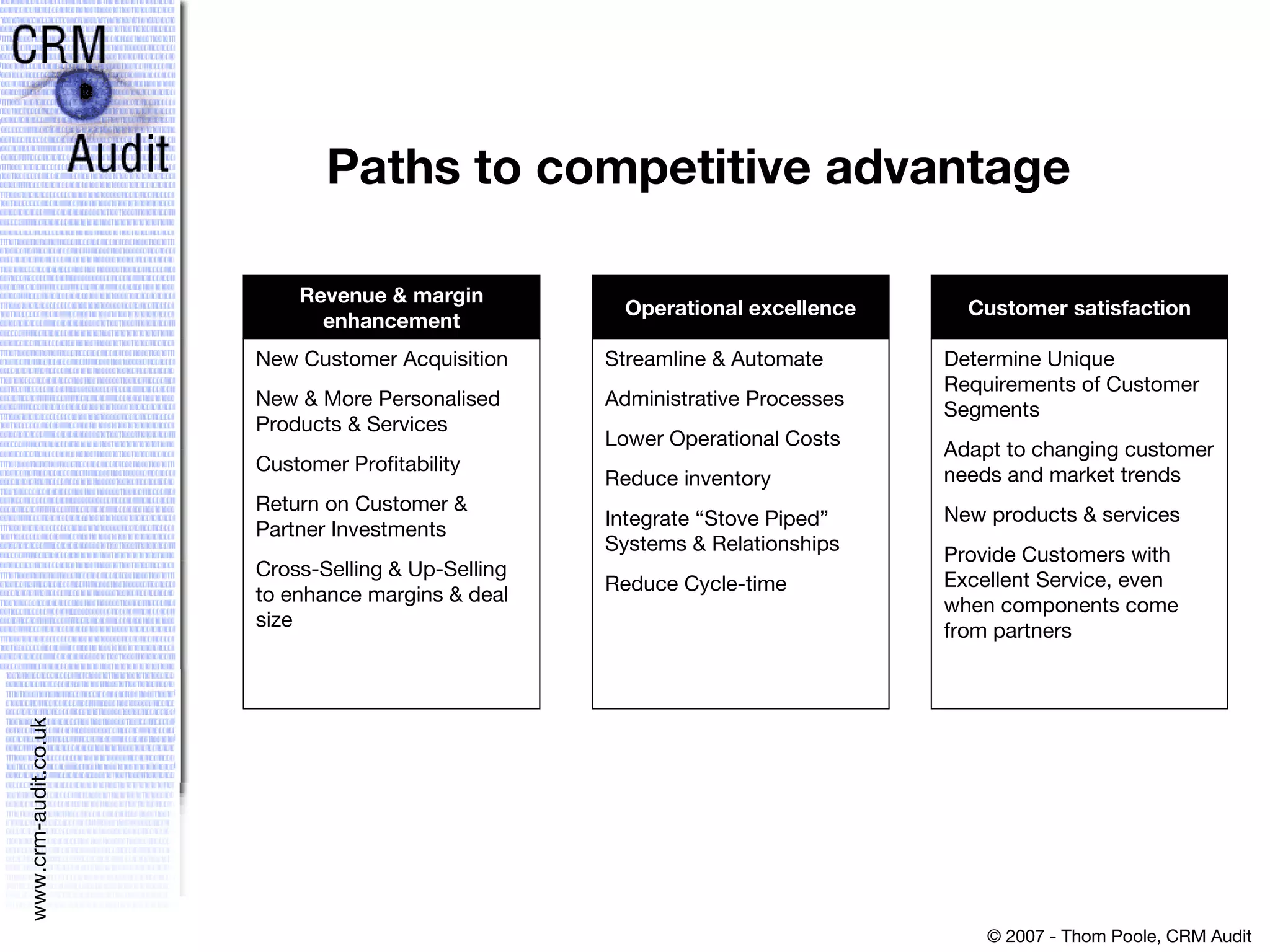
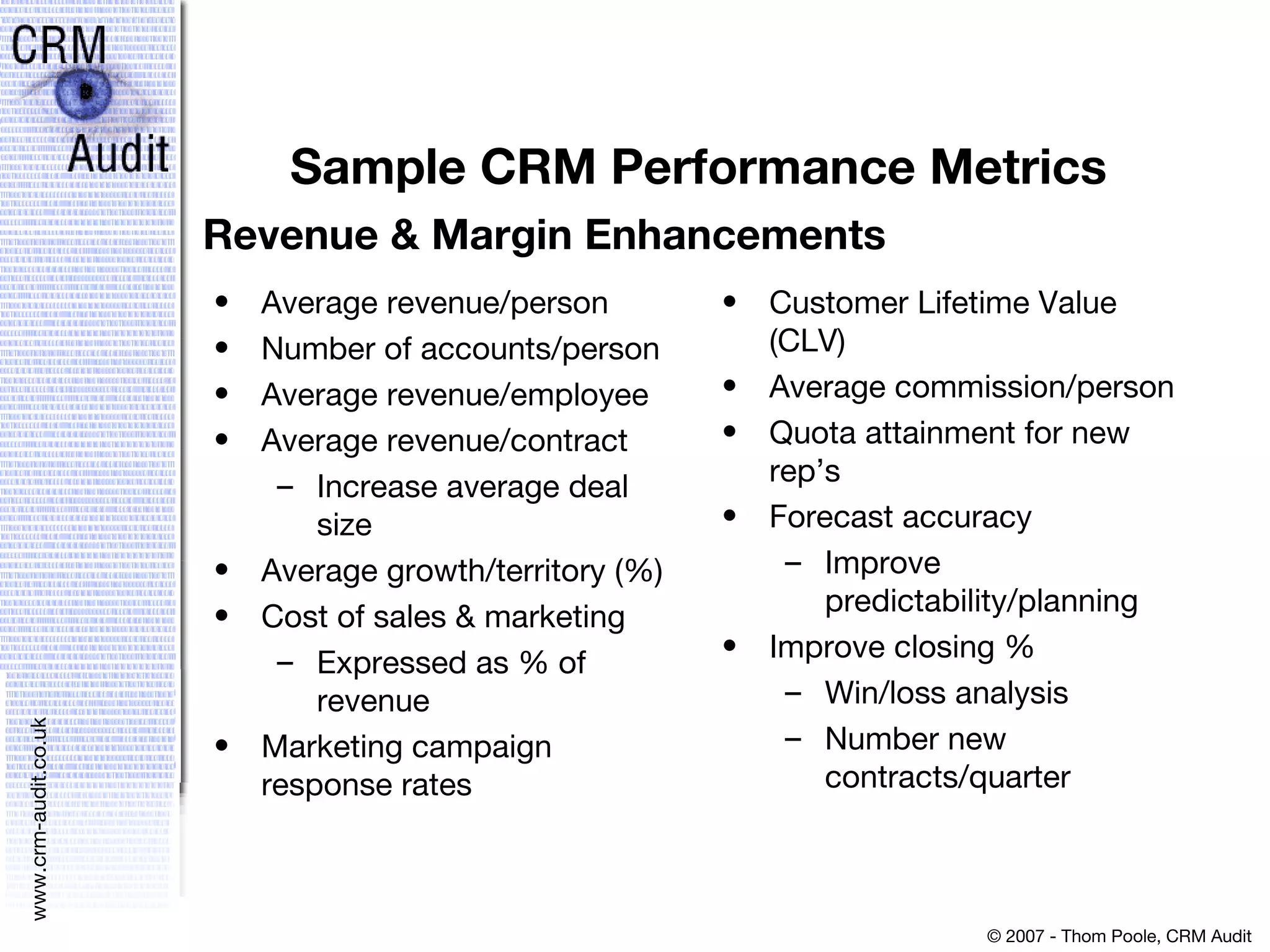
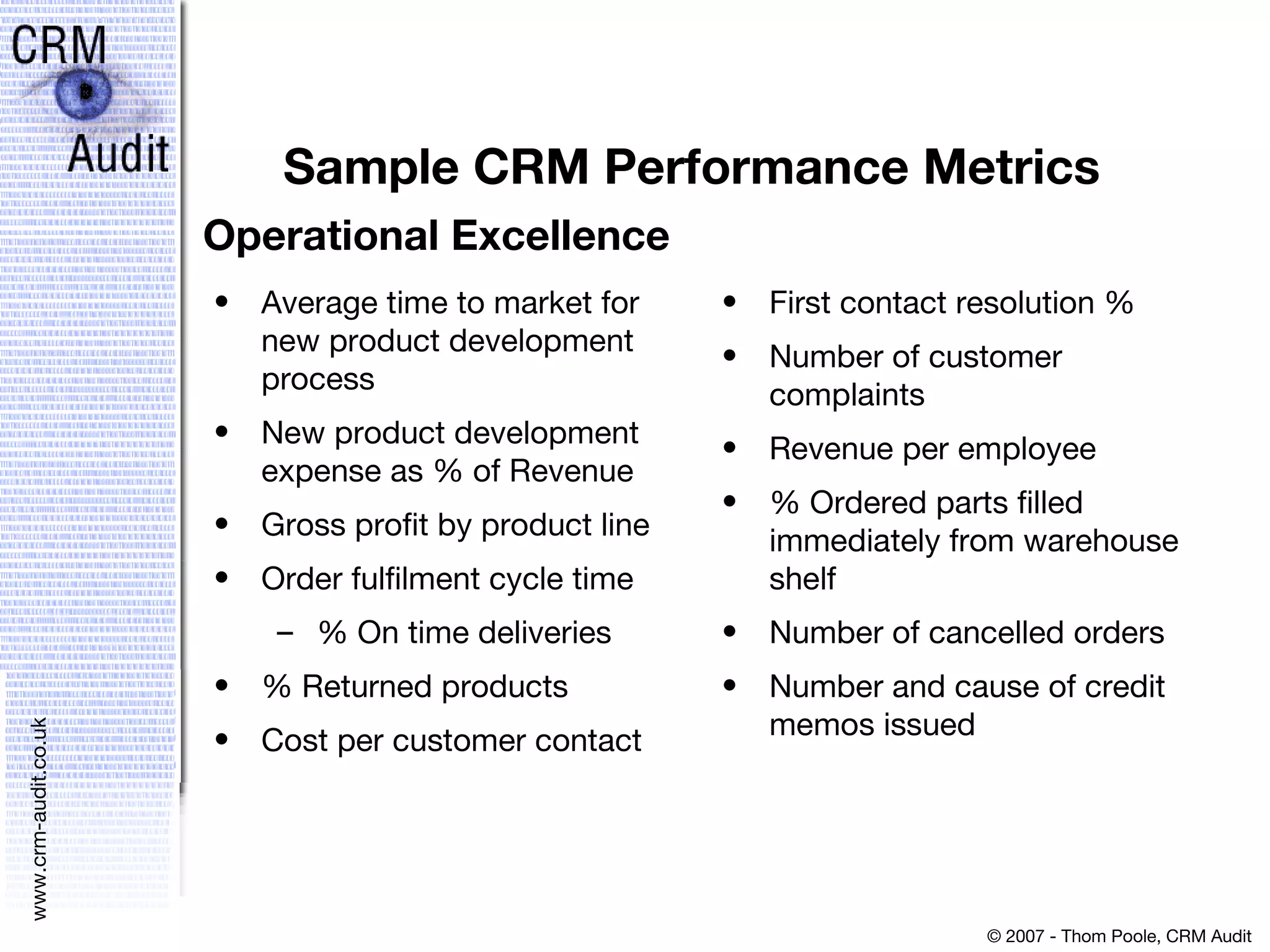
