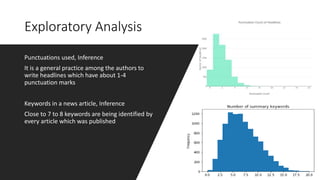
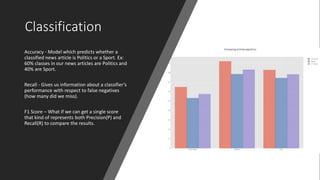
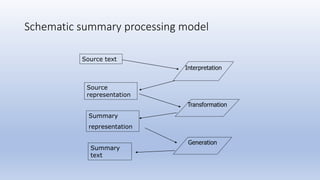
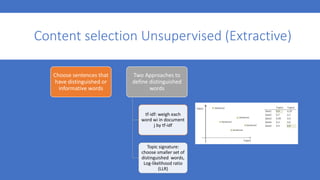
1. The document summarizes a capstone project on automatic text summarization using both extractive and abstractive techniques.
2. It discusses motivations for summarization, approaches to extractive and abstractive summarization, data collection and analysis, classification methods, and evaluation metrics.
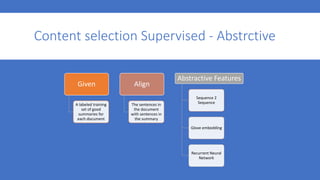
3. The project uses a BBC news dataset and develops sequence-to-sequence and GloVe embedding models to generate abstractive summaries that are evaluated using ROUGE scores against human-written references.