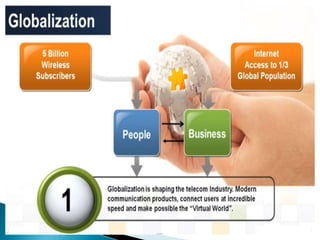
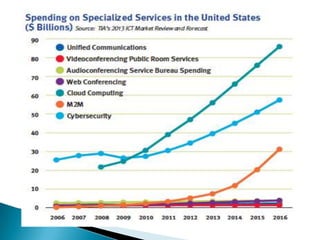
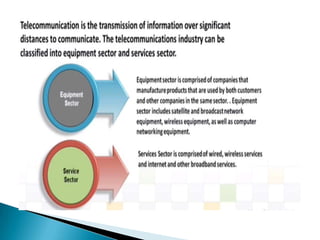
The telecommunications industry is growing, with global revenue projected to increase from $2.1 trillion in 2014 to $2.4 trillion in 2019. Growth is being driven by demand for wireless devices and services, as well as a shift to cloud-based solutions. Key trends include a rise in mobile subscriptions, expansion of 4G networks, and increasing broadband penetration. Operators are also focusing more on machine-to-machine opportunities and internet protocol TV. Global deregulation and technological innovation are transforming the industry and blurring traditional boundaries between services.