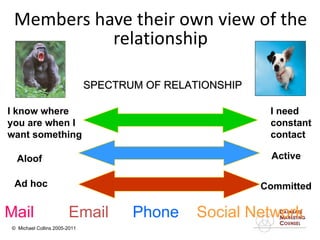
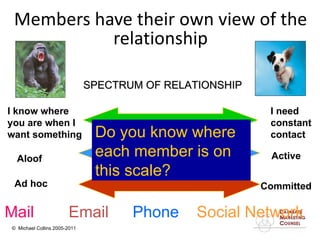
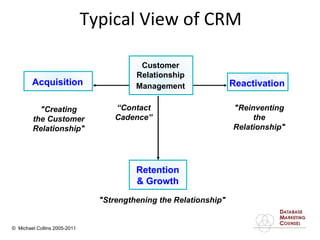
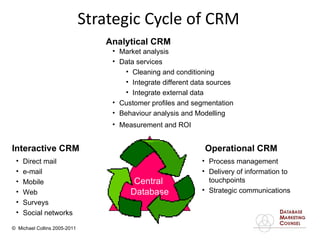
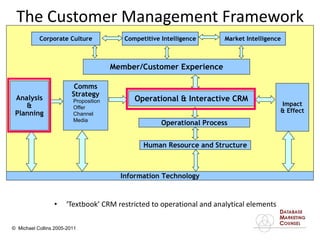
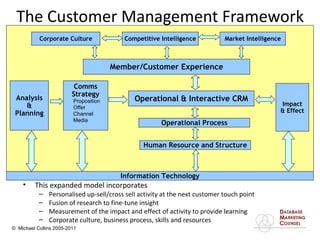
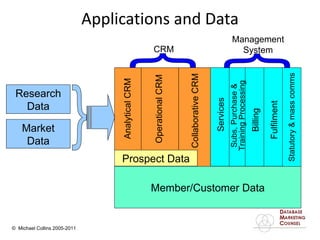
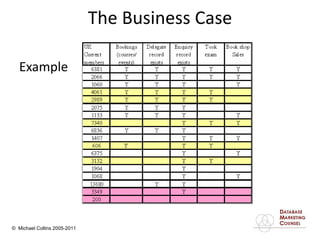
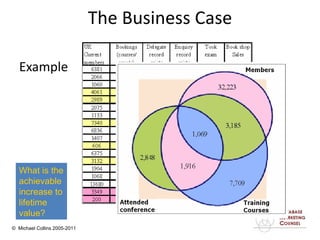
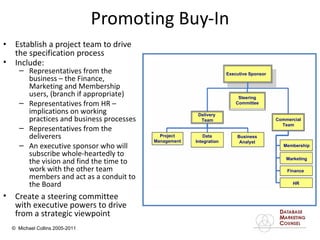
This document discusses implementing a customer relationship management (CRM) system for nonprofit organizations. It addresses key concerns around CRM implementation like data quality and buy-in. It compares CRM to legacy membership systems and outlines a customer management framework. It also provides questions to assess an organization's readiness for CRM and discusses promoting buy-in, creating a business plan, and how a consultant can help with implementation.