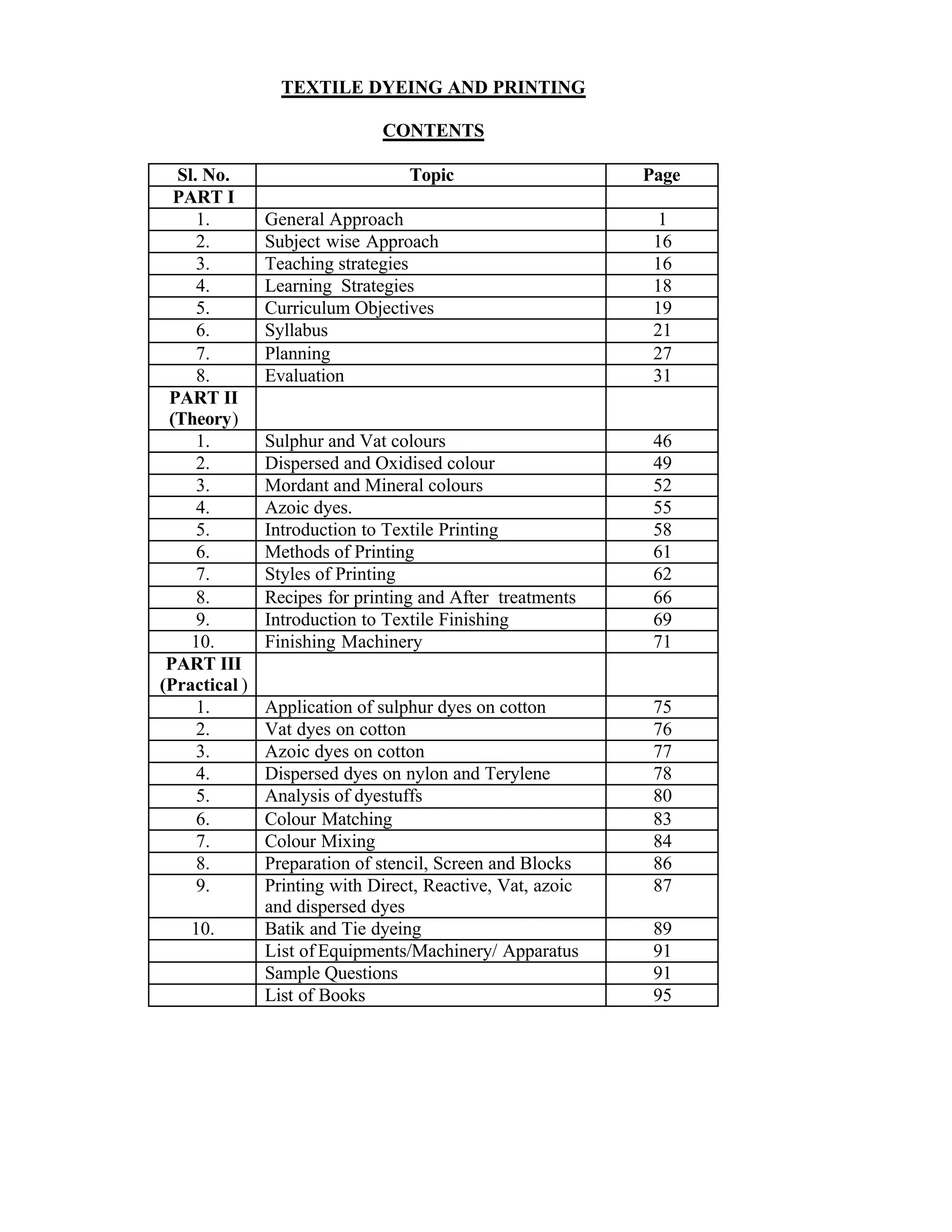
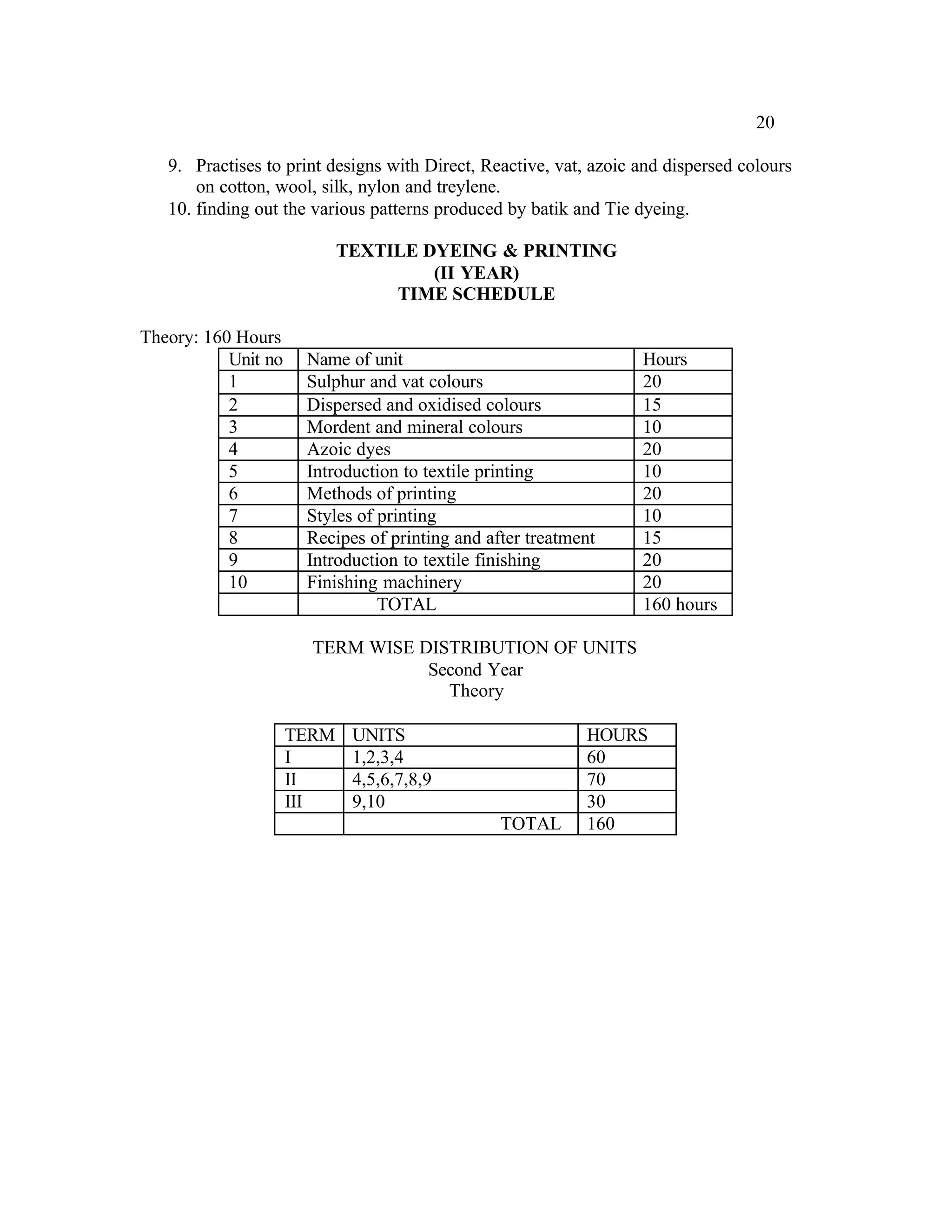
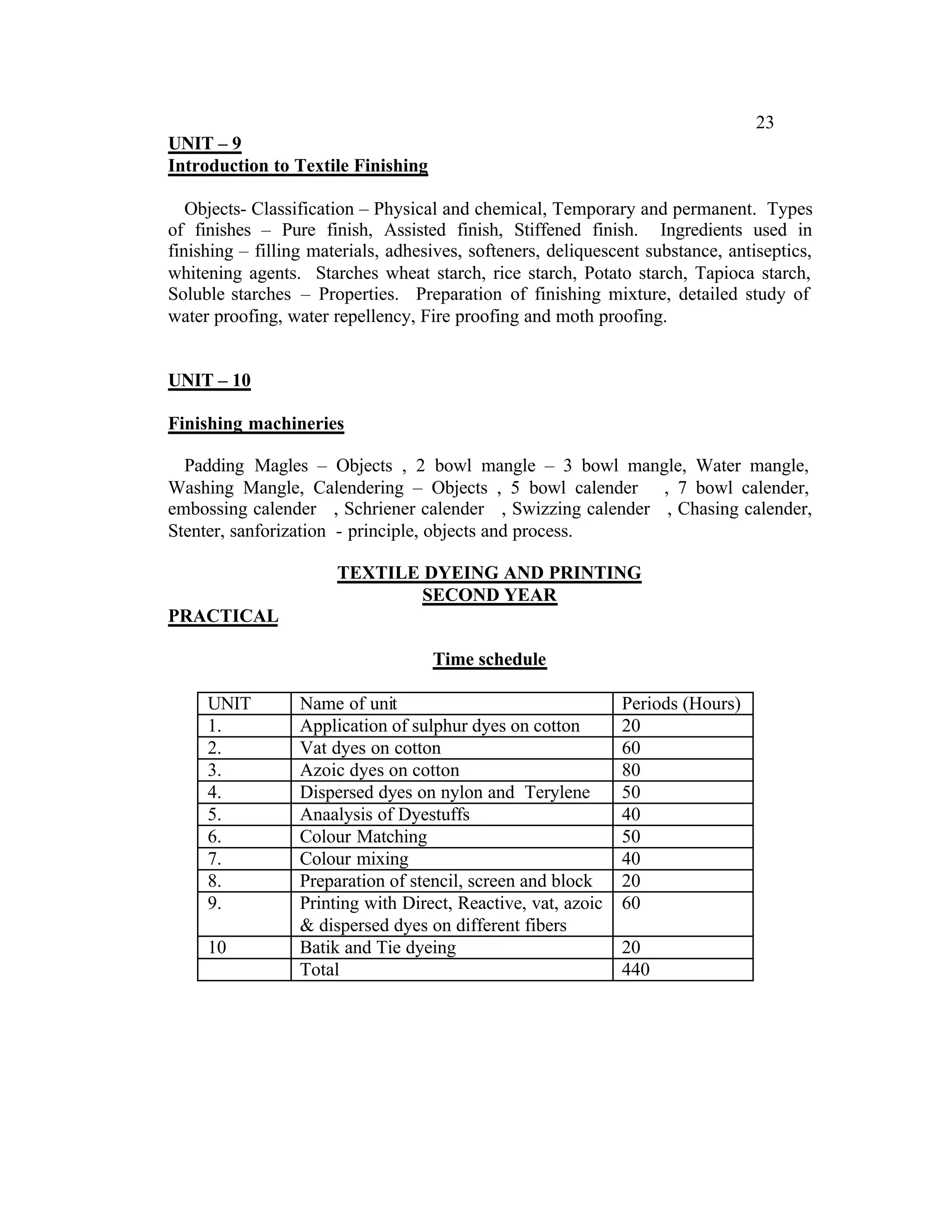
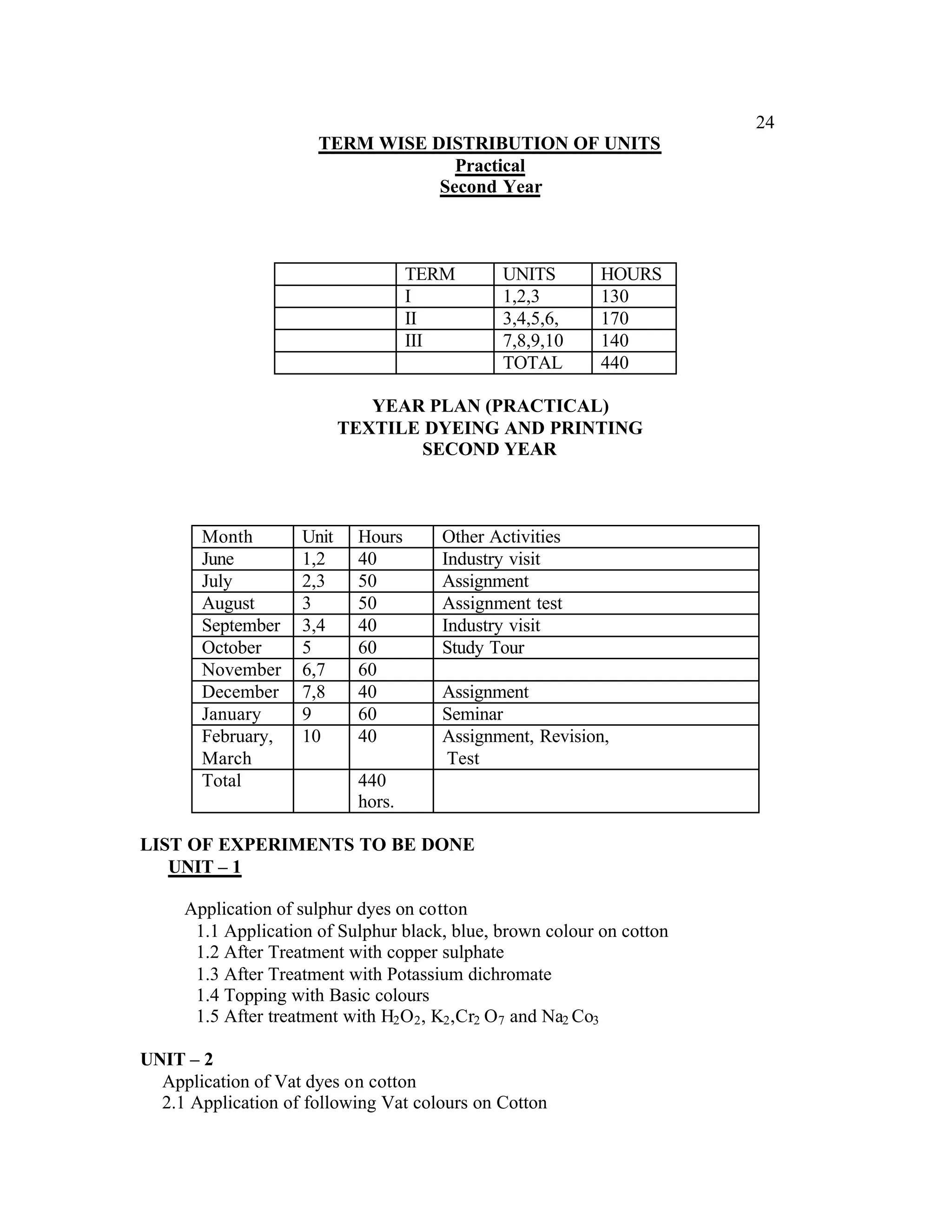
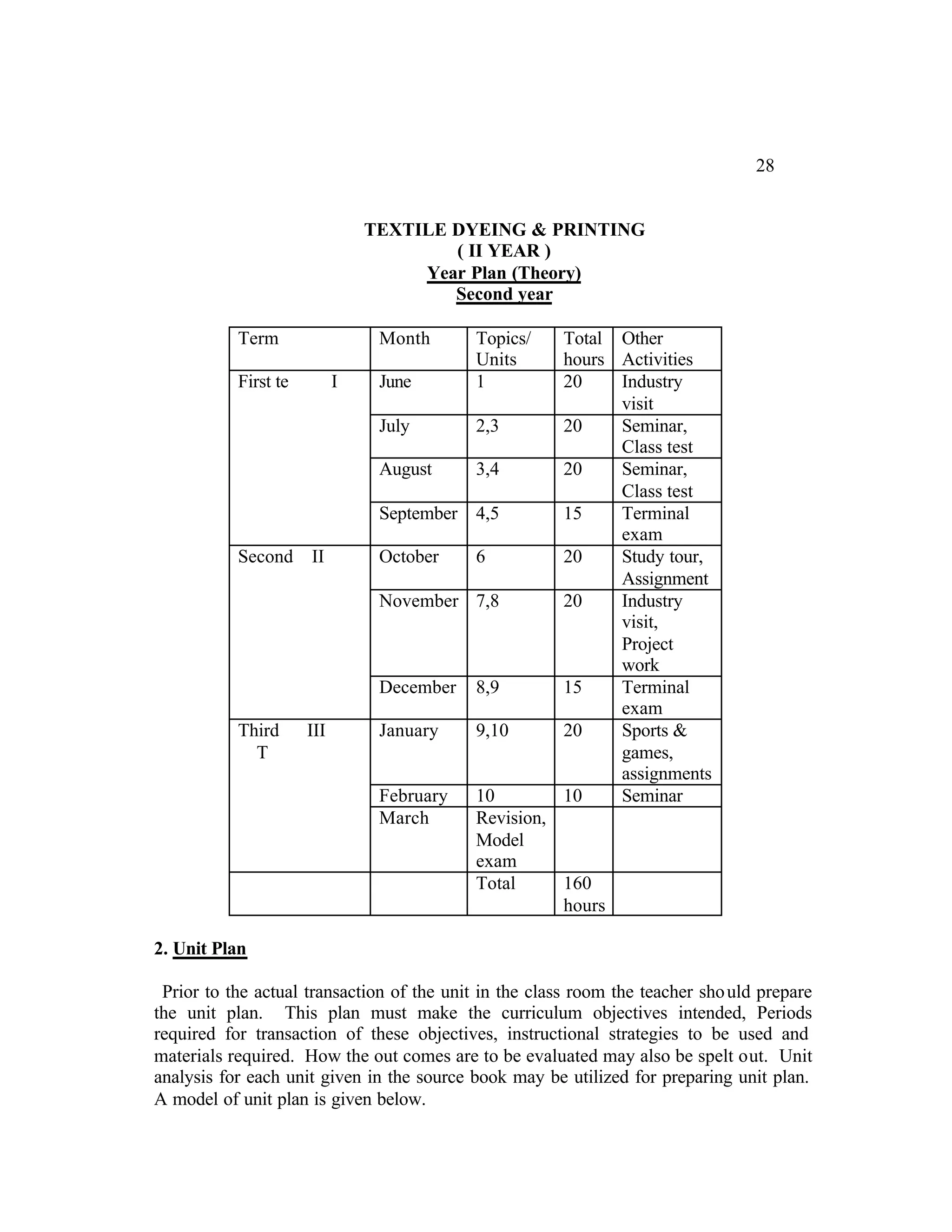
