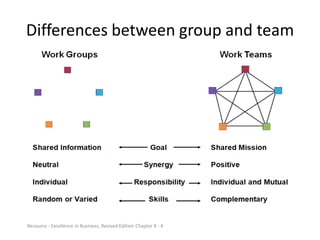
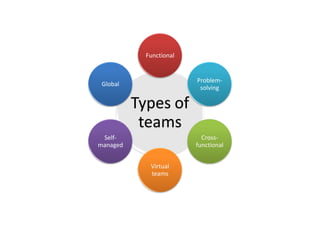
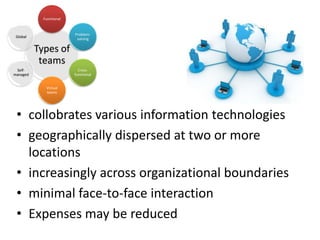
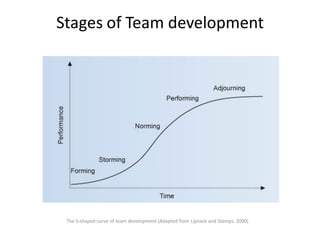
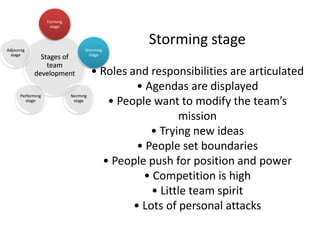
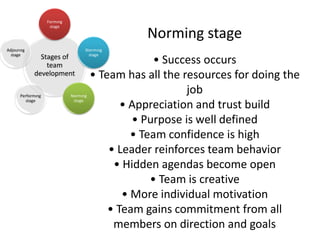
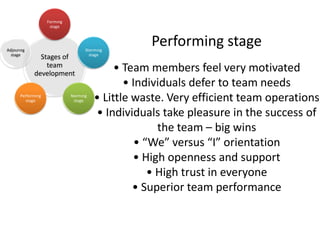
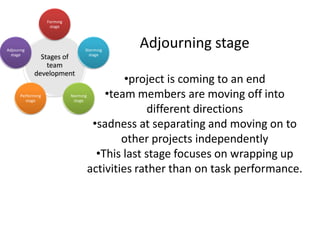
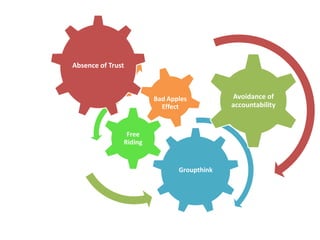
The document discusses teams and team development, defining teams and groups, describing types of work-related teams like functional, problem-solving, and virtual teams. It also outlines the stages of team development including forming, storming, norming, performing, and adjourning. Key characteristics of effective teams are identified such as having a clear goal, competent members, unified commitment, and receiving external support.