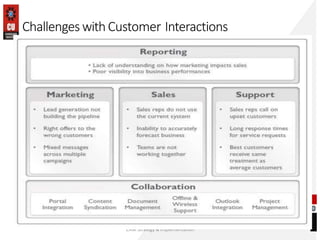
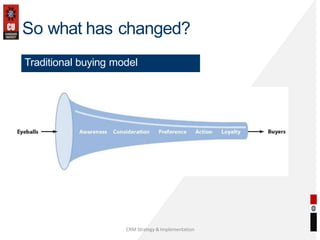
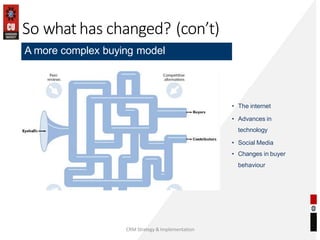
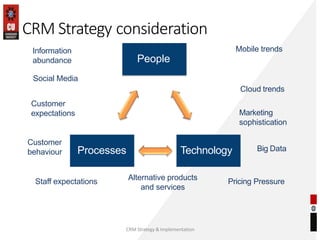
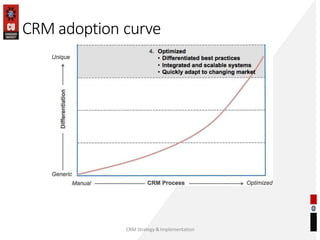
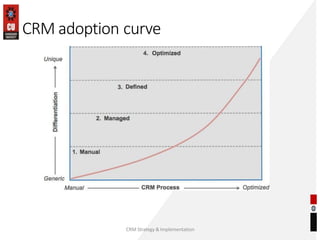
The document discusses the key building blocks of a successful customer relationship management (CRM) strategy. It outlines eight building blocks: 1) CRM vision, 2) strategy, 3) valued customer experience, 4) organizational collaboration, 5) CRM processes, 6) CRM information, 7) CRM technology, and 8) CRM metrics. For each building block, the document provides details on what organizations should consider to develop an effective CRM strategy, including understanding customer needs, creating a customer-centric culture, collecting and analyzing customer data, and continuously improving processes. It also discusses challenges of CRM adoption and moving from a product-focused to customer-centric approach.