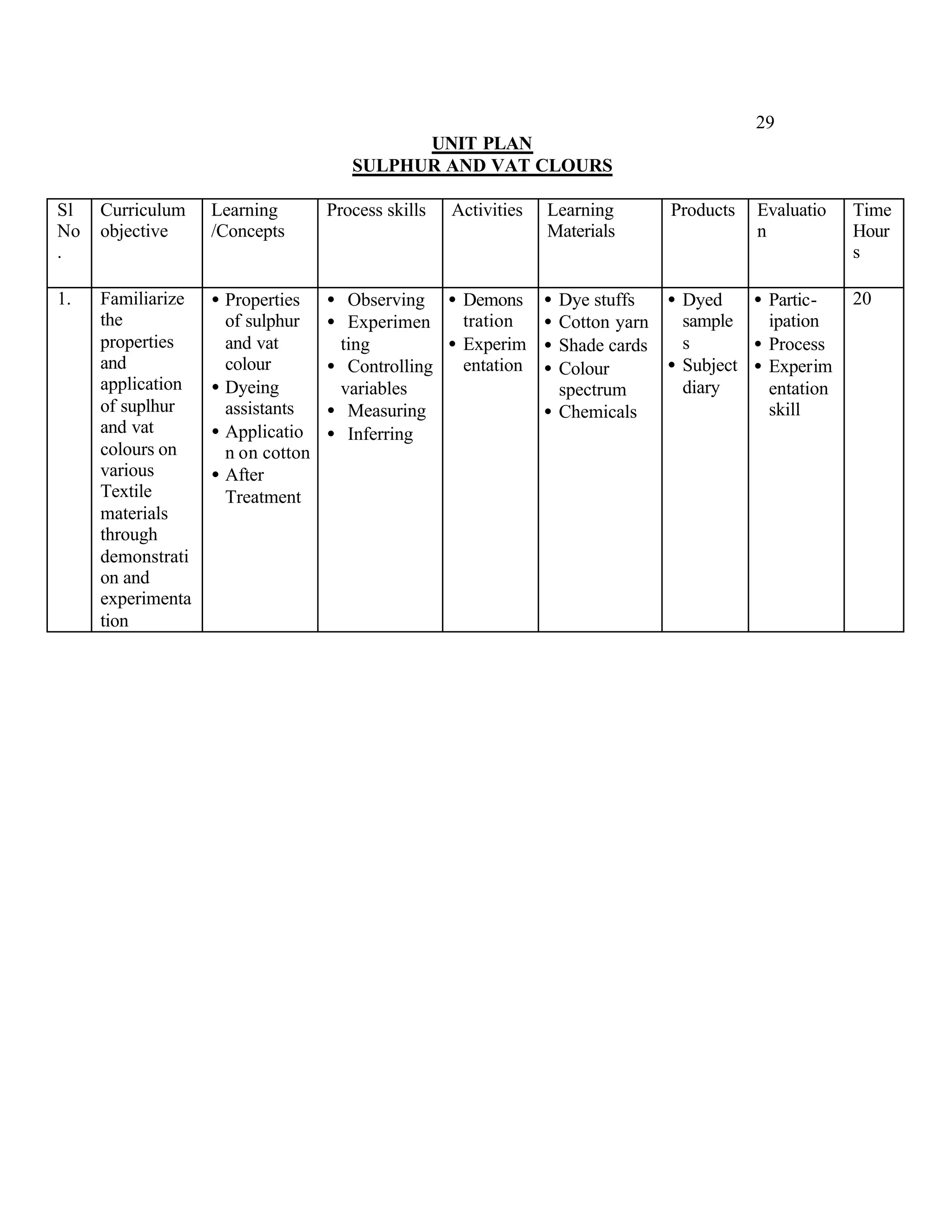
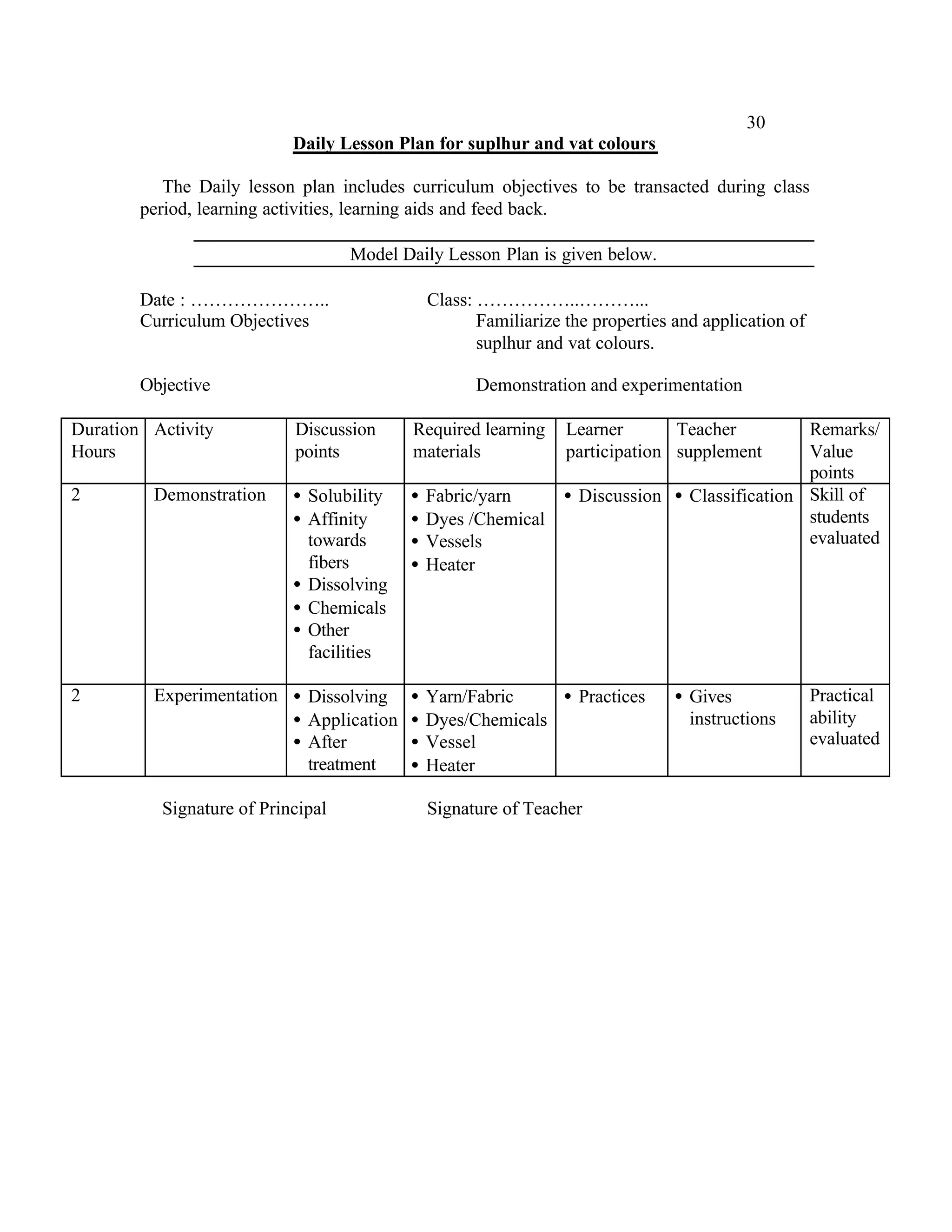
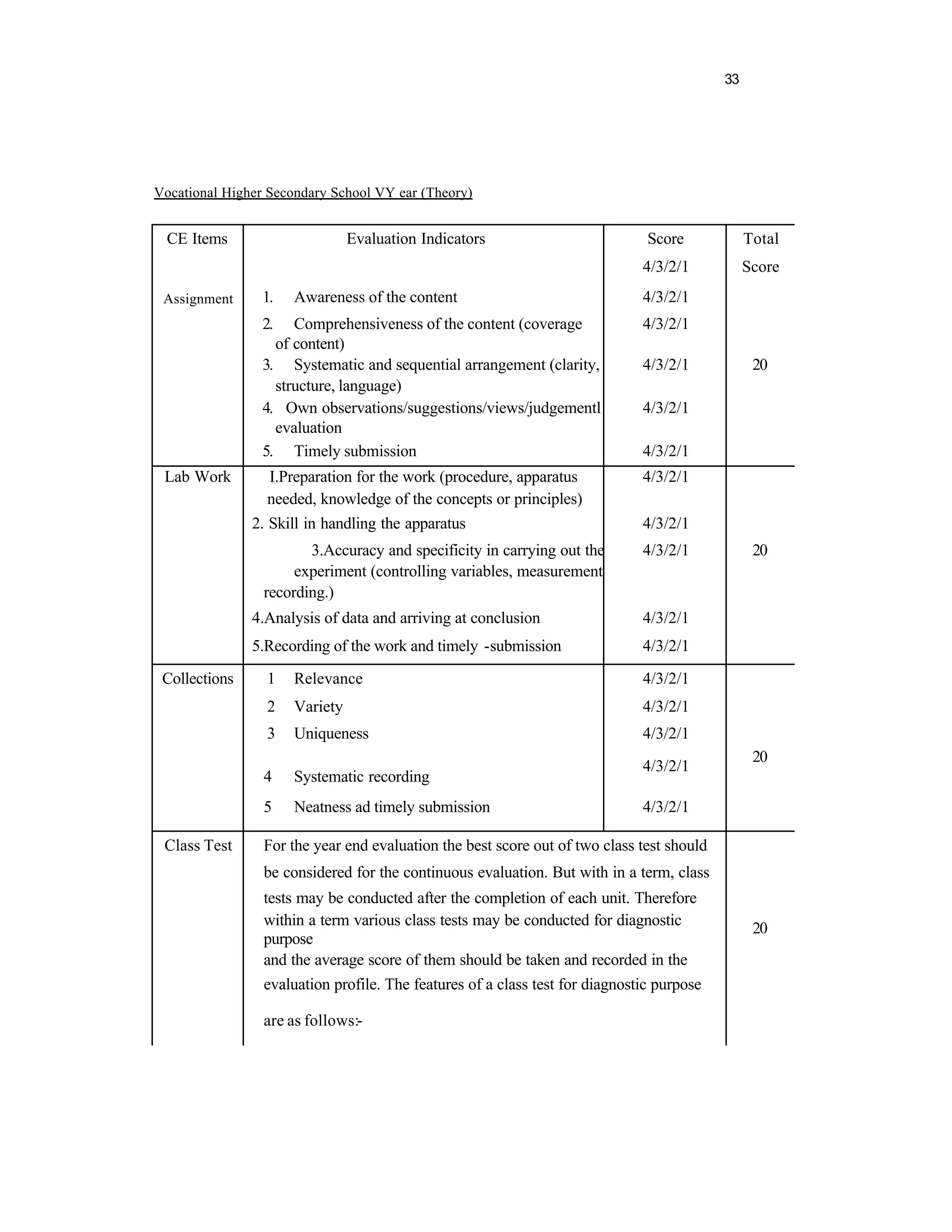
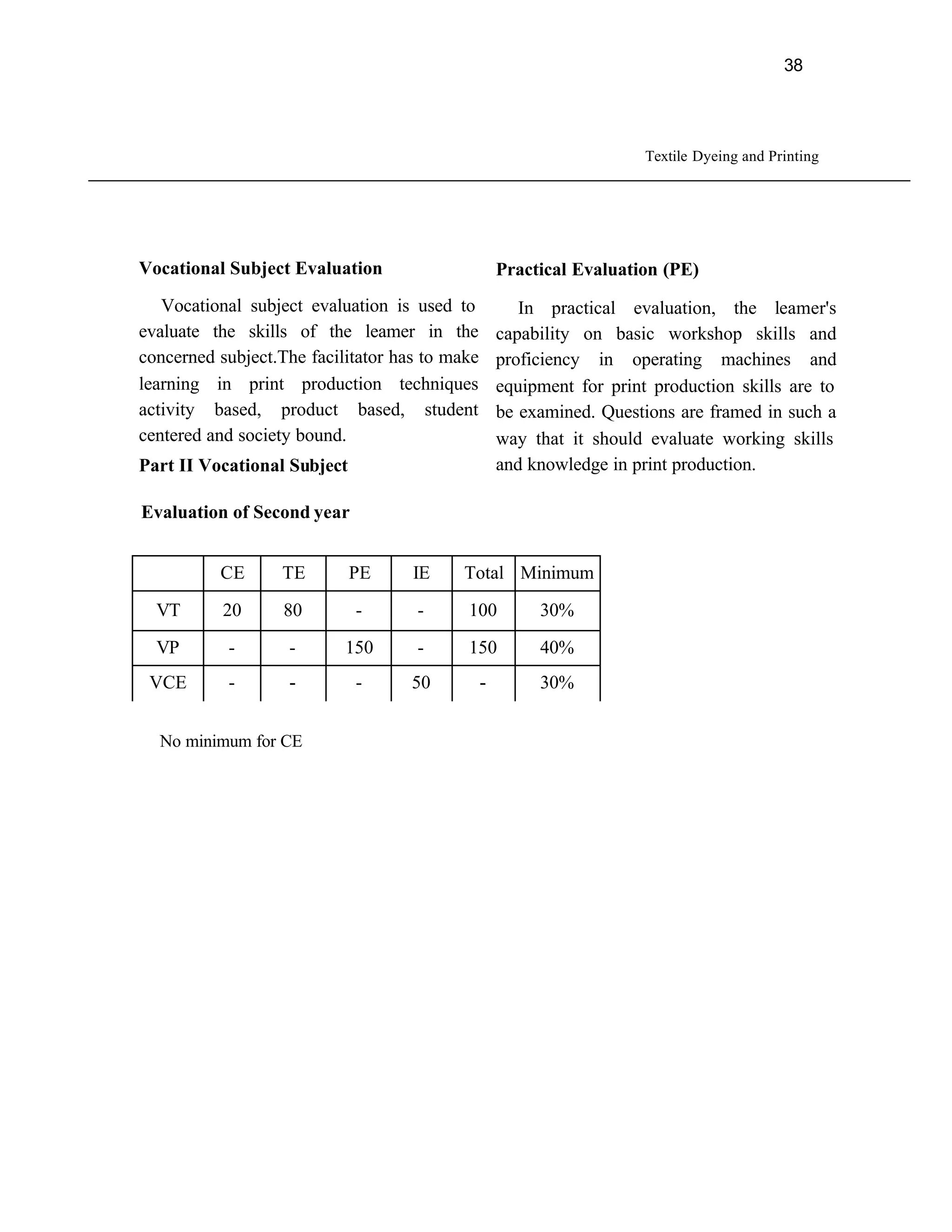
