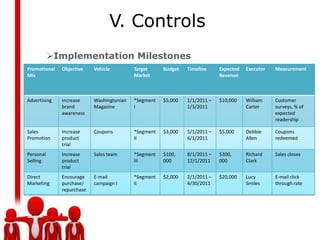
The document outlines the essential components of an effective marketing plan, emphasizing the importance of understanding customer needs and creating tailored products and promotional strategies. It details the structure of a marketing plan, including elements like market research, marketing strategy, financial forecasts, and controls. It also debunks common marketing myths while highlighting the significance of customer retention and the need for a customer-centric approach in business operations.