Anatomy of the Nose | SurgicoMed.com
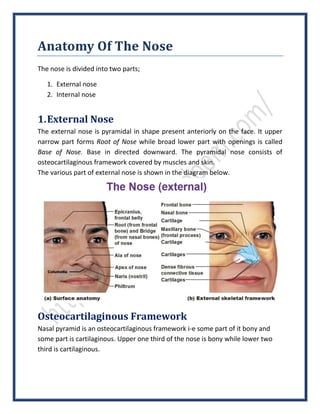
- 1. Anatomy Of The Nose The nose is divided into two parts; 1. External nose 2. Internal nose 1.External Nose The external nose is pyramidal in shape present anteriorly on the face. It upper narrow part forms Root of Nose while broad lower part with openings is called Base of Nose. Base in directed downward. The pyramidal nose consists of osteocartilaginous framework covered by muscles and skin. The various part of external nose is shown in the diagram below. Osteocartilaginous Framework Nasal pyramid is an osteocartilaginous framework i-e some part of it bony and some part is cartilaginous. Upper one third of the nose is bony while lower two third is cartilaginous.
- 2. Bony Part Upper one third of the external framework of nose is contributed by hard bone. The bony part is formed by two nasal bones which meet in midline and rest on upper part of nasal process of the frontal bones and are also themselves held between the frontal processes of the maxillae.
- 3. Cartilaginous Part The cartilaginous part of nose is formed by three type of cartilages; 1) Upper lateral cartilages 2) Lower lateral cartilages (alar cartilages) 3) Lesser alar cartilages (sesamoid cartilages) 4) Septal cartilage Upper Lateral Cartilages These cartilages extend from the undersurface of the nasal bones above, to the alar cartilages below. Anteriorly, these cartilages fuse with each other and with the upper border of the septal cartilage in the midline. The lower edge of upper
- 4. lateral cartilages is free and can be seen intranasally as limen vestibuli or nasal valve on each side separately. Lower Lateral Cartilages (Alar Cartilages) Each of the alar cartilages is U-shaped which has two crus i-e lateral crus and medial crus. The lateral crus form the ala of nose and medial crus becomes the part of columella. The lateral crus of alar cartilage overlap the lower edge of upper lateral cartilage on each side (covers the free edge of upper lateral cartilages which form limen vestibuli or nasal valve on each side). Lesser Alar Cartilages (Sesamoid Cartilages) These are two or more in numbers which lie above and lateral to the alar cartilages. Perichondrium and periosteum connects these cartilages with one another and with the adjoining bones. The free edge or margin of nostril is formed by the fibrofatty tissue in most of the part (posterior of the margin) and not by the alar cartilages (alar cartilages form only some portion of anterior of the margin of nostril).
- 5. Septal Cartilage Septal cartilage is the midline structure with its anterosuperior border running from undersurface of nasal bone to the nasal tip. It provides support to the dorsum of cartilaginous part of the nose. Clinical: - After removal of septal cartilage (completely or most of its part) as submucosal resection (SMR) operation, support of dorsum of nose is lost and supratip depression results. In order to correct it, we have to provide artificial support by surgery. Musculature Of Nose Nasal musculature covers the osteocartilaginous framework of the nose and is responsible for the movement of the nasal tip, ala and the overlying skin. These are the procerus, nasalis (transverse and alar parts), levator labii superioris alaeque nasi, anterior and posterior dilator nares and depressor septi. Nasal Skin The skin over the nasal bones and the upper lateral cartilages is thin and freely mobile, while that covering the alar cartilages is thick and closely adherent and rich of sebaceous gland. Clinical: - The hypertrophy of sebaceous gland in nasal skin gives rise to a lobulated tumor which is called rhinophyma. 2.Internal Nose Nasal septum divides the internal nose into right and left nasal cavities. Each nasal cavity has communication with the exterior through naris or nostril and with the Nasopharynx through posterior nasal aperture or choana. Nasal cavity is partitioned into two areas i-e skin lined portion, the vestibule and a mucosa lined portion, the nasal cavity proper. a) Vestibule of nose b) Nasal cavity proper
- 6. a) Vestibule Of Nose Vestibule is anterior and inferior part of the nasal cavity. It is lined by skin (keratinized stratified squamous epithelium) and contains sebaceous glands, hair follicles and hair called vibrissae. Note: - The hairs in the vestibule of nose are called vibrissae. The upper limit of the nasal vestibule is demarcated by nasal valve (limen nasi) a structure visible on the lateral wall while seen from inside. The limen vestibuli is actually the lower free edge of upper lateral cartilage seen intranasally and is same structure named as limen nasi. Nasal Valve Nasal valve is bounded laterally by the lower border of upper lateral cartilage (limen vestibuli) and fibrofatty tissue and anterior end of inferior turbinate. Medially the structure present is nasal septum, and caudally the floor of pyriform aperture. Note: - The angle between the nasal septum and lower border of upper lateral cartilage is about 300 . Nasal Valve Area Nasal valve area is the least cross sectional area of the nose that functions to regulate airflow and resistance on inspiration. It is the cross sectional area bounded by the structures forming the nasal valve. b) Nasal Cavity Proper The nasal cavity proper is the rest portion of internal nose other than the vestibule. Each nasal cavity has a lateral wall, a medial wall, a roof and a floor. i. Lateral nasal wall ii. Medial nasal wall iii. Roof iv. Floor
- 7. i. Lateral Nasal Wall On the lateral wall of the nose, three and occasionally four turbinates or conchae are well demarcated. Conchae or turbinates are scroll like bony projections covered by the mucous membrane. The spaces between the turbinates are called meatuses. Note: - Inferior turbinate is the most prominent bony projection and the superior turbinate is the least prominent bony projection. Inferior Turbinate Inferior turbinate is the separate bone while the other turbinates are the bony projections of various bones. Below it, into the inferior meatus, opens the nasolacrimal duct. At the terminal end of the nasolacrimal duct, a mucosal valve called Hasner’s valve is present that guard it.
