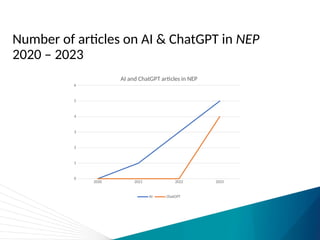
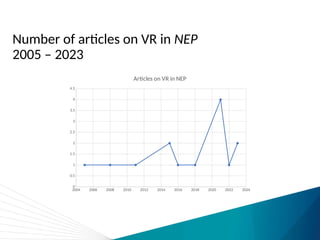
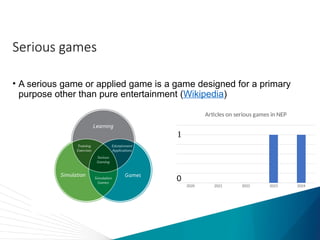
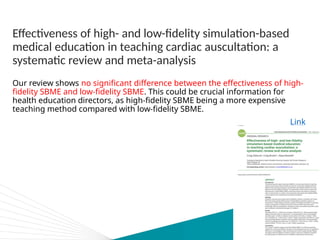
The document discusses the impact of technology on nursing education, highlighting how tools like simulations, virtual reality (VR), and artificial intelligence (AI) are revolutionizing training. While some studies suggest technology improves learning outcomes, meta-analyses reveal mixed results, particularly questioning the superiority of high-fidelity simulations over low-fidelity options. The conclusion raises uncertainty about the integration of AI with other technologies and its potential benefits.