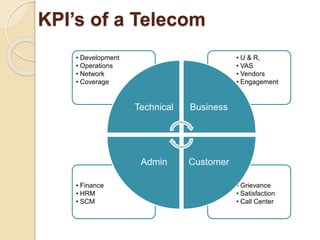
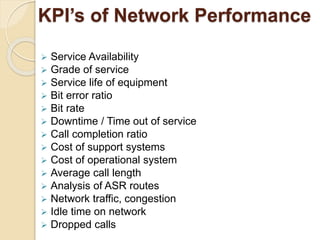
The document discusses the role of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) in the telecom industry, emphasizing their importance in measuring performance, making data-driven decisions, and improving customer satisfaction. It categorizes various KPIs related to business processes, network performance, customer satisfaction, and marketing, outlining the necessity for real-time business intelligence to enhance operational efficiency. Additionally, it stresses the need for actionable insights derived from accurate, timely data to support strategic decision-making in a competitive environment.