- 8. Middle Turbinate Middle turbinate is ethmoturbinal i-e middle turbinate is the part of ethmoid bone. It’s attachment to the lateral wall is by a bony lamella called ground or basal lamella which is in S-shaped manner, not in straight line. In the anterior third, it lies in sagittal plane and is attached to lateral edge of cribriform plate. In the middle third, it lies in frontal plane and is attached to lamina papyracea while in its posterior third, it runs horizontally and forms roof of the middle meatus and is attached to lamina papyracea and medial wall of maxillary sinus. The anterior group of paranasal sinuses is the ostia of various sinuses draining anterior to basal lamina while the posterior group of paranasal sinuses is those opening into posterior and superior to basal lamina. Middle Meatus Middle meatus is related with several important structures which are important in endoscopic surgery of the sinuses. Uncinate process is a hook like structure running in from anterosuperior to posteroinferior direction. It posterior border is sharp and runs parallel to anterior border of bulla ethmoidalis. The gap between the two is called is hiatus semilunaris (inferior), a two dimensional space 1-2 mm in width.
- 9. The anteroinferior border of uncinate process is attached to the lateral wall and the posteroinferior end of uncinate process is attached to inferior turbinate dividing the membranous part of lower middle meatus into anterior and posterior fontanelle. Clinical: - The fontanel area is devoid of bone and consists of membrane only and leads into maxillary sinus when perforated. Upper attachment of uncinate process shows great variations and may be inserted into the lateral nasal wall, upward into the base of skull or medially into the middle turbinate which accounts for variations in drainage of frontal sinus. The space limited medially by the uncinate process and frontal process of maxilla and sometimes lacrimal bone and laterally by the lamina papyracea is called infundibulum. The natural ostium of the maxillary sinus is situated in the lower part of infundibulum. The accessory ostium or ostia of maxillary sinus are sometimes seen in the anterior or posterior fontanel.
- 10. Bulla Ethmoidalis Bulla ethmoidalis is an ethmoidal cell situated behind the uncinate process. The anterior surface of the bulla forms the posterior boundary of hiatus semilunaris. Bulla ethmoidalis may be a pnematized cell or a solid bony prominence depending upon the degree of pnematization. It may be extended superiorly to the base of skull and posteriorly to fuse with the ground lamella. Sometimes, space is present above or behind the bulla, it is called suprabullar or retrobullar recesses respectively. The suprabullar and retrobullar recesses together form the lateral sinus (sinus lateralis of Grunwald). The lateral sinus is thus bounded superiorly by the skull base, laterally by lamina papyracea, medially by middle turbinate and inferiorly by the bulla ethmoidalis. Posteriorly, the sinus lateralis may extend up to basal lamella of meddle turbinate. The cleft like communication between the bulla and skull base and opening into middle meatus in also called hiatus semilunaris superior in contrast to hiatus semilunaris inferior referred to before. Atrium Of The Middle Meatus Atrium of the middle meatus is a shallow depression lying in front of middle turbinate and above the nasal vestibule.
- 11. Agger Nasi Agger nasi is an elevation just anterior to the attachment of middle turbinate. When pnematized it contains air cells, the agger nasi cells, which communicate with frontal recess. An enlarged agger nasi cell may encroach on frontal recess area, constricting it and causing mechanical obstruction to frontal sinus drainage. The pnematization of middle turbinate leads to an enlarged ballooned out middle turbinate called concha bullosa. It drains into frontal recess directly or through agger nasi cells. Haller cells are air cells situated in the roof of maxillary sinus. They are peneumatized from anterior or posterior ethmoid cells. Enlargement of Haller cells encroaches on ethmoid infundibulum, impeding draining of maxillary sinus. Superior Turbinate Superior turbinate is also an ethmoturbinal i-e a part of ethmoidal bone. It is situated posterior and superior to middle turbinate. It may also get pnematized by one or more cells. It is an important landmark to identify ostium of sphenoid sinus which lies medial to it. Superior Meatus Likewise other meatus, superior meatus is the space present below the superior turbinate respectively. Posterior ethmoidal cells have opening into it. Posterior ethmoidal cells vary from 1-5 in numbers. Onodi cell is a posterior ethmoidal cell which may grow posteriorly by the side of sphenoid sinus or superior to it for as much distance as 1.5 cm from the anterior surface of sphenoid. Clinical: - Onodi cell have surgical importance as the optic nerve may be related to its lateral wall. Sphenoethmoidal Recess Sphenoethmoidal recess is situated above the superior turbinate. Sphenoid sinus opens into it. Supreme Turbinate Sometimes, a fourth turbinate called supreme turbinate is also present above the superior turbinate and has a narrow meatus beneath it.