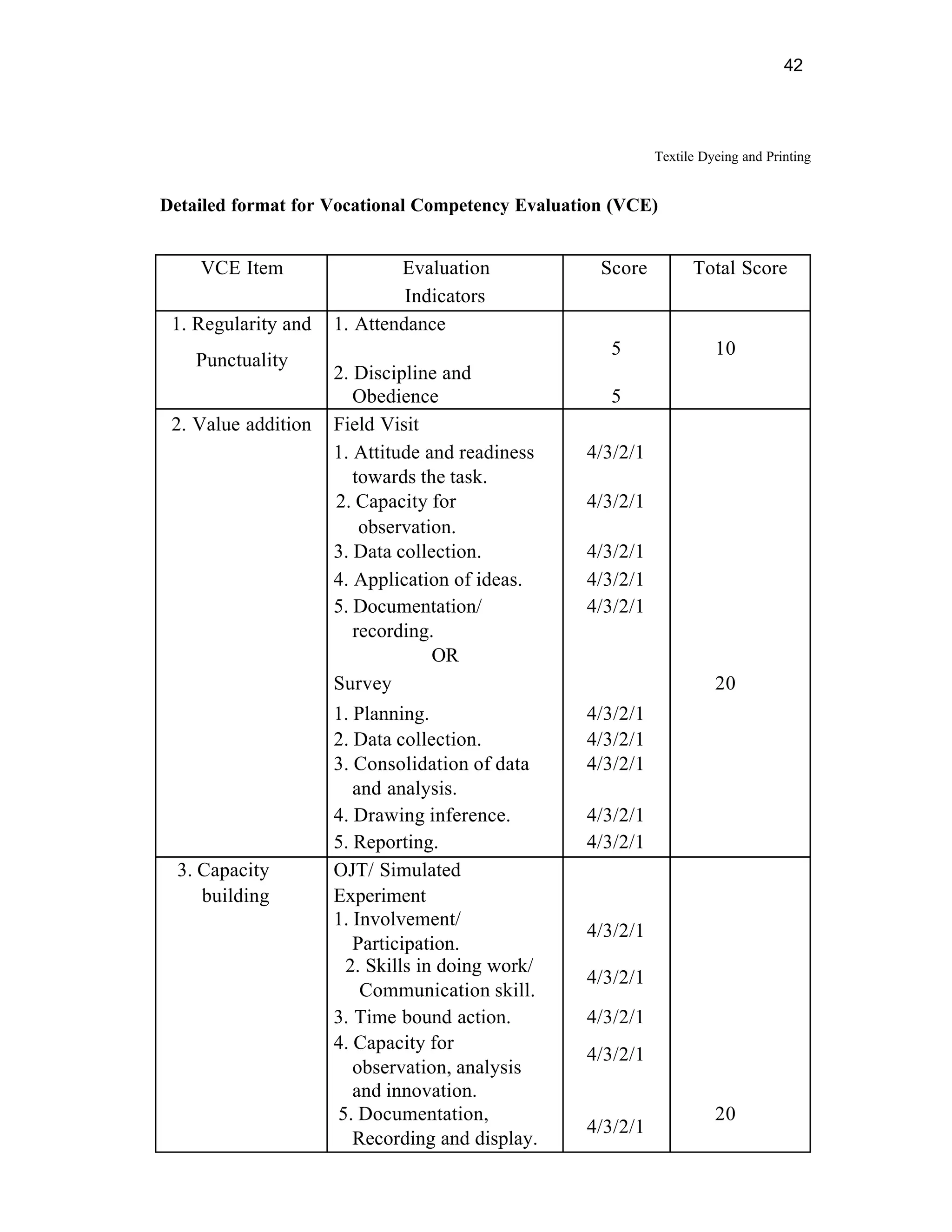
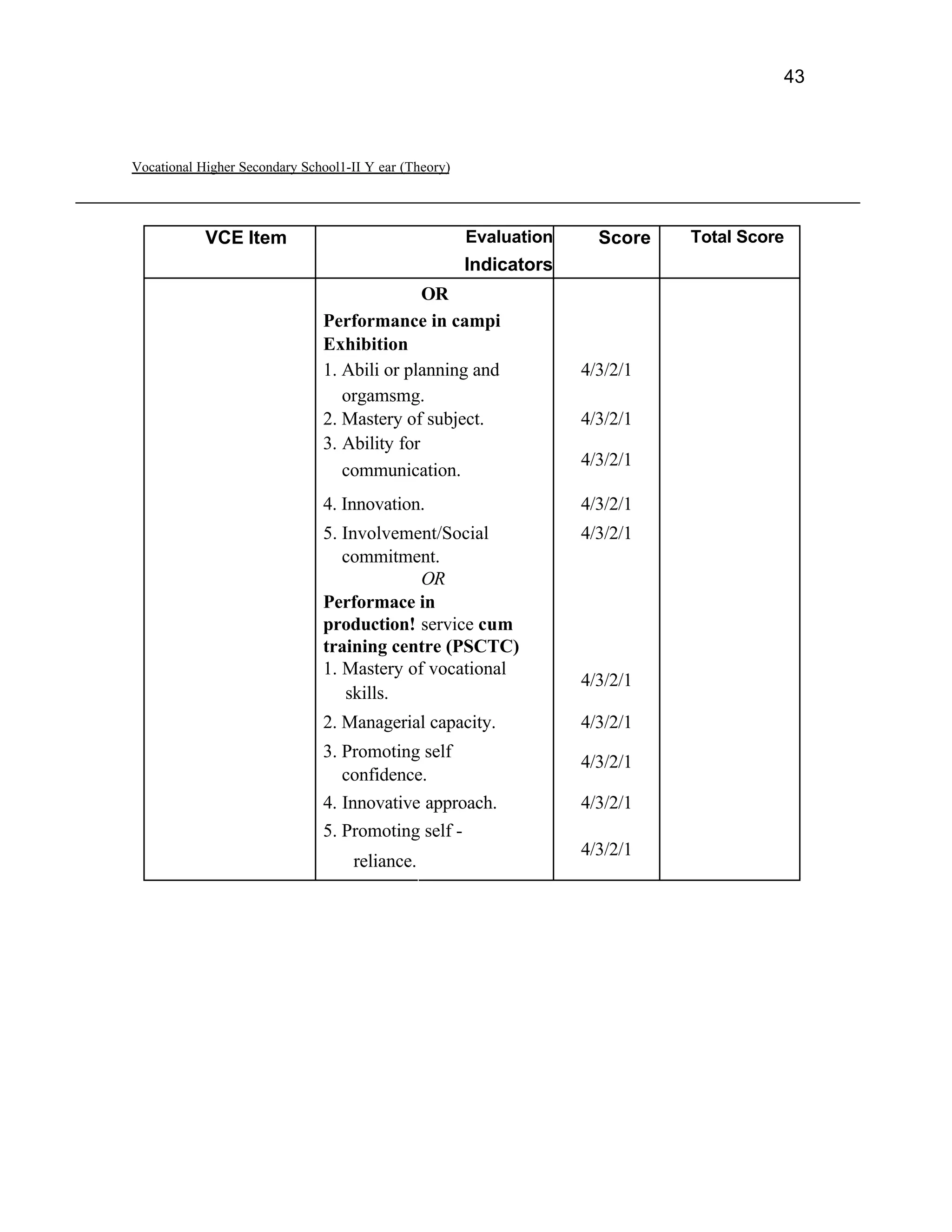
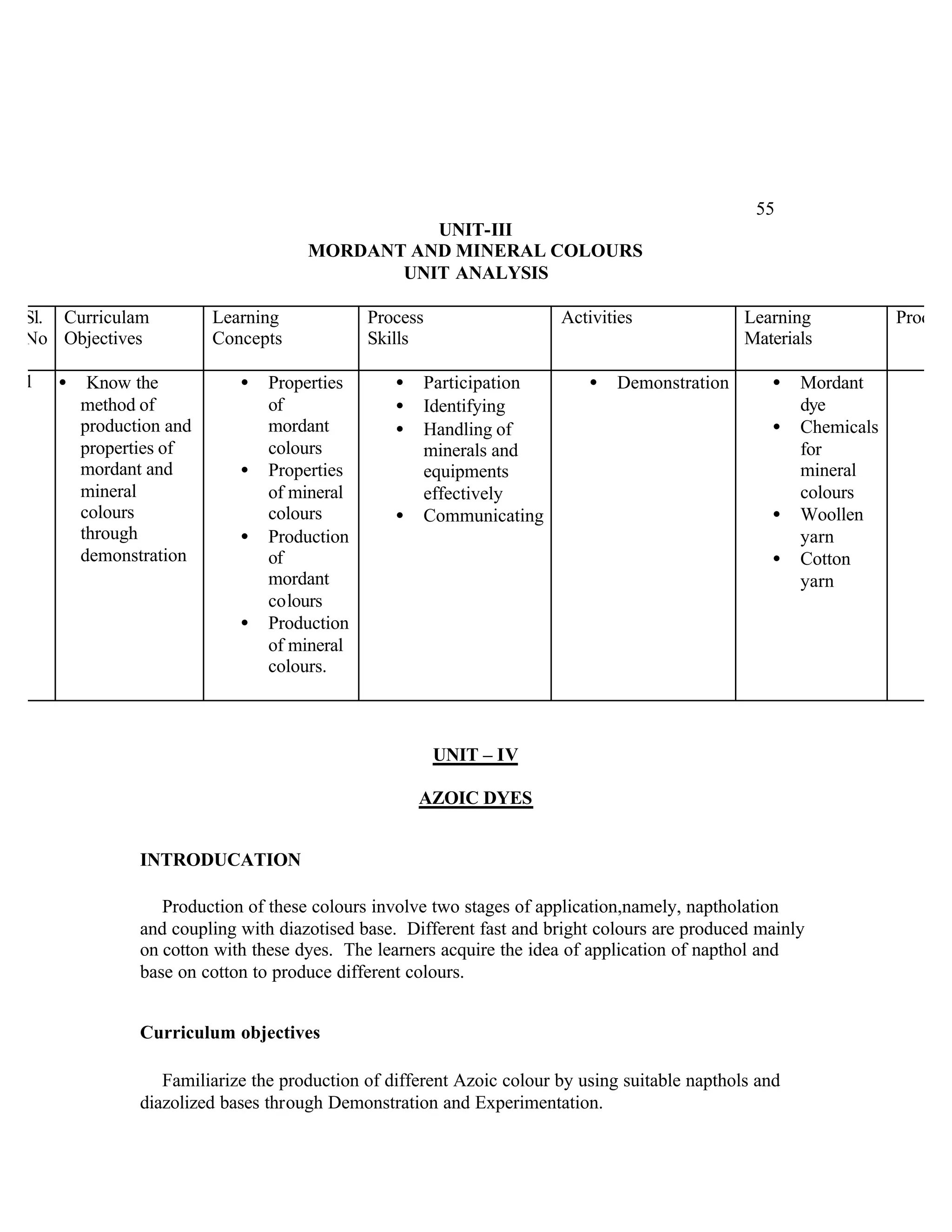
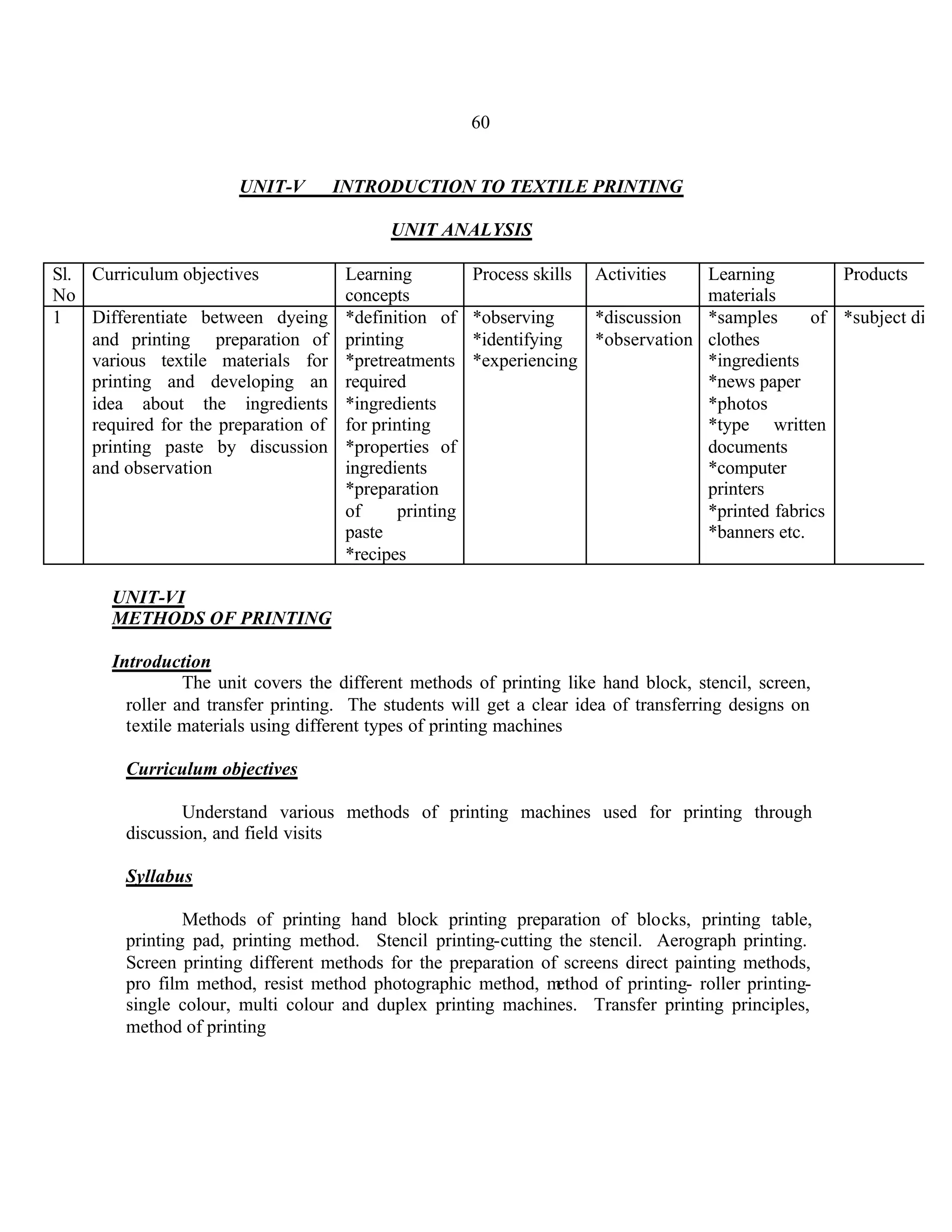
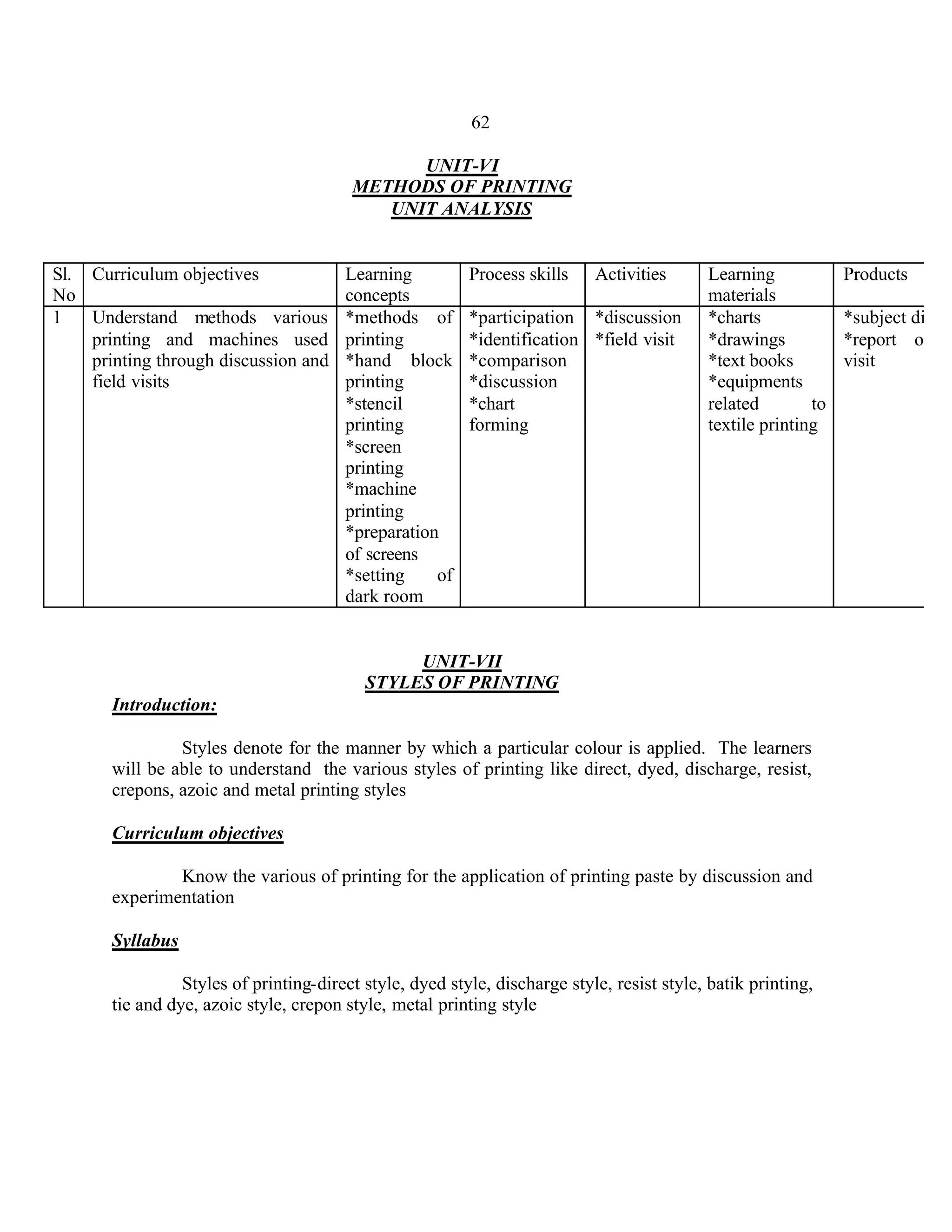
