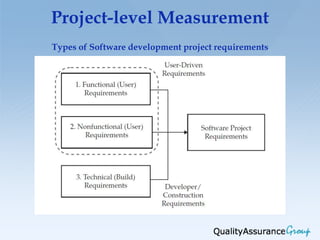
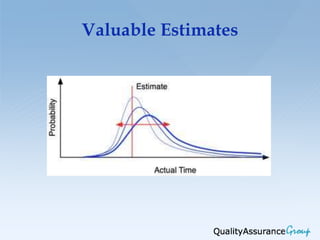
This document discusses different approaches and techniques for estimating software development and testing projects. It describes measuring projects at different levels, from overall project level down to individual task levels. It outlines common software estimation approaches like macro estimation using equations, comparisons, or analogies, and micro estimation using work breakdown. It provides examples of estimating the effort for individual project activities and a five step process for bottom-up estimating. Finally, it notes the tradeoff between project quality, scope, cost and time.