The document describes processes for optimizing various GSM network performance metrics including:
1. TBF Success Rate by identifying poor cells, failure reasons, defining PDCHs, checking for congestion and alarms.
2. GPRS/EDGE Throughput by identifying poor cells, failure reasons, defining PDCHs, checking radio quality and congestion.
3. Downlink Multislot Assignment Success Rate by identifying poor cells, defining PDCHs, checking radio quality and congestion.
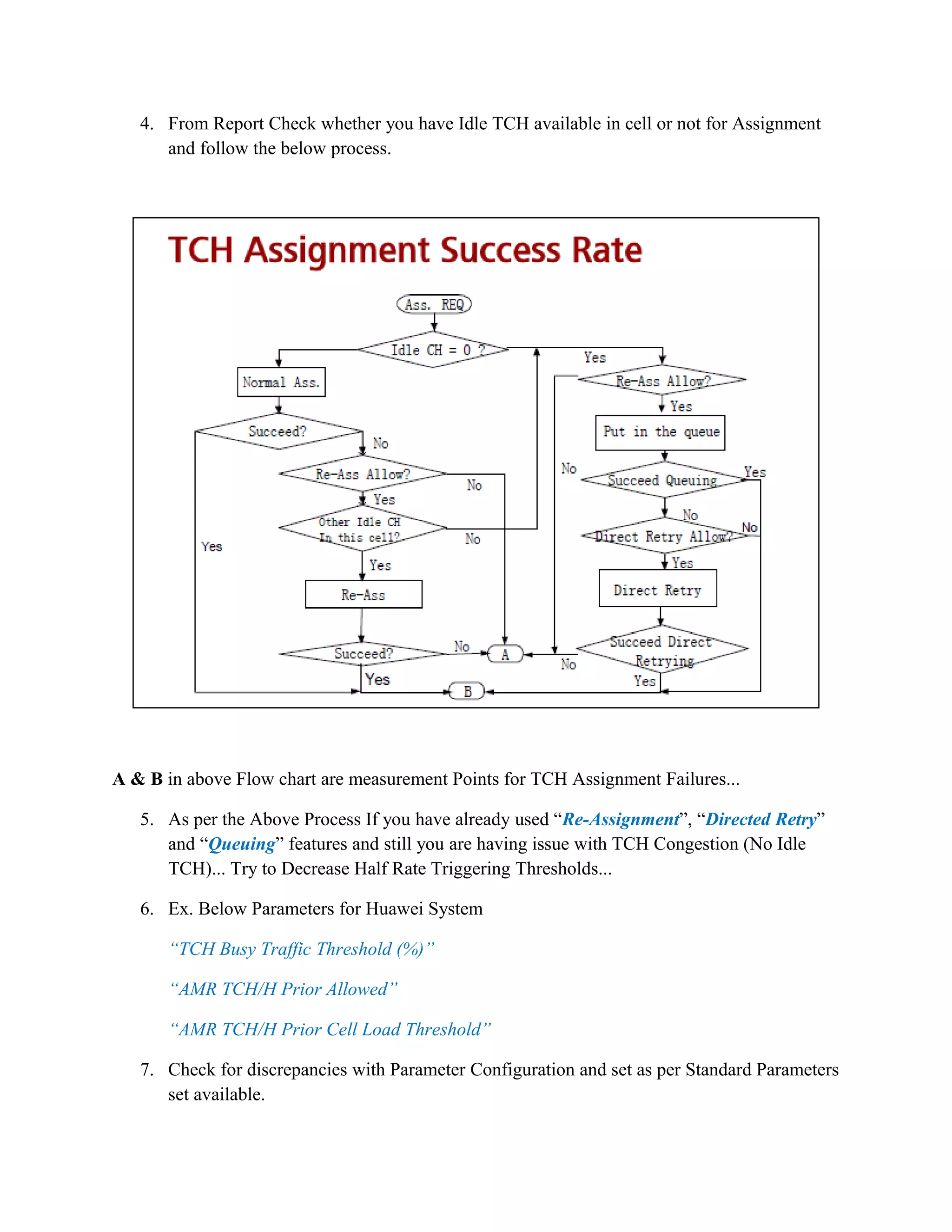
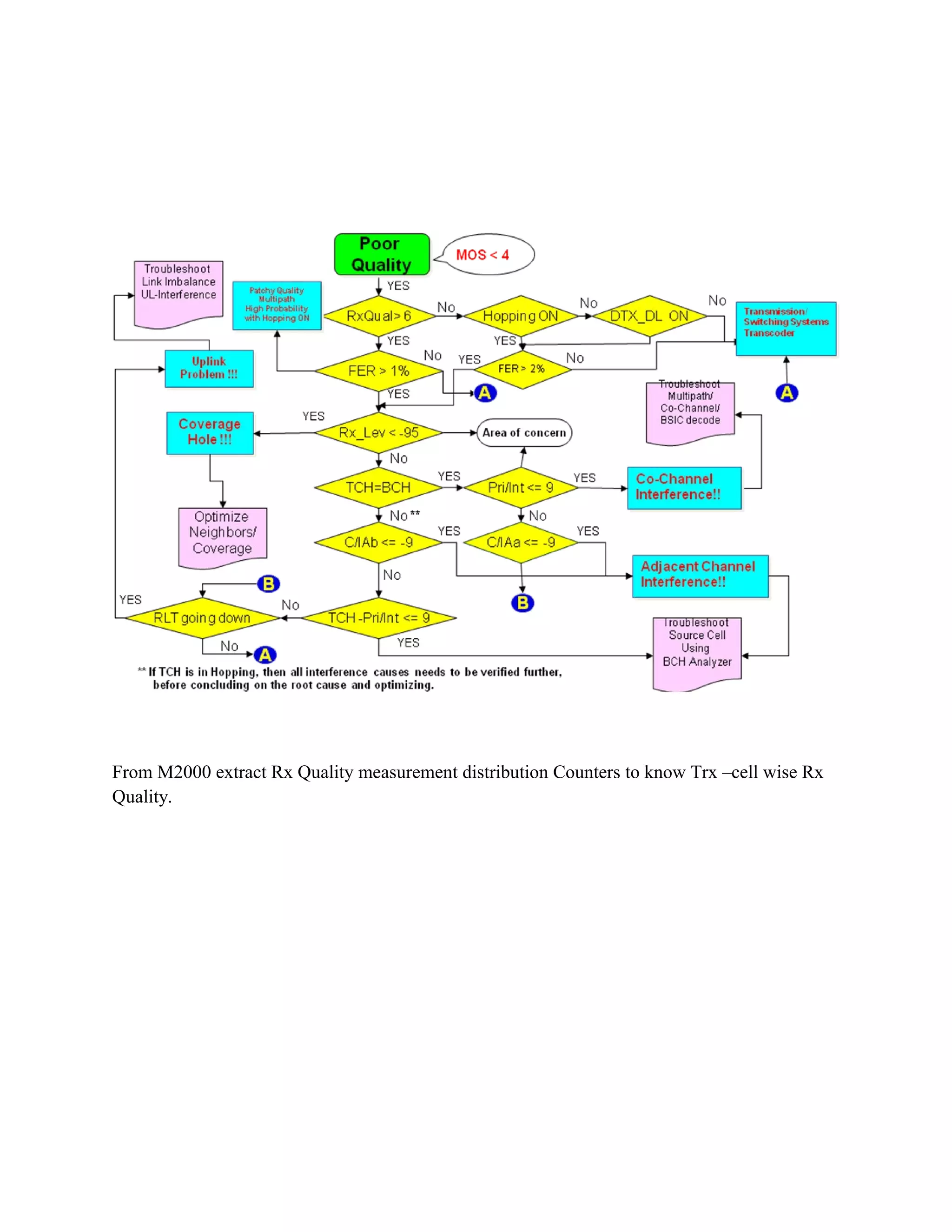
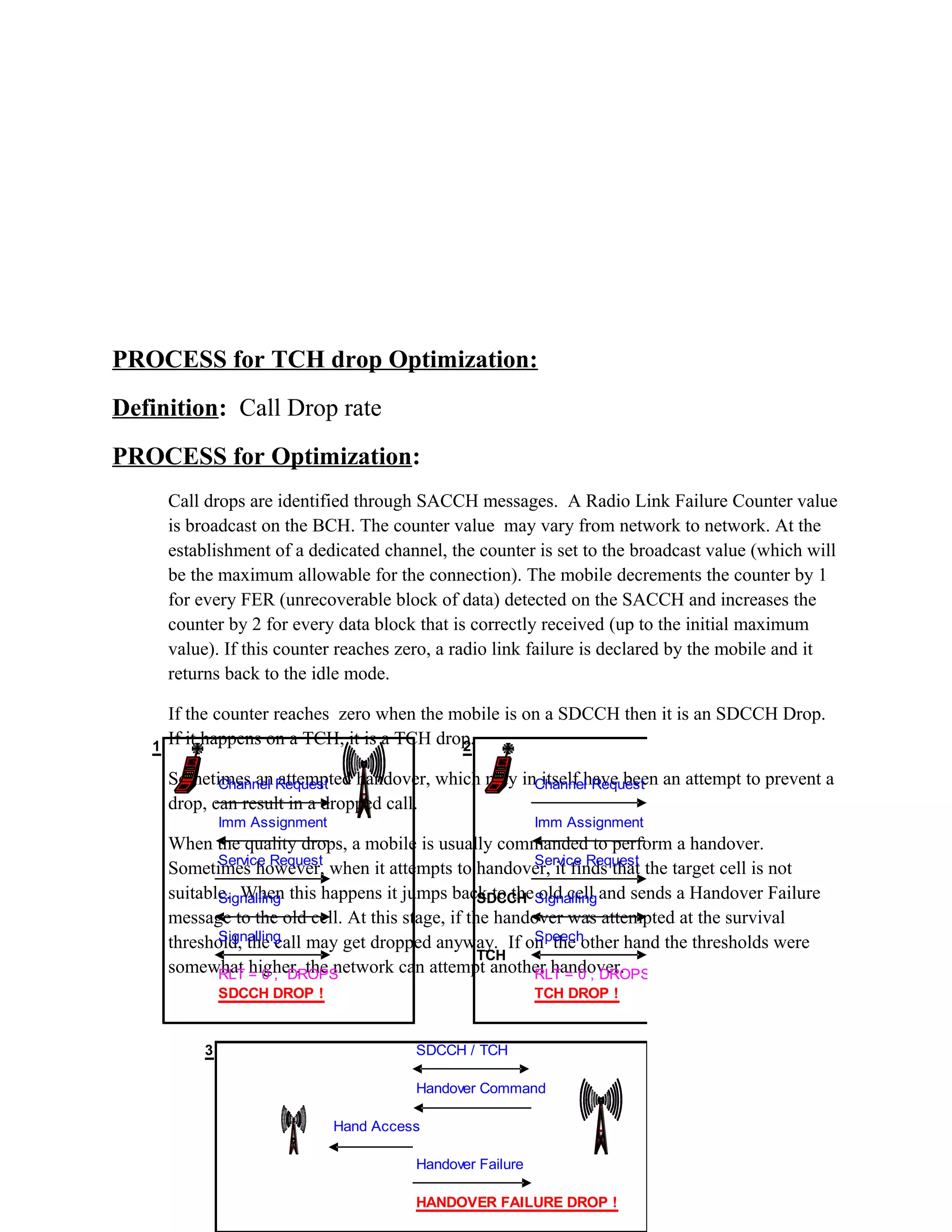
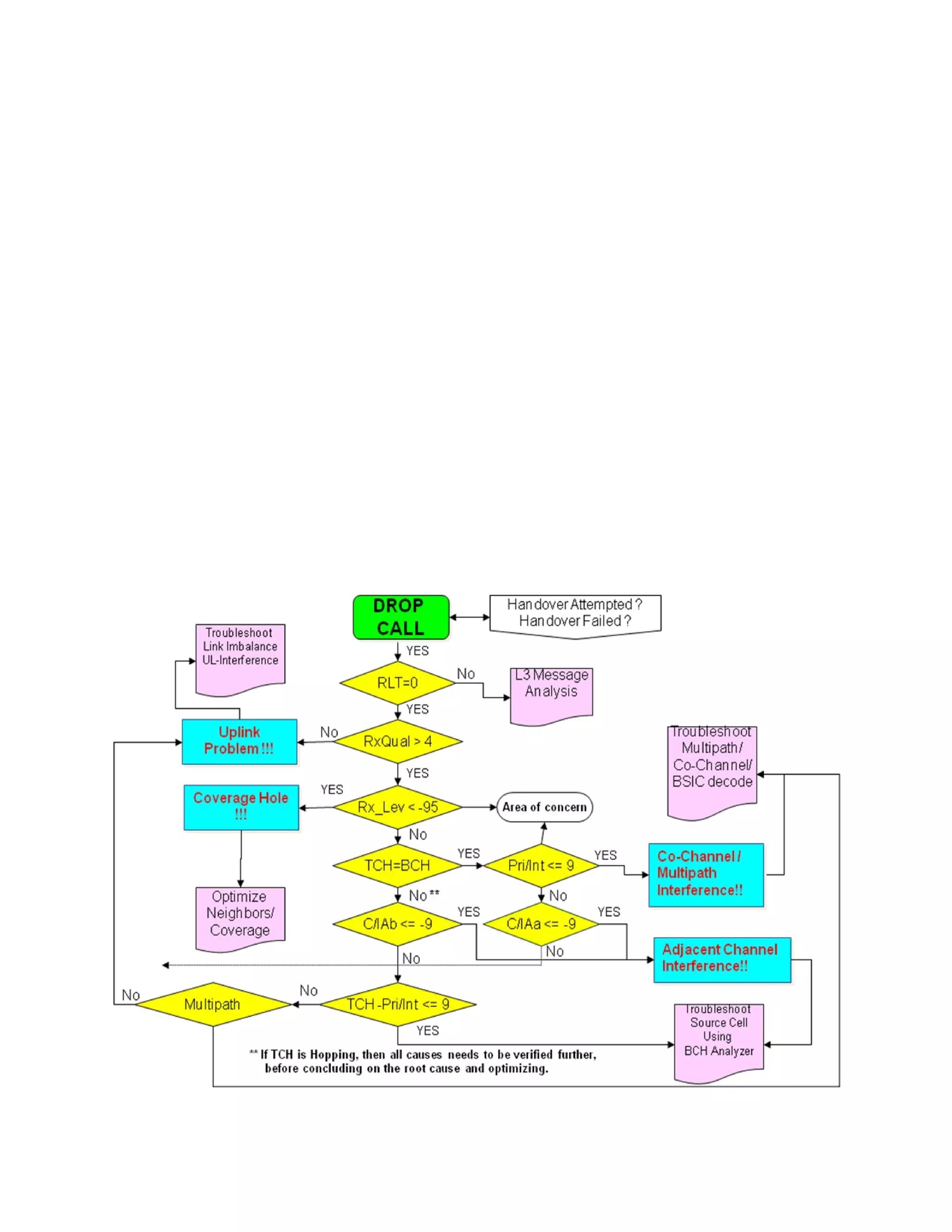
4. SDCCH Assignment Success Rate by identifying poor cells, checking for congestion, defining parameters correctly.
5. RACH Success Rate by identifying poor cells, checking configuration parameters and hardware issues.