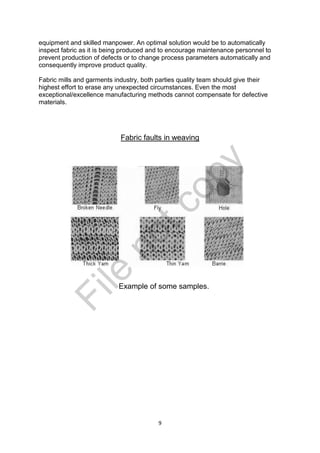
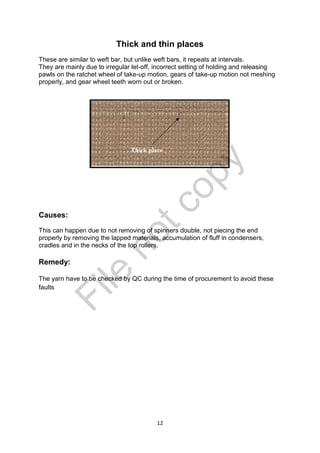
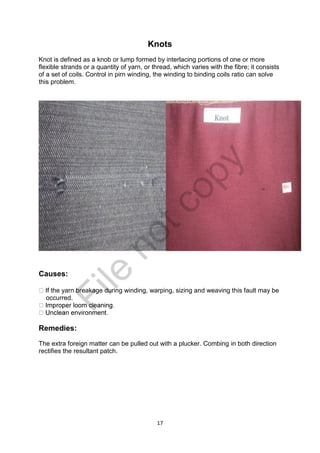
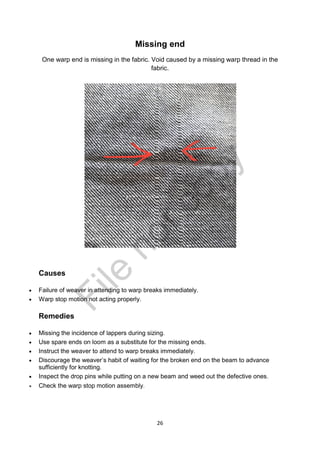
The document is a project report submitted by Mr. Gaurav U. Dandekar as part of his Bachelor's degree in Textile Science at Nagpur University, focusing on fabric defects and their automated detection methods. It highlights the importance of quality control in the textile industry, detailing various types of defects, their causes, and solutions, as well as the benefits of using machine vision for improved inspection accuracy. The report concludes that minimizing fabric defects is crucial for maintaining product quality and reducing costs in textile manufacturing.