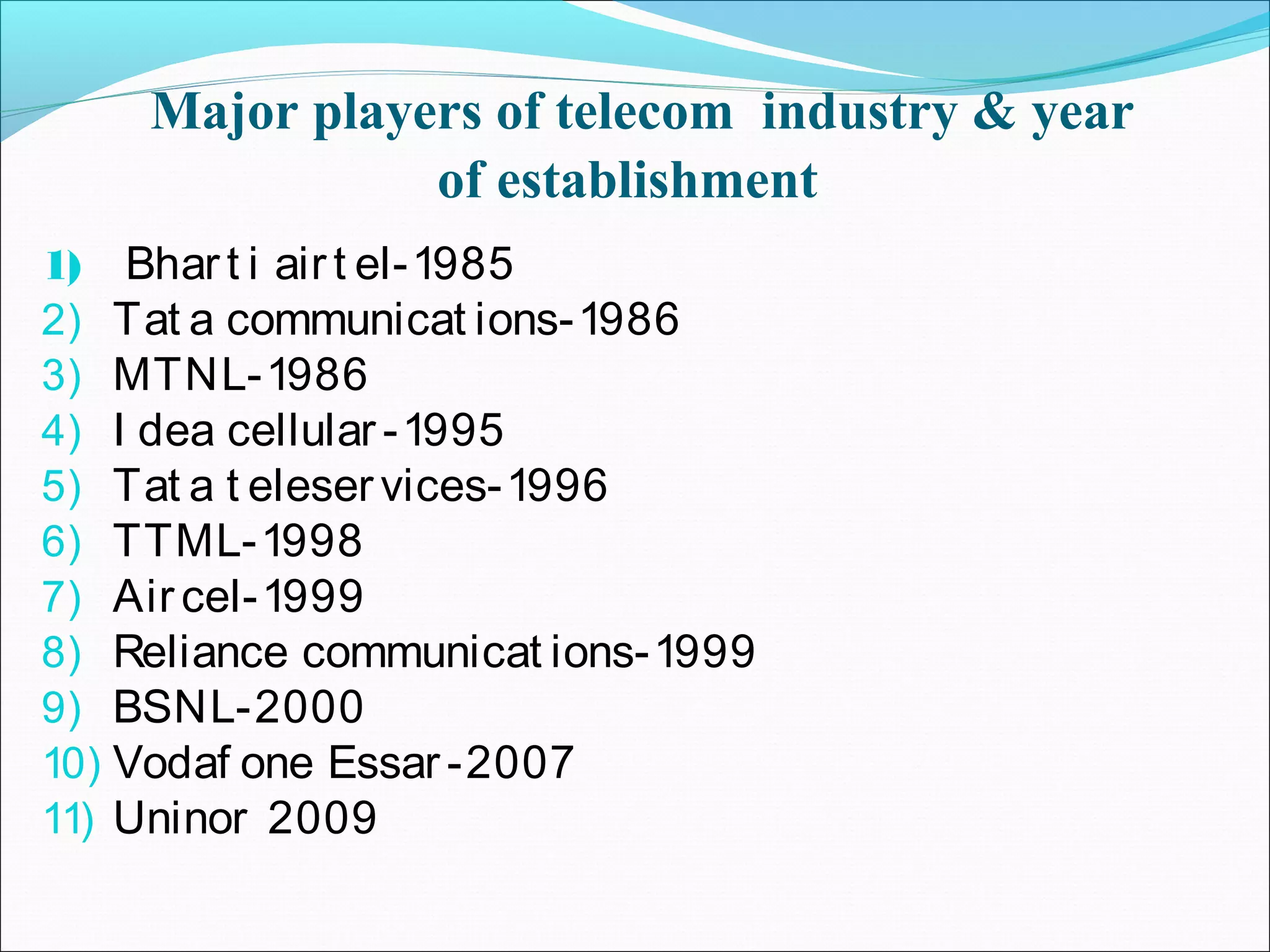
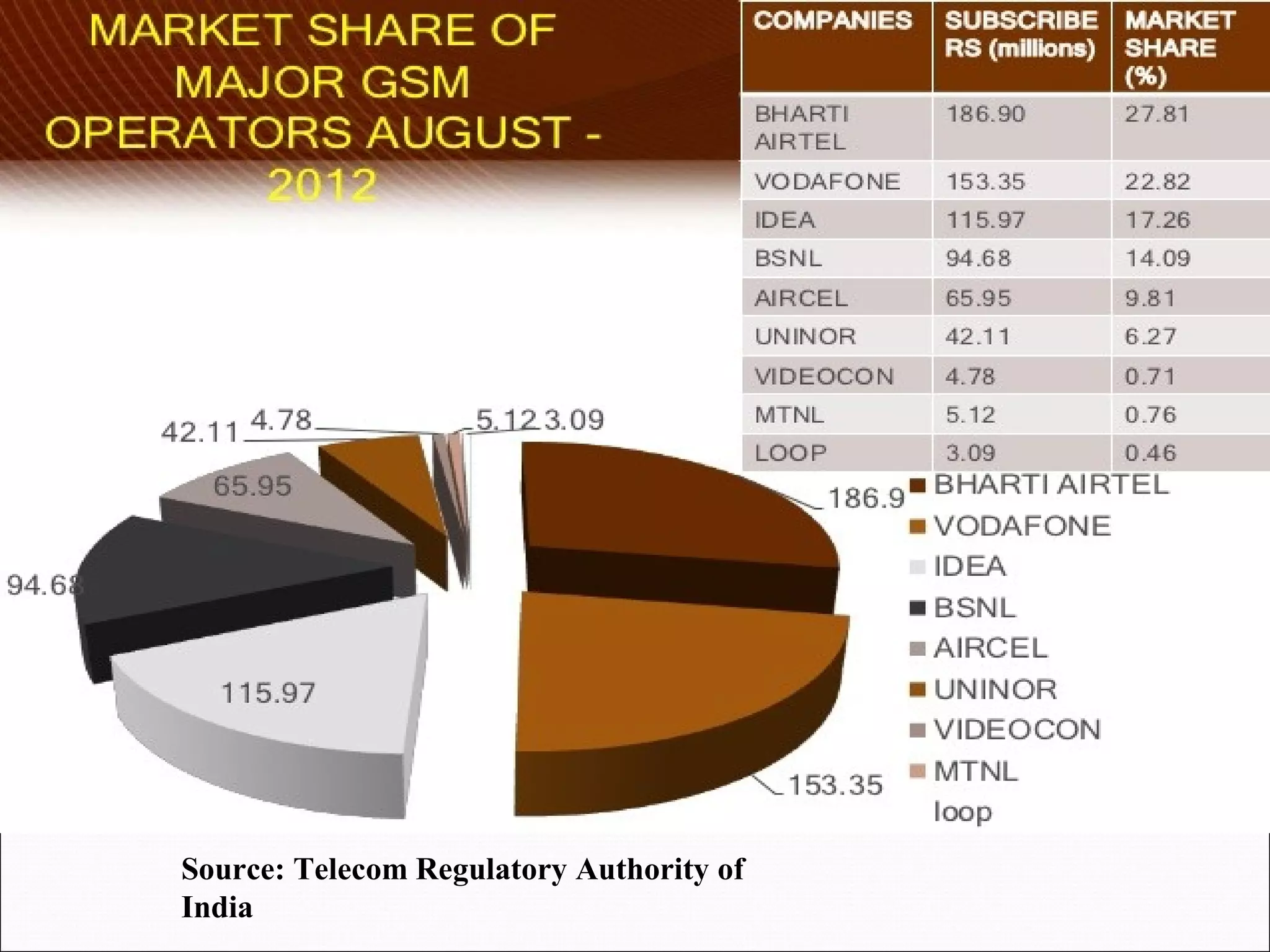
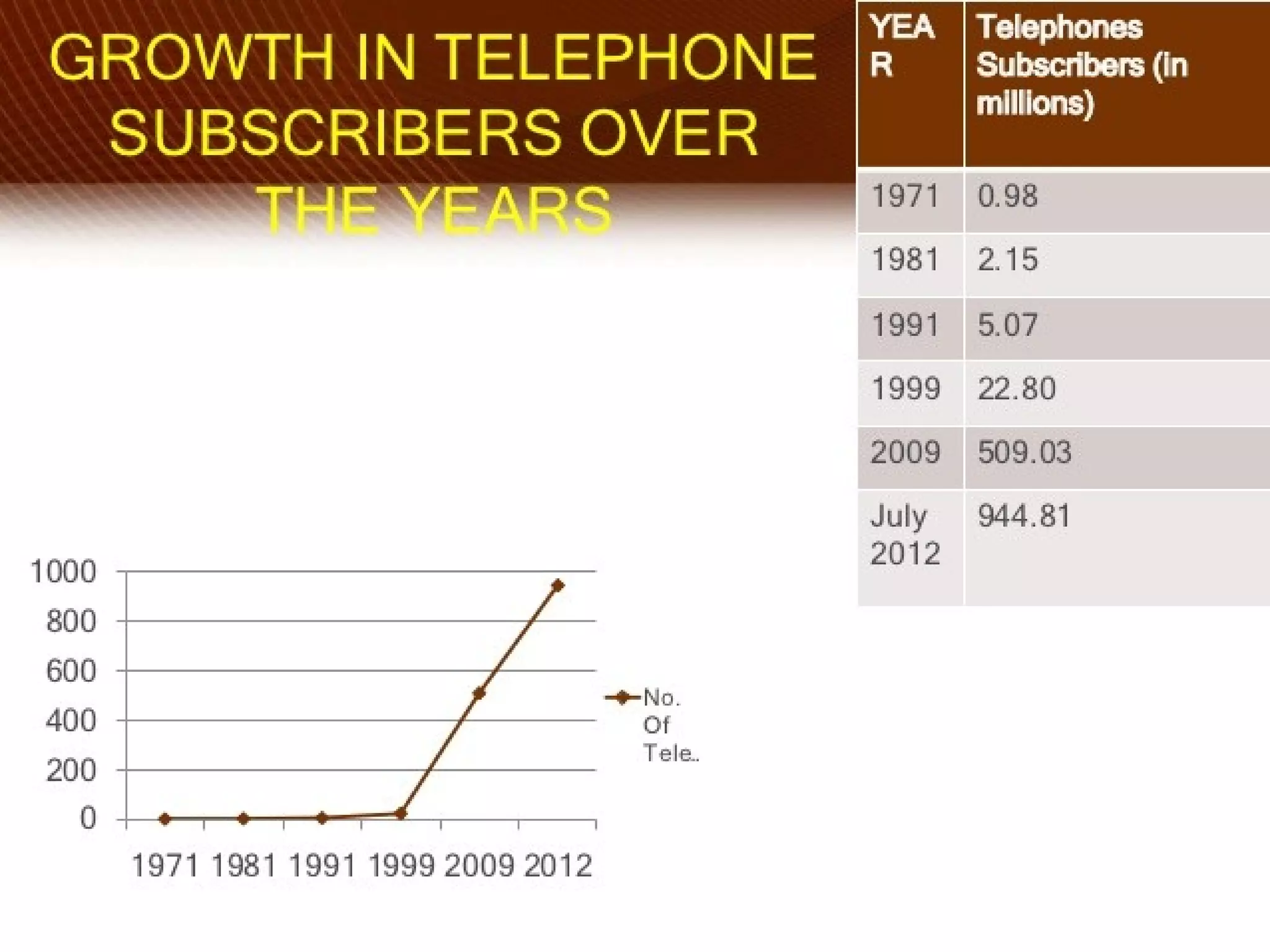
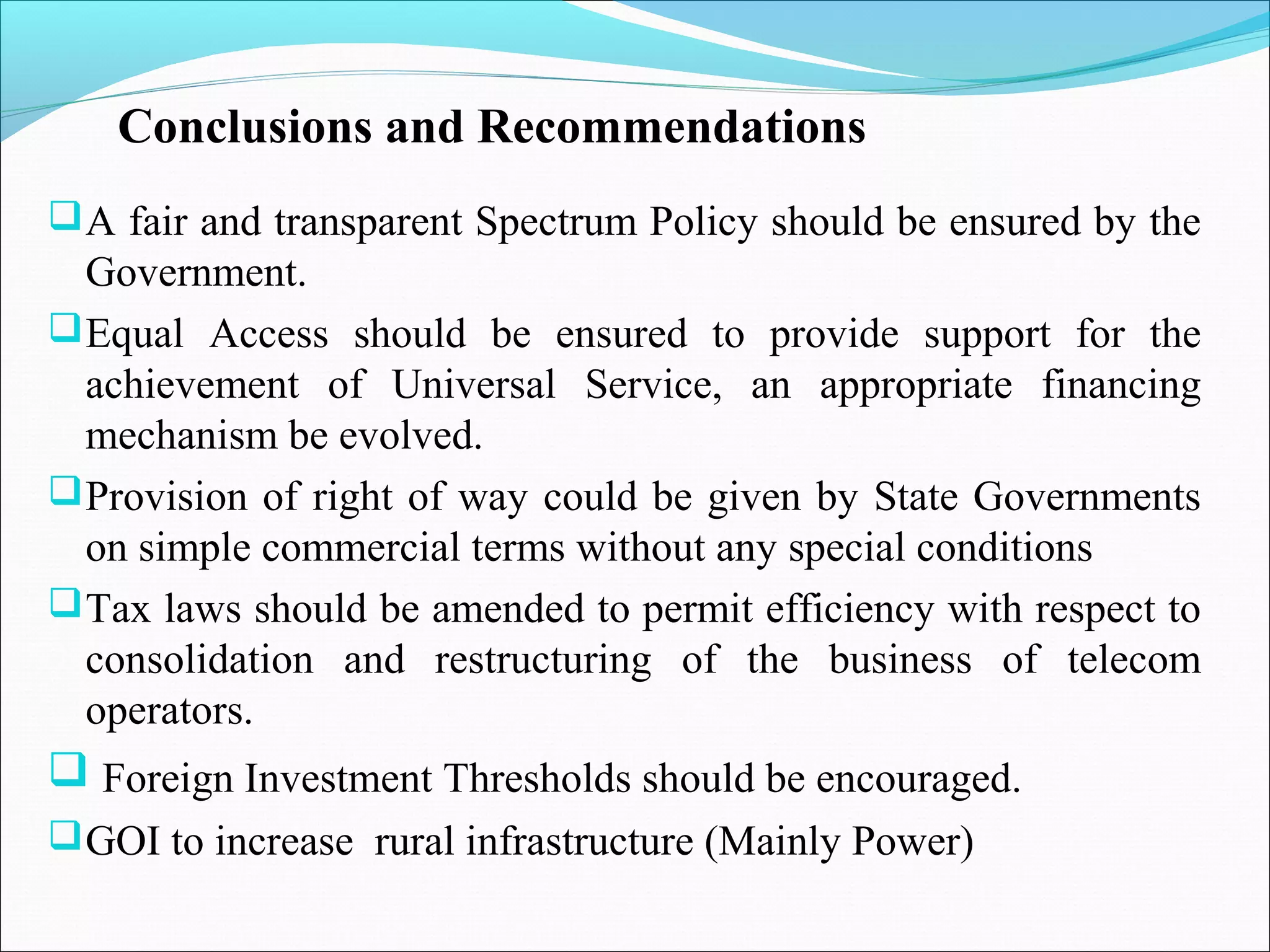
The telecom industry in India has grown significantly since market reforms began in 1991. It has expanded from primarily landline services to having over 900 million mobile subscribers as of 2012, accounting for nearly 12% of global users. Key drivers of growth have been low cost mobile phones, rural connectivity initiatives, and value-added services. However, challenges remain such as limited spectrum availability, lack of rural infrastructure, and high taxes. The industry has proven resilient during the global economic slowdown. Moving forward, recommendations include ensuring fair spectrum and access policies, rural infrastructure development, and tax reforms to further strengthen the telecom sector.