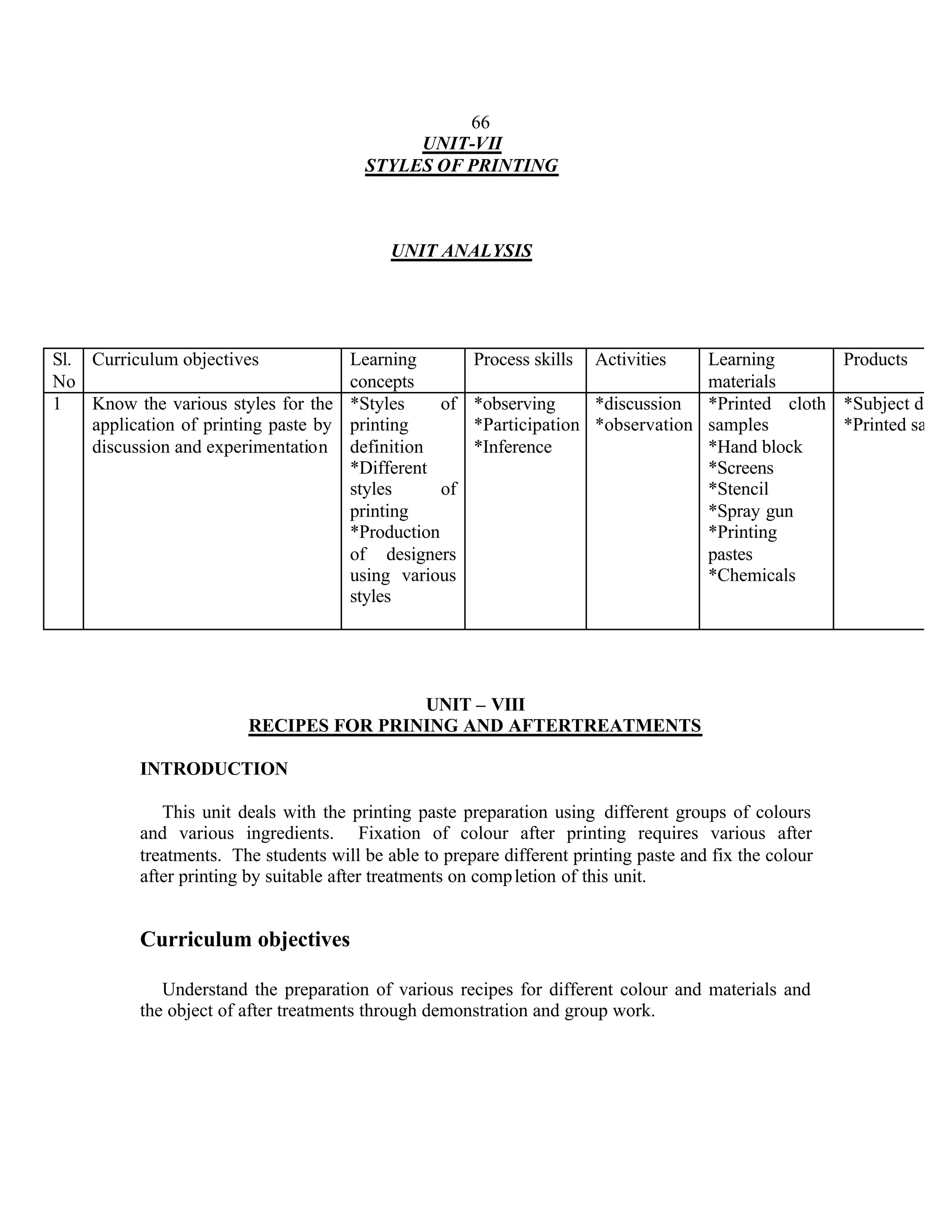
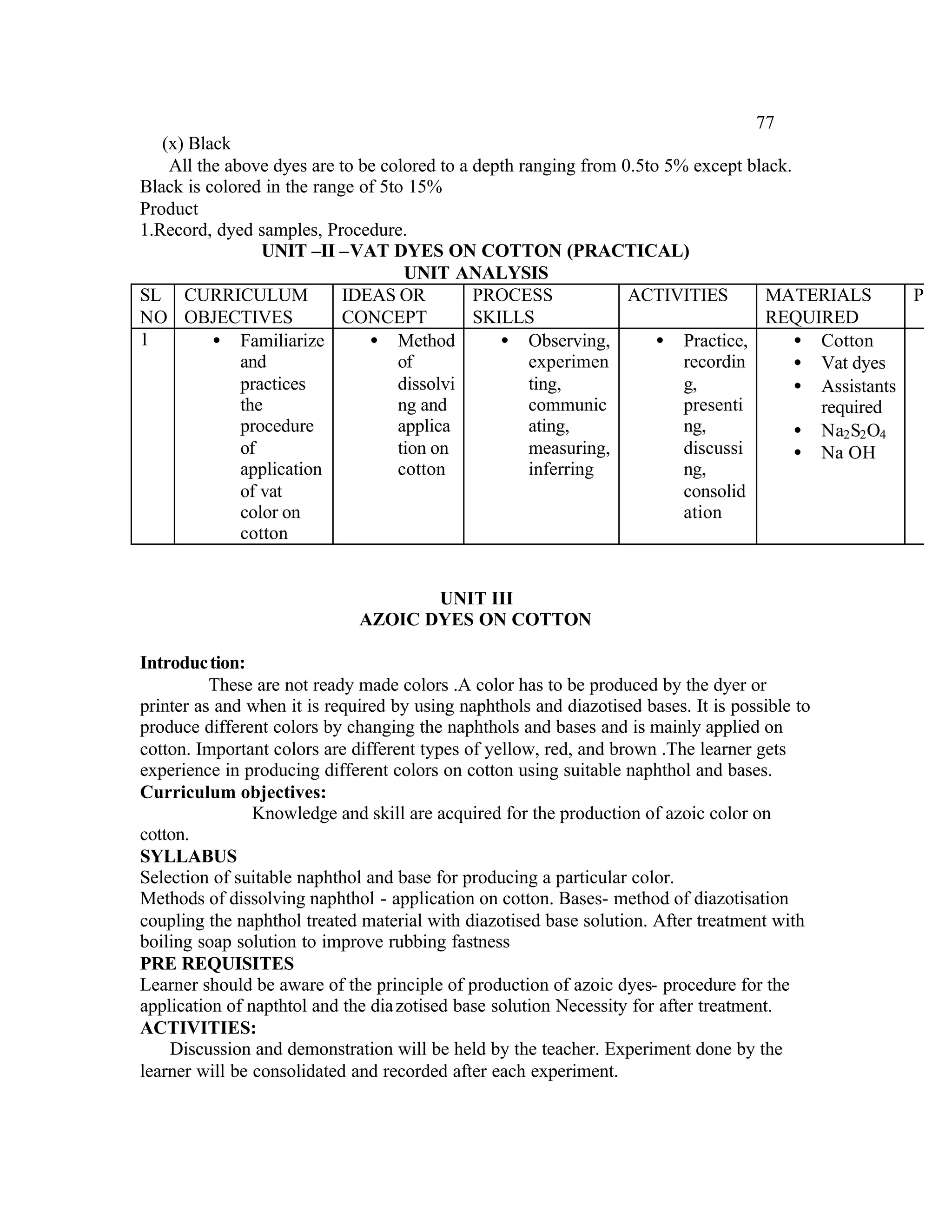
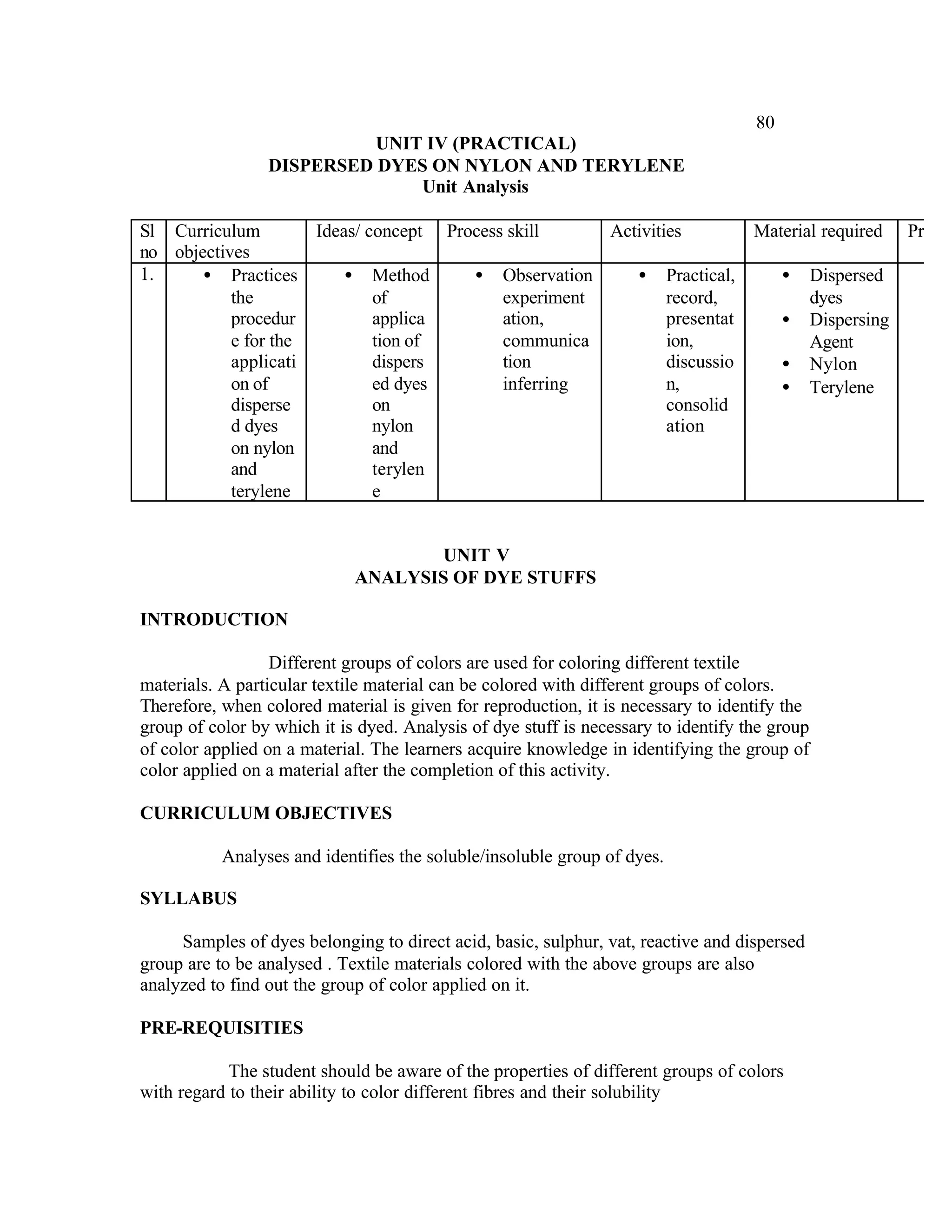
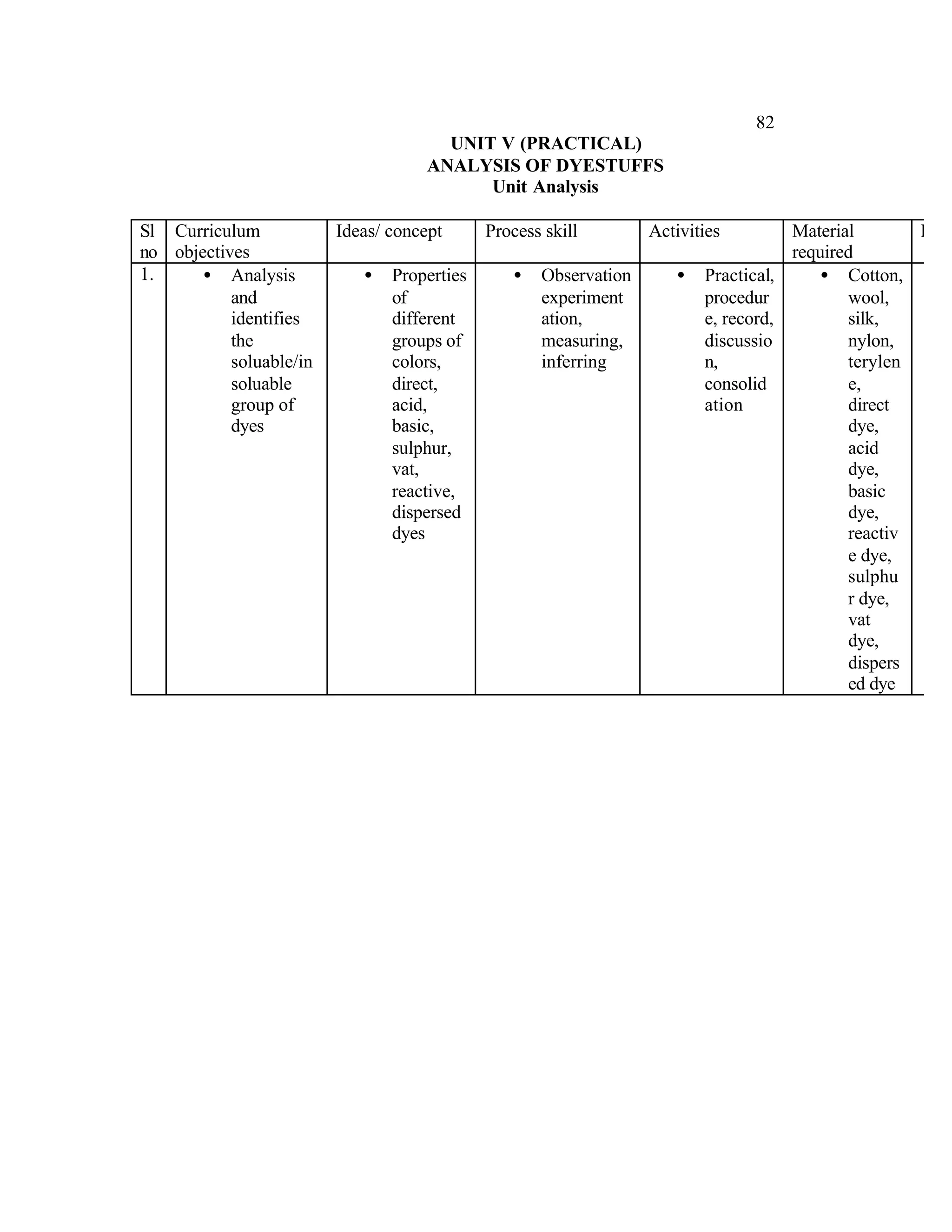