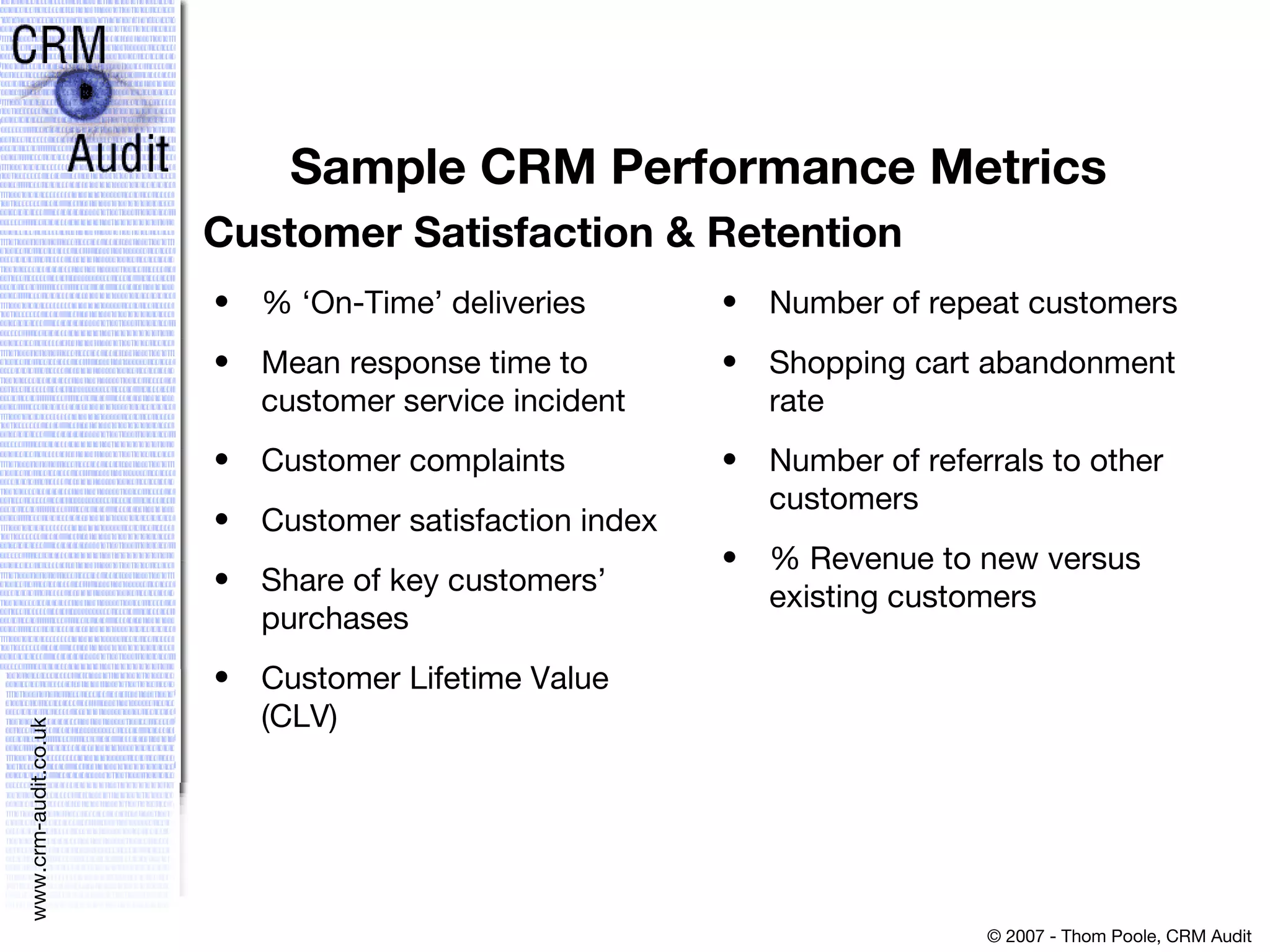
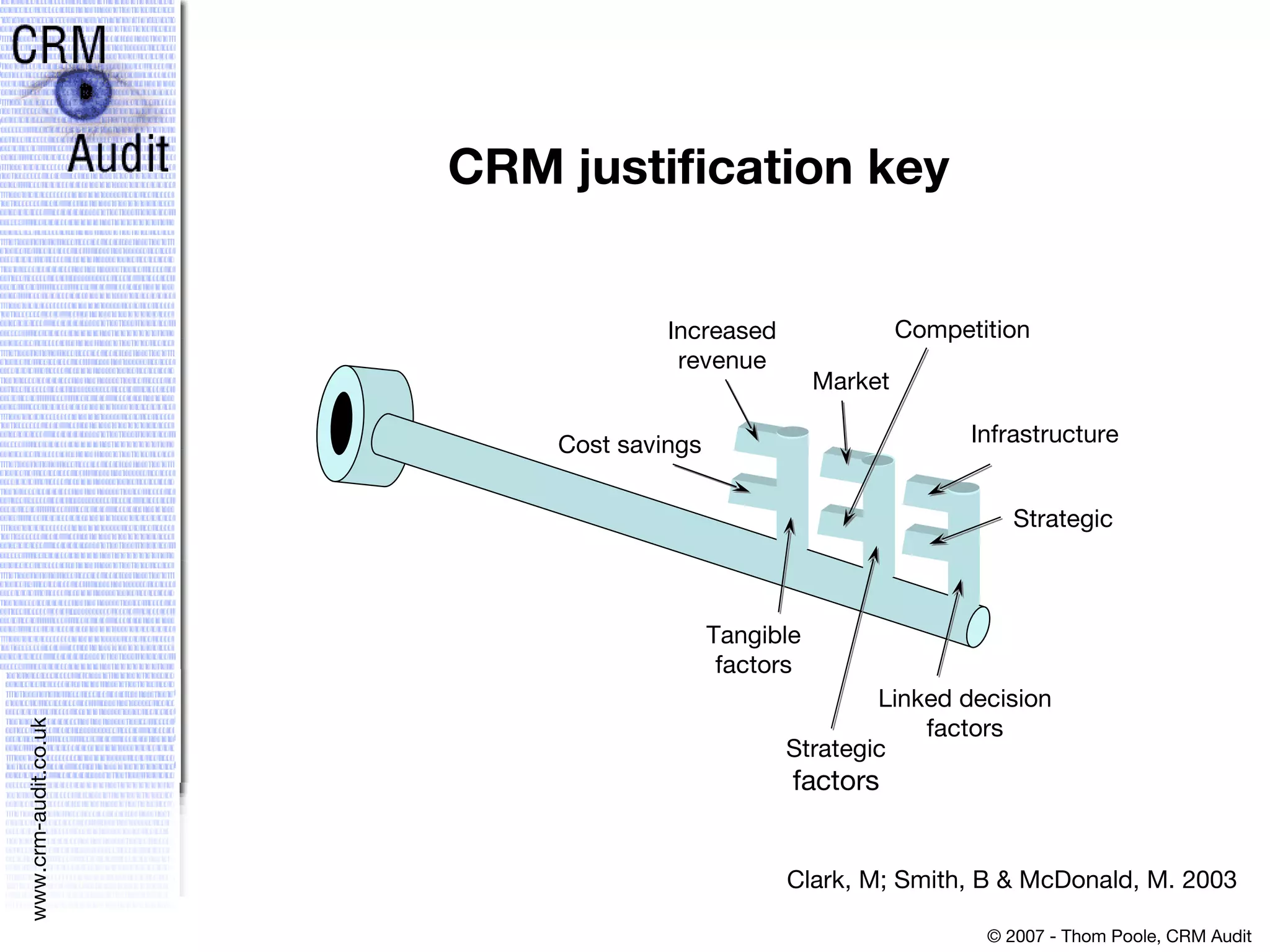
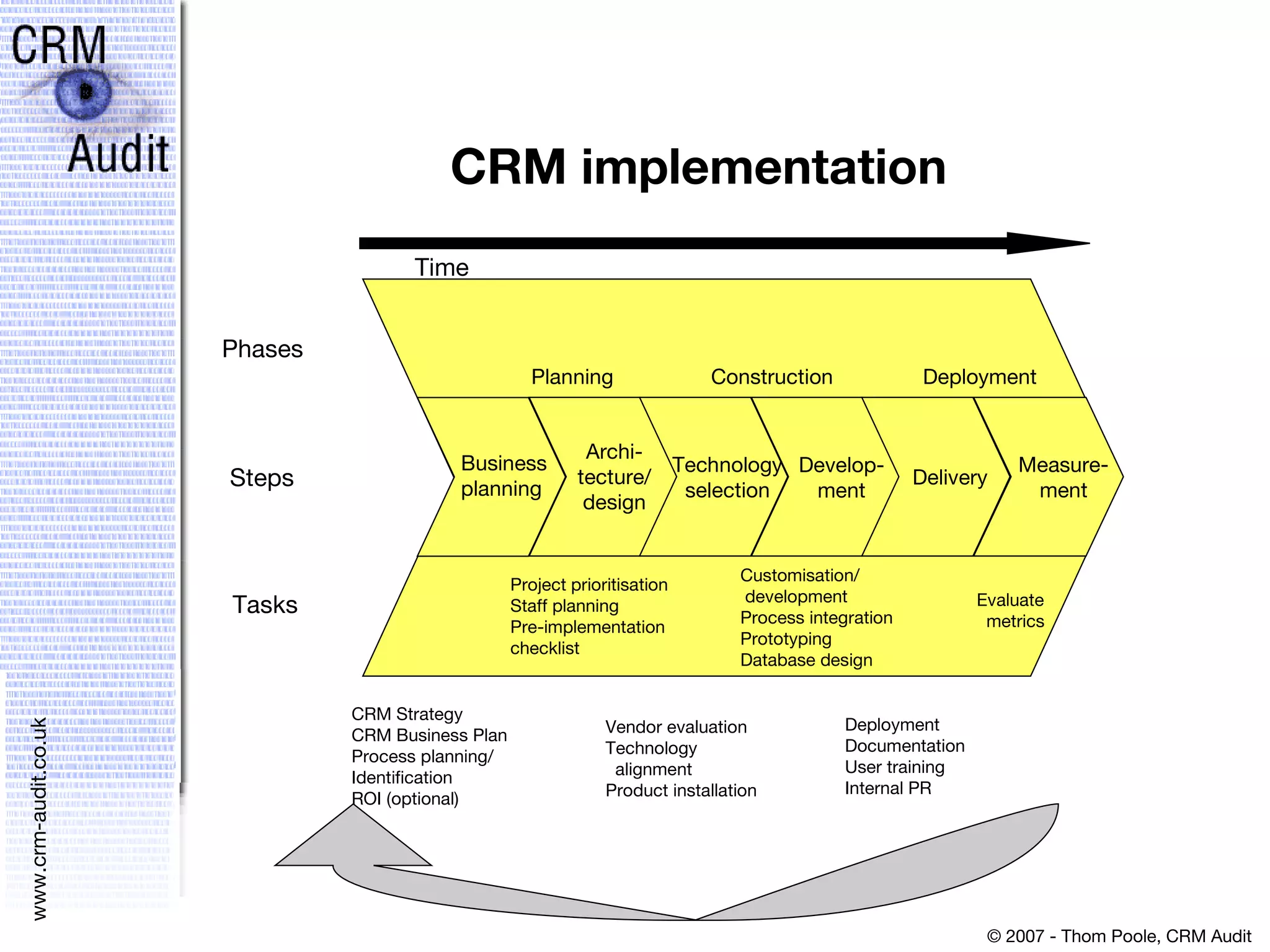
This document discusses justifying a CRM investment through a strong business case and ROI analysis. It provides examples of CRM performance metrics and considerations for CRM implementation planning. Key factors for a successful CRM justification include tangible benefits like increased revenue and cost savings, strategic alignment, and linking the decision to other strategic and infrastructure factors.










![Thank you [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cim-crm2-110413124905-phpapp01/75/The-Business-Case-for-CRM-21-2048.jpg)