- 12. The ostium of sphenoid sinus is situated in the sphenoehtmoidal recess medial to the superior or supreme turbinate. It can be located endosceopically about 1 cm above the upper margin of posterior choana close to the posterior border of the septum. ii. Medial Nasal Wall Nasal septum forms the medial wall of the nose. The detail anatomy is described separately as it is a structure of utmost importance and has surgical value in clinical cases. iii. Roof The roof the nose has three parts i-e anterior part, middle part and posterior part of roof. The anterior sloping part of the roof is formed by the nasal bones, posterior sloping part is formed by the body of sphenoid bone and the middle horizontal part is formed by cribriform plate of ethmoid through which the olfactory nerves enter the nasal cavity. iv. Floor The floor of the nose is formed by palatine process of the maxilla in its anterior three-fourths and horizontal part of the palatine bone in its posterior one-fourth. Lining Membrane Of Internal Nose Lining membrane of the internal nose is different is it various part i-e vestibule and other areas of internal nose have different lining membrane related with their functions. a) Vestibule Vestibule is lined by normal skin containing hair, hair follicles and sebaceous glands. b) Olfactory Region Upper one third of the lateral wall (up to superior concha), corresponding part of nasal septum and the roof of nasal cavity form the olfactory region. Here mucous membrane in paler in color.
- 13. c) Respiratory Region Lower two thirds of the nasal cavity form the respiratory region. Here mucous membrane shows variable thickness being thickest over nasal conchae especially at their ends, quite thick over the nasal septum but very thin in the meatuses and floor of the nose. This part of the membrane is highly vascular and also contains erectile tissue. The lining epithelium is pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium which contains plenty of goblet cells. In the submucous layer of mucous membrane are situated serous, mucous, both serous and mucous secreting glands, the ducts of which open on the surface of mucosa. Nerve Supply Of The Nose Three types of nerves supply the nose; 1. Olfactory nerves 2. The nerves of common sensation 3. Autonomic nerves 1. Olfactory Nerves These nerves carry the sense of smell and supply the olfactory region of the nose. These are the central filaments of the olfactory cells and are arranged into 12-20 nerves which pass through the cribriform plate and end in the olfactory bulb. Clinical: - These nerves can carry the sheaths of dura, arachnoid and pia with them into the nose. So the injury to these nerves may open CSF space leading to CSF rhinorrhea or meningitis.
- 14. 2. The Nerves Of Common Sensation The following nerves carry common sensations from the nose; Anterior ethmoidal nerve The braches of sphenopalatine ganglion The braches of infraorbital nerve (These supply vestibules of the nose both on its medial and lateral side) The most of the posterior two-third of nasal cavity (both septum and nasal wall) are supplied by braches of sphenopalatine ganglion.
- 15. Clinical 1: - The sensation from this area can be blocked by placing a pledge of cotton soaked in anaesthetic solution near the sphenopalatine foramen situated at the posterior extremity of middle turbinate. Clinical 2: -Anterior ethmoidal nerve which supplies anterior and superior part of the nasal cavity (lateral wall and septum) cam be blocked by placing the pledge high up on the inside of nasal bones where the nerve enters. 3. Autonomic Nerves The parasympathetic nerve fibers supply the nasal glands and control the nasal secretions. These come from greater superficial petrosal nerve, travel in the nerve of pterygoid canal (vidian nerve) and reach the sphenopalatine ganglion where
- 16. these relay before reaching the nasal cavity. These nerves also supply the blood vessels of the nose and cause vasodilation. Sympathetic nerve fibers come from upper two thoracic segments of spinal cord, pass through superior cervical ganglion, travel in deep petrosal nerve and join the parasympathetic fibers of greater petrosal nerve to form the nerve of pterygoid canal (vidian nerve). These nerves reach the nasal cavity without relay in the sphenopalatine ganglion. The stimulation of these nerves causes vasoconstriction. Clinical: - The excessive rhinorrhea in cases of vasomotor and allergic rhinitis can be controlled by secretion of the vidian nerve. Blood Supply Of The Nose Branches from both the internal and external carotid systems supply the nose. The detail of these arteries will be in anatomy section.
- 17. Lymphatic Drainage Lymphatics from the external nose and anterior part of nasal cavity drain into submandibular lymph nodes while those from the rest of nasal cavity drain into upper jugular nodes either directly or through the retropharyngeal nodes. Lymphatics of the upper part of the nasal cavity communicate with subarachnoid space along the olfactory nerves.
- 18. Feedback us @ http://mukhdoom.com for more data & info. Like us @ https://www.facebook.com/StairsOfSuccess