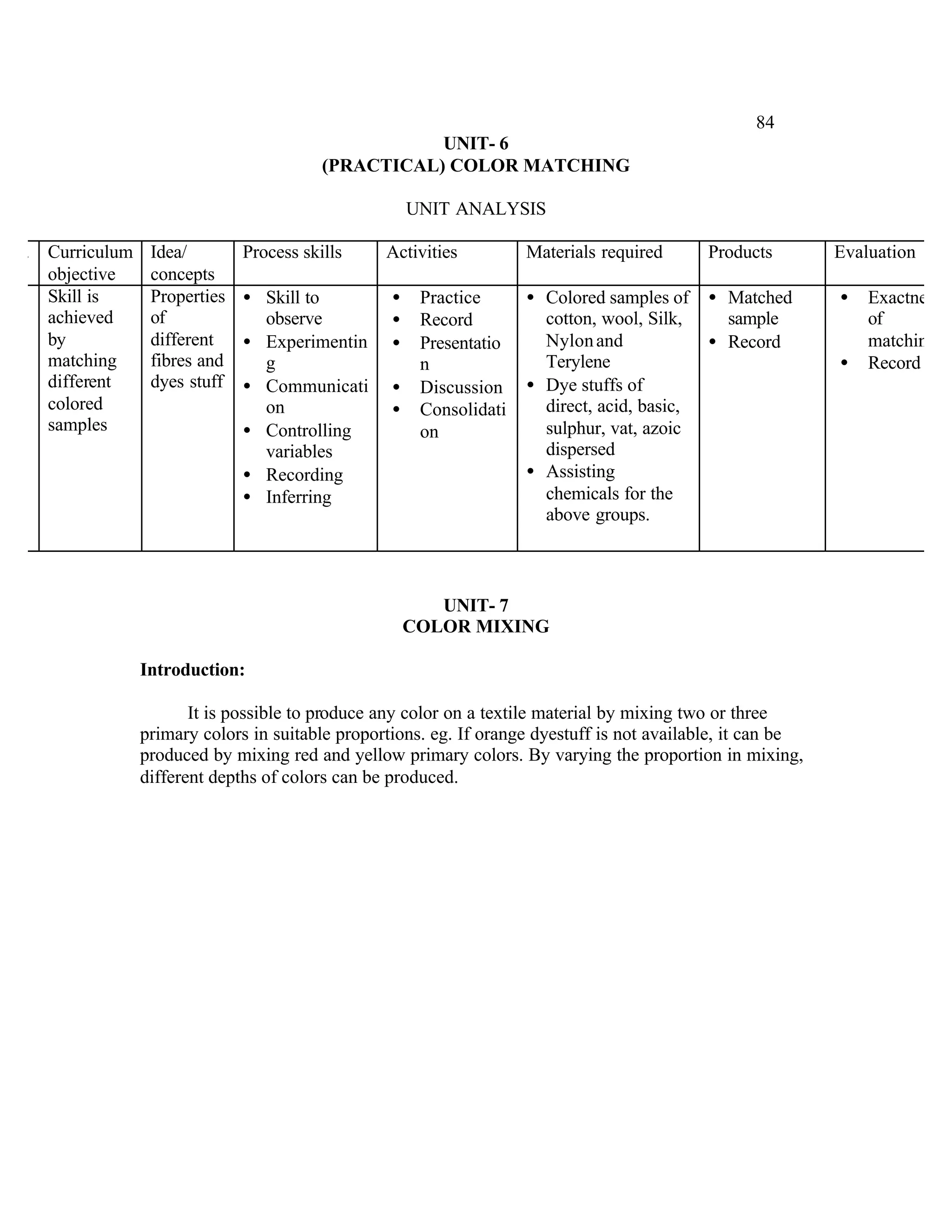
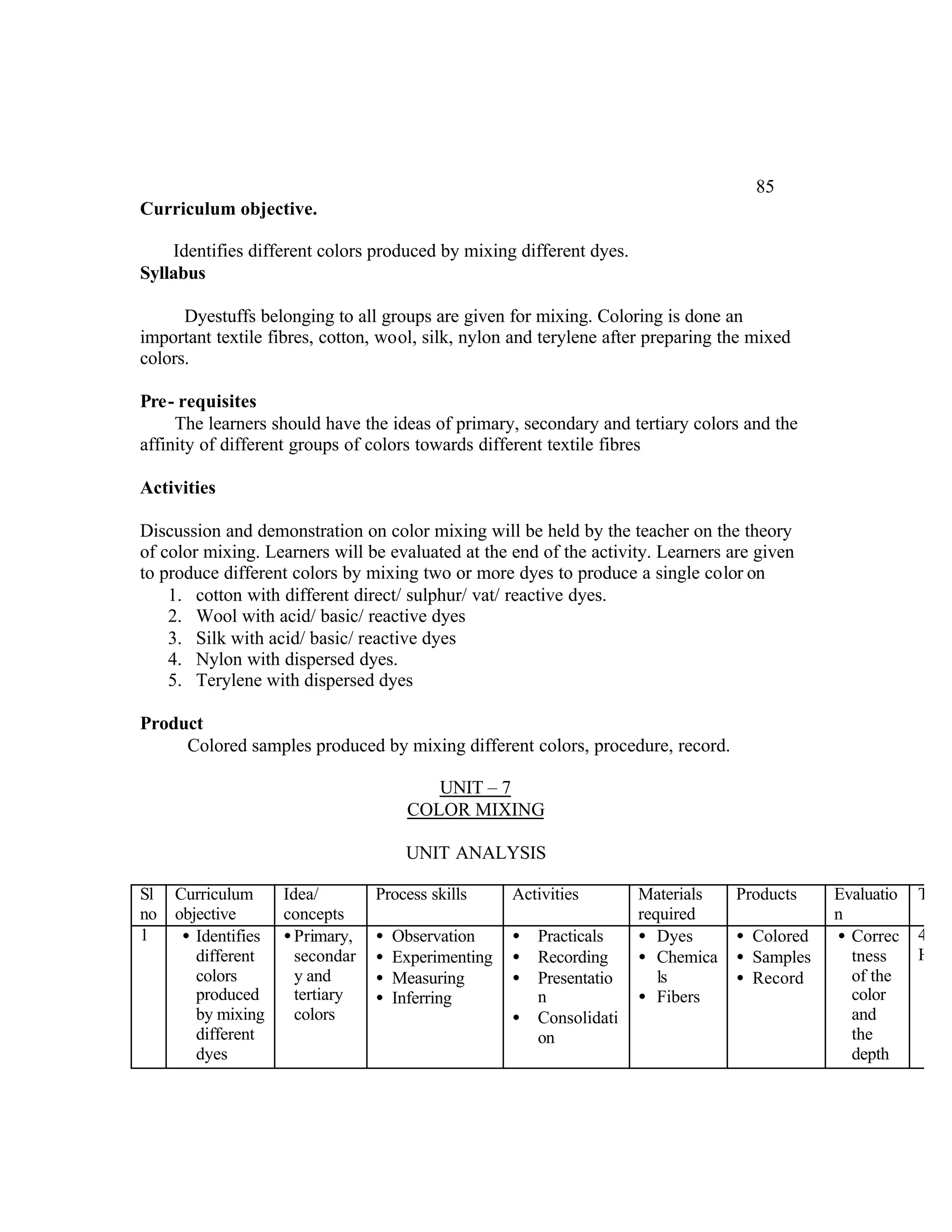
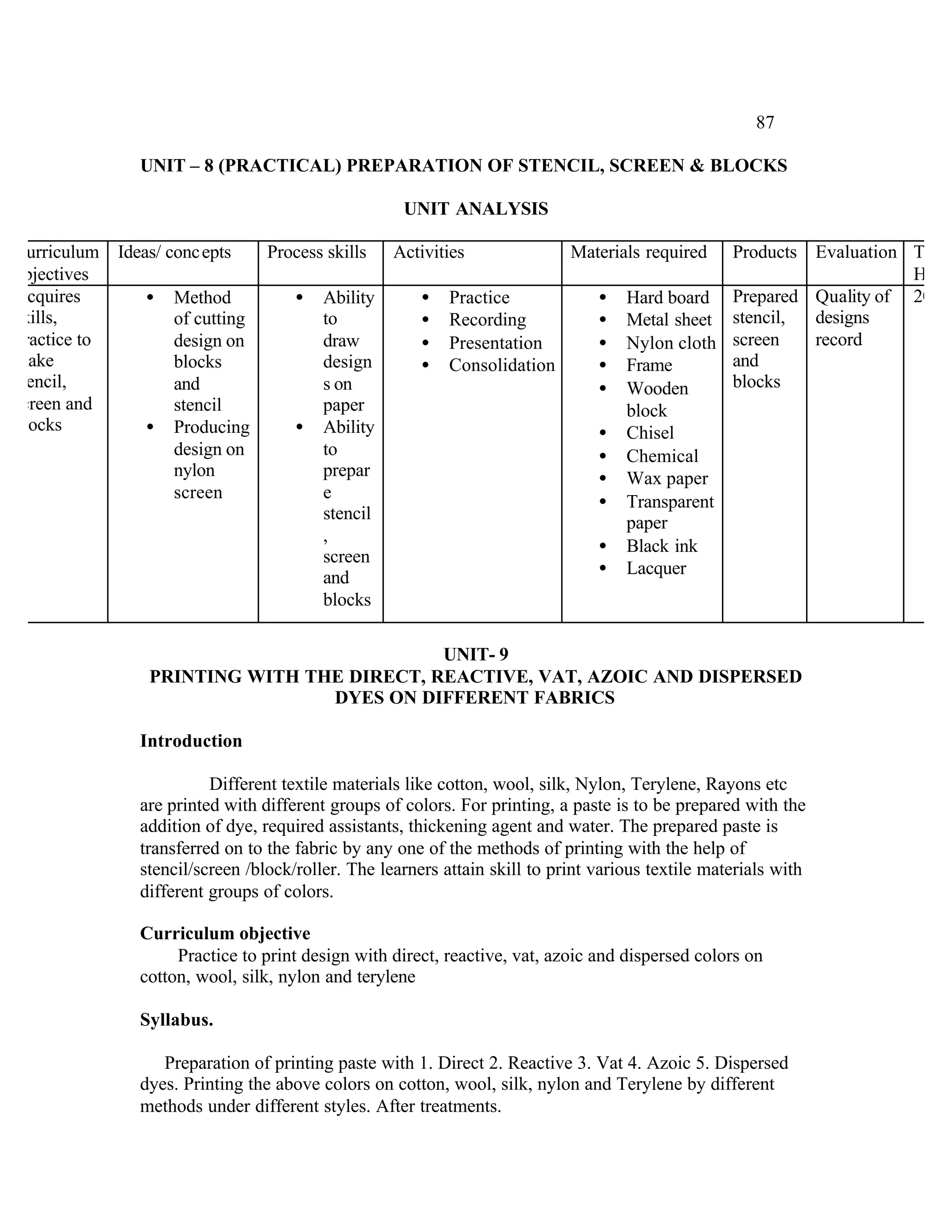
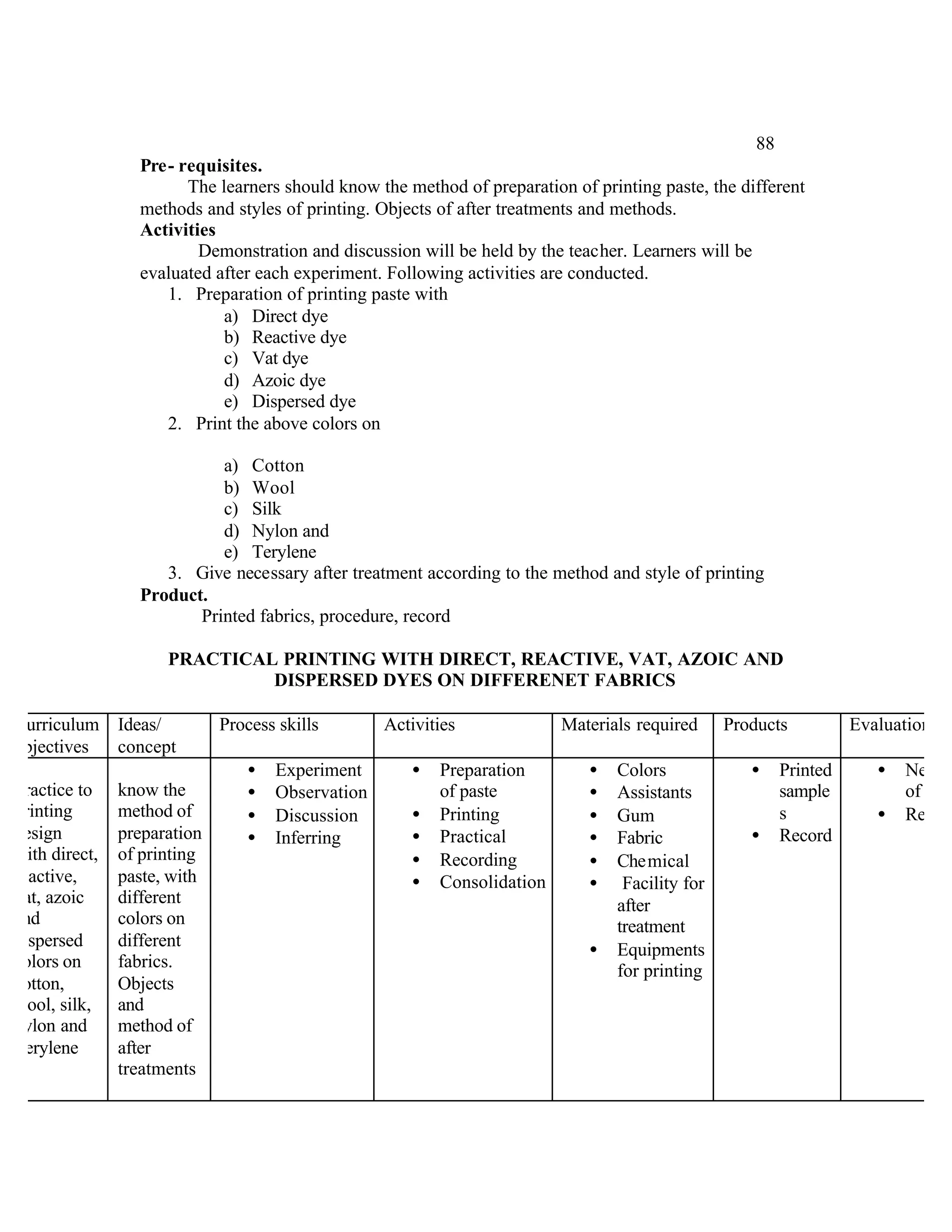
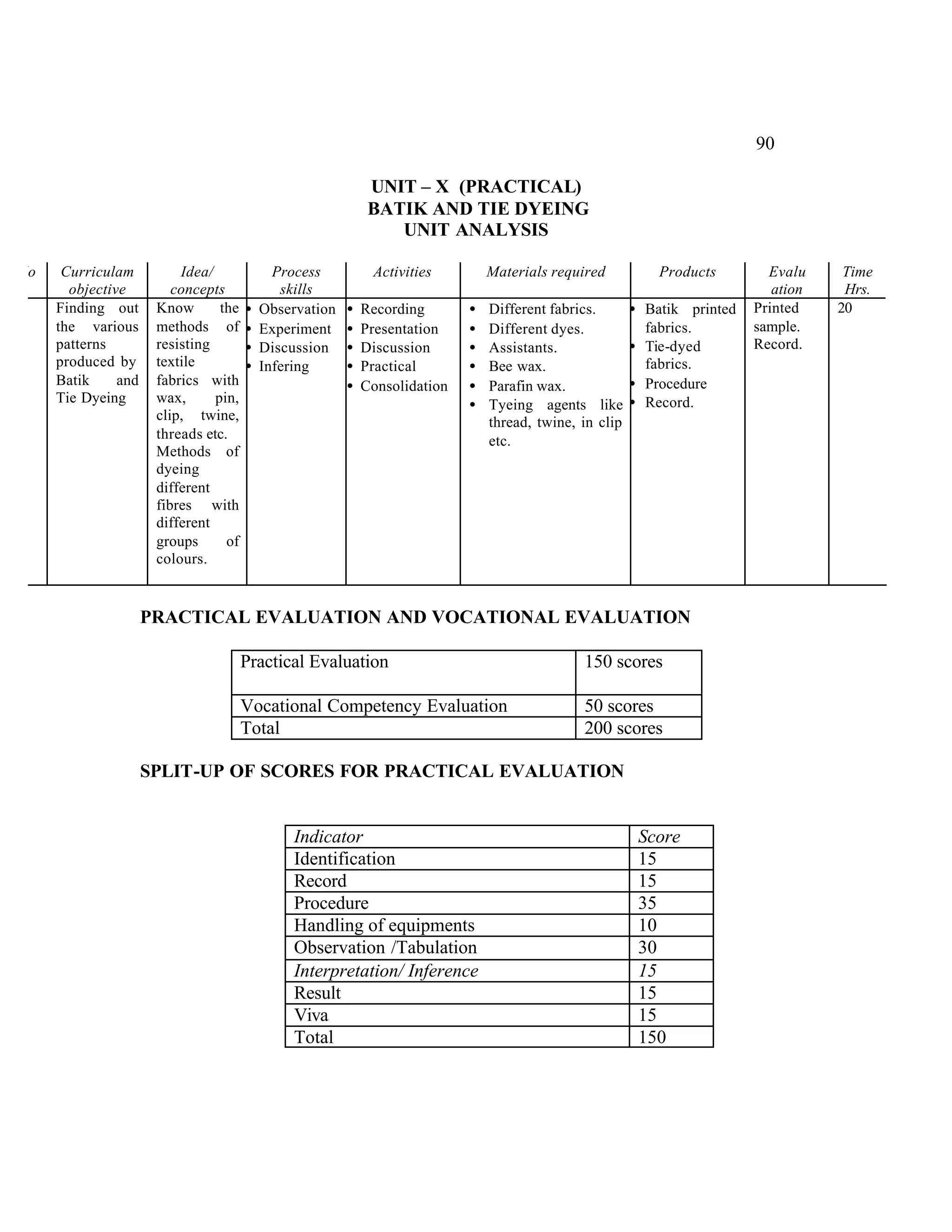
This document provides an introduction and overview for the teacher's sourcebook on Textile Dyeing and Printing for Class XII. It discusses the general approach to teaching and learning for the subject. The objectives of vocational education are outlined, including ensuring opportunities for jobs as well as developing a positive work culture. The curriculum is designed to recognize each learner's personality and develop it in a desirable way. It aims to provide novel ideas and critical thinking skills through experiential learning.