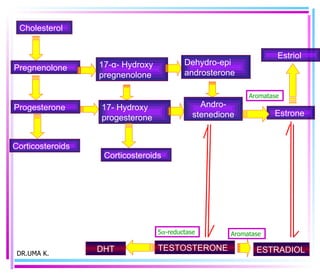
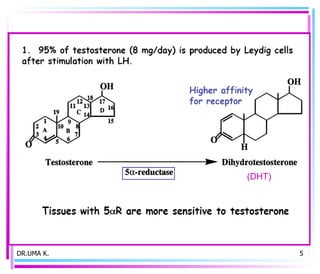
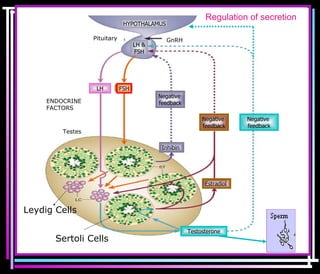
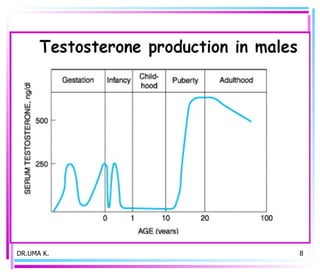
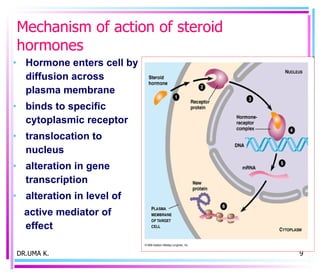
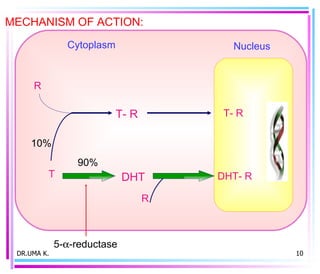
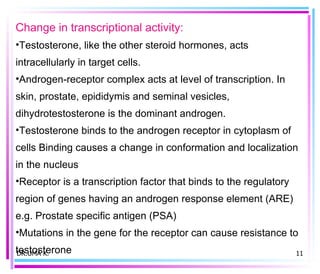
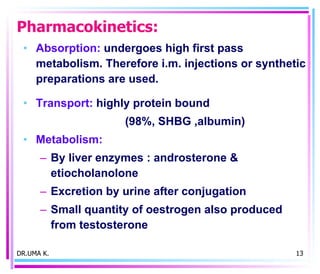
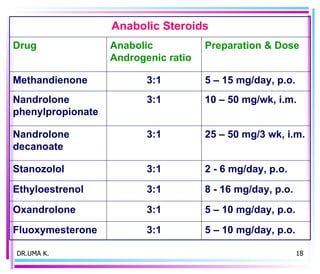
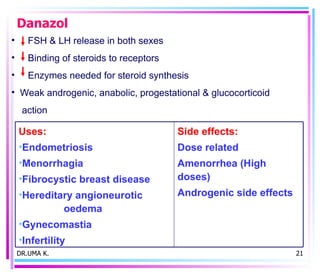
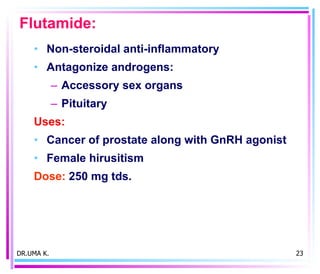
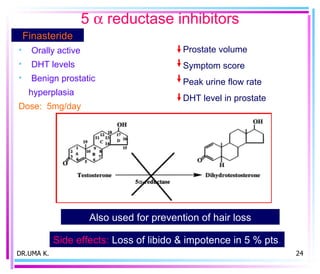
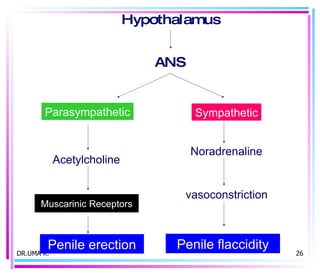
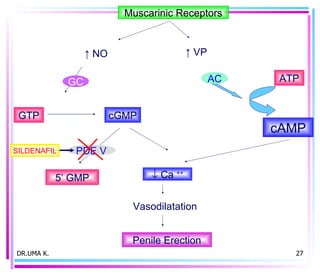
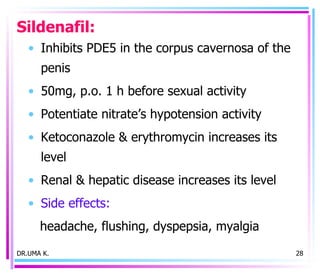
Male sex hormones include testosterone and dihydrotestosterone. Testosterone is produced in the testes and regulates the development of male sexual characteristics. It acts through binding to androgen receptors and altering gene expression. Common therapeutic uses of testosterone and related compounds include treating testicular failure, muscle wasting, osteoporosis, and symptoms of aging in men. Side effects can include virilization, acne, and risks to the prostate.