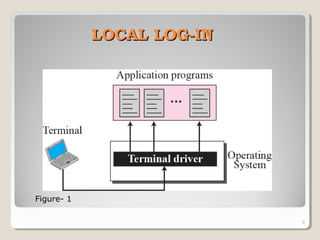
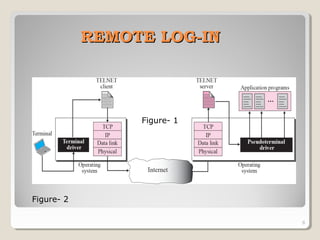
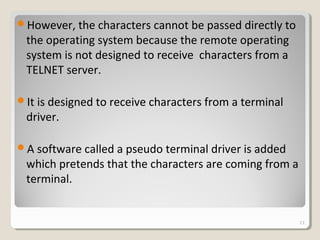
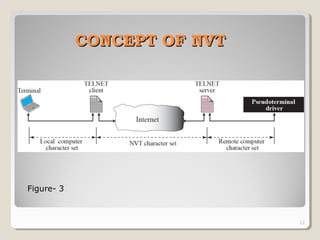
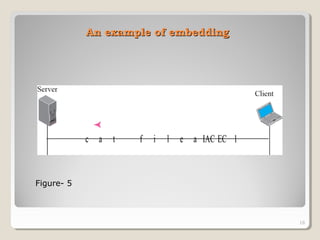
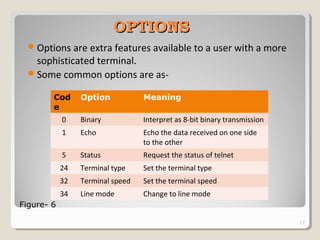
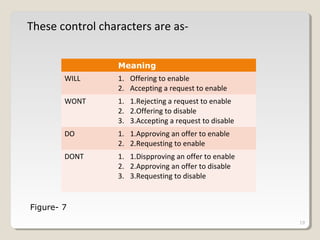
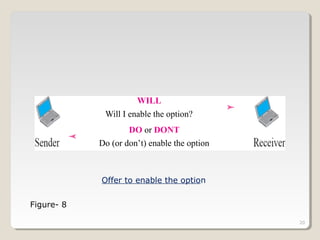
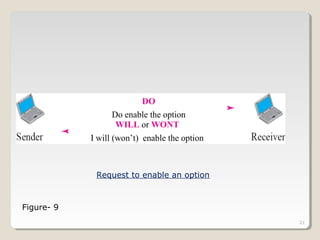
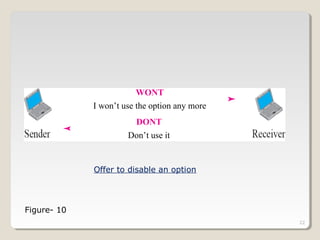
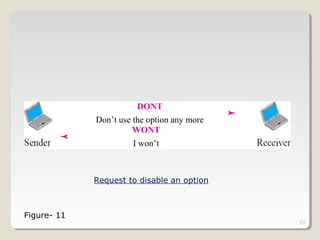
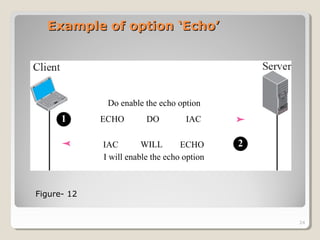
TELNET is a protocol that allows users to connect to remote systems and access services as if they were directly connected to that system. It establishes a connection between the local terminal and remote system so that the local terminal acts as a terminal for the remote system. Users can log into remote systems using TELNET, access applications and services, and transfer results back to their local system. TELNET uses options and option negotiation to allow extra features and configure settings like terminal type and speed. It embeds control characters in the data stream and uses various modes like default, character, and line mode for operation.
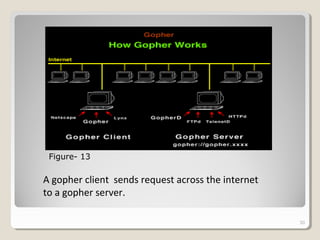
Gopher is a protocol for locating and transferring documents over the internet. It presents content as hierarchical directories and documents that